The Silent Epidemic
Many people are living with diabetes without realizing it, which is a major problem. Unlike some health issues that show clear signs, diabetes can be sneaky.
Often, there are no outward indications like feeling unwell or looking sick. This lack of obvious symptoms means that many individuals may not seek medical help until the condition has progressed, leading to potential health complications. Regular check-ups are essential for early detection. The insidious nature of diabetes highlights the need for a heightened awareness of the risks and the importance of routine screening, particularly for those with risk factors such as family history or lifestyle factors that make them prone to the disease.
Why It's Undetected
There are several reasons why diabetes often goes unnoticed. Firstly, the early stages of Type 2 diabetes may not exhibit any noticeable symptoms. Secondly, people may attribute vague symptoms, such as fatigue or increased thirst, to other causes, leading them to delay seeking medical attention. Moreover, some people may not have access to regular healthcare or may not be aware of their risk factors, further contributing to delayed diagnosis. Societal factors can also play a role, as a lack of awareness about diabetes and its potential impact on health can prevent individuals from recognizing the urgency of preventative measures and prompt testing.
Hidden Risk Factors
Certain factors increase a person's risk of developing diabetes, whether they recognize them or not. Family history is a significant risk factor; if your relatives have had diabetes, you are also at higher risk. Lifestyle choices, such as an unhealthy diet, a sedentary lifestyle, and excess weight, contribute significantly. The prevalence of these risk factors in some communities can make the condition more widespread. Also, some ethnic groups are at higher risk of developing diabetes than others. Understanding these risk factors is the first step toward prevention and early detection. Awareness of your personal risk factors is critical for proactive health management.
The Long-Term Impact
Undiagnosed or poorly managed diabetes can lead to severe long-term health complications. Cardiovascular disease is a significant risk; diabetes increases the likelihood of heart disease, stroke, and high blood pressure. Additionally, diabetes can damage the kidneys, potentially causing kidney failure, and impair vision, even leading to blindness. Nerve damage (neuropathy) is another common complication, causing pain and numbness, especially in the extremities. Early detection and management are therefore crucial to prevent or delay these serious complications and improve the quality of life.
Taking Proactive Steps
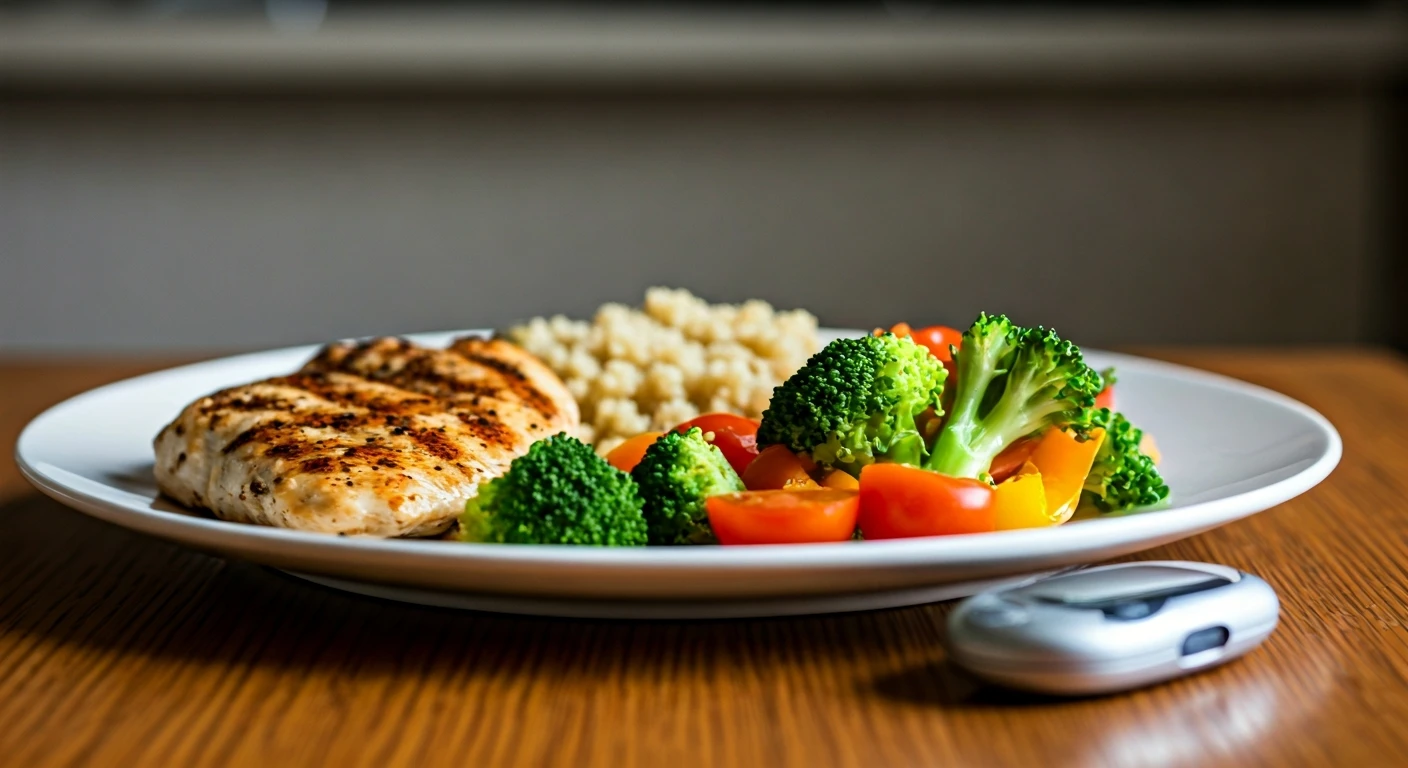
Early detection involves routine health check-ups and regular blood sugar screenings. It's crucial, particularly if you have risk factors or notice early signs like frequent urination or excessive thirst. Adopting healthy lifestyle changes is essential for preventing or managing diabetes. This includes eating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains while limiting processed foods, sugary drinks, and unhealthy fats. Regular physical activity also contributes to blood sugar control. If diagnosed with diabetes, it's vital to follow your doctor's recommendations, which may include medication, regular monitoring, and lifestyle adjustments. Empowering yourself with knowledge and making informed choices is important.