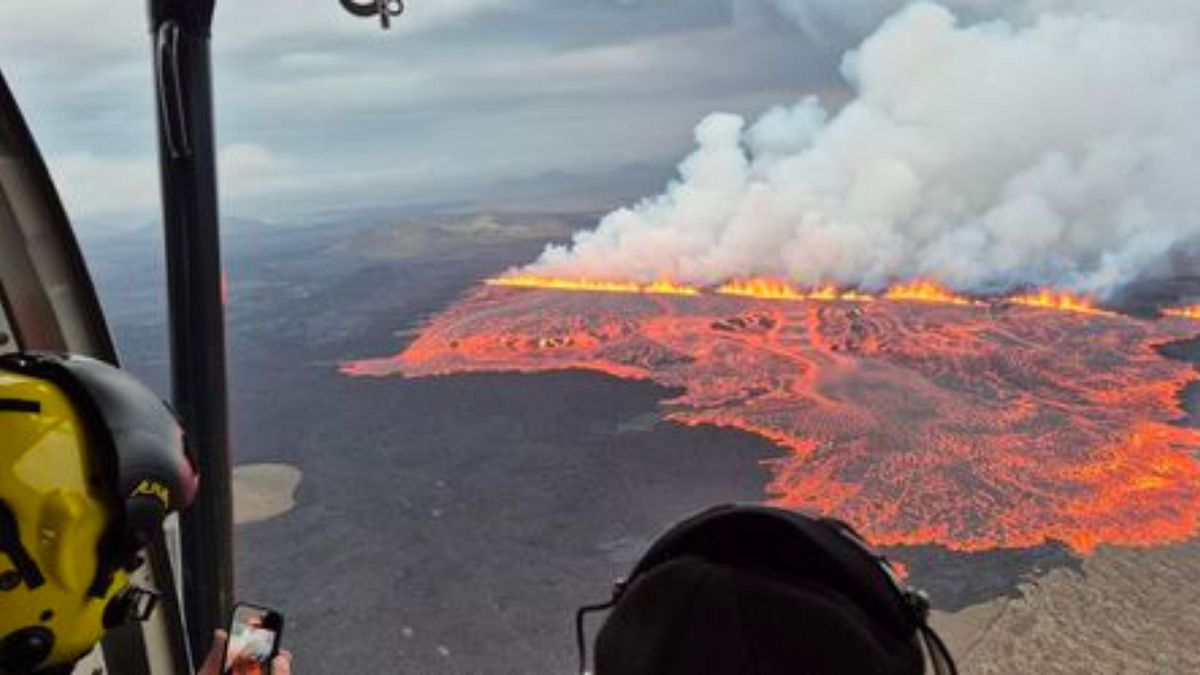
Iceland is grappling with a troubling pattern of volcanic activity as the Sundhnúkur volcano has erupted for the ninth time since December 2023. This ongoing geological tumult has spurred significant evacuations
Did You Know
There’s a species of jellyfish that’s immortal.
?
AD
in the region, particularly affecting the renowned Blue Lagoon geothermal spa and the nearby fishing town of Grindavík. Authorities have swiftly mobilized to ensure the safety of locals and tourists alike, underscoring the pressing need for preparedness in the face of nature's unpredictability.
The recent eruption highlights concerns surrounding the impact of such events on residents and the thriving tourism industry. With a total of 12 eruptions reported on the Reykjanes Peninsula in the past four years, the region's geological volatility has become a focal point for both scientists and safety officials. Guests at luxury resorts and spas have been evacuated, showcasing the delicate balance between the allure of Iceland's stunning landscapes and the potential dangers lurking beneath the surface.
As the eruptions continue to draw media attention and frighten local communities, the call for enhanced safety measures has never been more pressing. Though the beauty of Iceland's natural wonders captivates thousands of tourists every year, the threat of volcanic eruptions serves as a potent reminder of the power of nature. Iceland must navigate the dual challenges of protecting its residents and welcoming tourists, striving to ensure that visitors can safely enjoy the country's breathtaking splendor without jeopardizing public safety.
Q&A (Auto-generated by AI)
What causes volcanic eruptions in Iceland?
Volcanic eruptions in Iceland are primarily caused by the movement of tectonic plates. The country sits on the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, where the North American and Eurasian plates diverge, allowing magma from the mantle to rise to the surface. This geological activity is further influenced by Iceland's unique volcanic systems, which are characterized by fissures and central volcanoes. The interaction of magma with groundwater can lead to explosive eruptions, as seen with the Sundhnúkur volcano.
How does Iceland manage volcanic emergencies?
Iceland has a comprehensive emergency management system that includes continuous monitoring of volcanic activity through the Icelandic Meteorological Office. Authorities conduct regular drills and have established evacuation plans for at-risk areas, such as Grindavík and the Blue Lagoon. Collaboration with scientists helps to predict eruptions, while local police and emergency services are trained to respond quickly to evacuate residents and tourists, ensuring public safety during crises.
What impact do eruptions have on tourism?
Volcanic eruptions can significantly impact tourism in Iceland, both positively and negatively. While eruptions may lead to temporary evacuations and closures of attractions like the Blue Lagoon, they can also attract tourists interested in volcanic activity. The dramatic landscapes created by eruptions, such as new lava fields and craters, offer unique experiences. However, safety concerns and travel disruptions can deter visitors, affecting local economies dependent on tourism.
What is the history of the Sundhnúkur volcano?
The Sundhnúkur volcano has a history of eruptions, with the recent activity marking its ninth eruption since December 2023. Located in southwestern Iceland, it has been closely monitored due to its potential impact on nearby communities, including Grindavík. Historically, eruptions in this region have shaped the landscape and influenced local settlement patterns, as residents adapt to the risks posed by volcanic activity.
How do geothermal spas operate near volcanoes?
Geothermal spas in Iceland, such as the Blue Lagoon, operate by utilizing the natural heat from volcanic activity. Water is heated by geothermal energy, which is abundant in volcanic regions. The spas are designed to harness this energy safely, providing therapeutic experiences. However, their proximity to volcanoes necessitates strict safety protocols to ensure the well-being of guests, particularly during eruptions or seismic activity.