Delve into the enigma of dark matter shaping our universe. Explore its mysteries and India's role in unlocking its secrets
For decades, scientists have been grappling with one of the universe's biggest
mysteries: dark matter. This elusive substance makes up a significant portion of the universe's mass, yet it doesn't interact with light, making it invisible to our telescopes. But don't think it's not important!

This invisible force is believed to be crucial in holding galaxies together and shaping the very structure of the cosmos. Indian scientists are also playing a vital role in this global quest to unravel the secrets of dark matter.
Observations of galaxies lead to the concept of dark matter
The concept of dark matter arose from observations of galaxies and galaxy clusters. Scientists noticed that these structures were spinning much faster than they should be, based on the amount of visible matter they contained – stars, gas, and dust.

If only the visible matter were present, the galaxies would simply fly apart . There had to be something else providing the extra gravitational pull to keep them intact. This 'something else' , which cannot be seen, was dubbed "dark matter." Think of it like this: imagine a spinning top.
If it spins too fast without enough weight, it'll wobble and fall. Dark matter acts as the extra weight that keeps the cosmic top – galaxies – spinning smoothly. This has led to considerable research, experiments and theories in the world. It is a complex field and something which will take time to solve, but the possibilities are endless
Evidence for dark matter: gravitational lensing and CMB clues
The evidence for dark matter extends beyond the rotation of galaxies. Gravitational lensing, where light from distant objects bends around massive objects closer to us, provides another compelling piece of the puzzle.
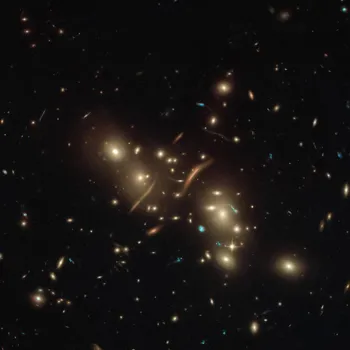
The amount of bending observed often exceeds what can be accounted for by the visible matter alone, suggesting the presence of unseen dark matter. This phenomenon is like looking through a distorted lens. The more mass there is, the more distorted the image becomes.
The observed distortions are much larger than what the visible matter can explain, hence dark matter. The Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB), the afterglow of the Big Bang, also provides clues.
By studying the subtle temperature fluctuations in the CMB, scientists can infer the amount of dark matter present in the early universe.
Scientists explore dark matter composition: WIMPs, axions, black holes
The million-dollar question, of course, is what exactly dark matter is made of. Scientists have proposed various candidates, ranging from hypothetical particles to more exotic objects. One popular theory suggests that dark matter consists of Weakly Interacting Massive Particles (WIMPs).
These particles, as the name suggests, would interact very weakly with ordinary matter, making them incredibly difficult to detect. Another possibility is axions, hypothetical particles with extremely low mass.
Other theories propose that dark matter could be made up of primordial black holes, tiny black holes formed in the early universe. Research continues with new methods and new possibilities.
Scientists working worldwide aim to solve the mystery of dark matter
These WIMPs interact through gravity and perhaps the weak nuclear force, making detection challenging but not impossible. Scientists are designing detectors to spot these interactions. Axions, on the other hand, are much lighter and also interact weakly.

Finding them is like searching for a very faint signal amidst a lot of noise. Primordial black holes, if they exist, would have been formed right after the Big Bang. Their size and distribution could explain the observed effects of dark matter.
Identifying the true nature of dark matter remains a major goal in physics and astronomy. Scientists around the world, including those in India, are working hard to crack this cosmic code
Indian scientists lead global dark matter research, using detectors and simulations for insights
Indian scientists are actively involved in the global search for dark matter. Several research institutions and universities are conducting experiments and theoretical studies aimed at understanding the nature of this mysterious substance.

One approach involves building sensitive detectors deep underground to shield them from background radiation, increasing the chances of detecting WIMPs. Indian researchers are also contributing to the analysis of data from international dark matter experiments.
And they perform simulations to explore different dark matter models. Another exciting area of research focuses on using astronomical observations like the effect of gravitational lensing to probe the distribution of dark matter in galaxies.
Indian scientists leading global search for dark matter
The search for dark matter is a captivating global endeavour. Indian scientists are at the forefront, working together to unravel the mysteries of the universe, contributing their expertise to solve one of science's most challenging questions.

The quest for dark matter involves cutting-edge technology, collaborative research, and a deep understanding of the universe. It is a testament to human curiosity and the pursuit of knowledge. Let's hope that with sustained effort, the real nature of dark matter will be revealed, revolutionizing our understanding of the cosmos














