Unraveling the mysteries of the sun's impact on Earth's cycles and technology. Dive into the solar phenomenon!
The sun, our nearest star, is the engine that drives life on Earth. Its energy provides us
with light and warmth, crucial for plant growth and, ultimately, our survival. But the sun isn't a constant, unchanging source of energy.

It goes through cycles of activity, called solar cycles, which can have significant effects on our planet, impacting everything from satellite communication to weather patterns. Understanding these cycles is becoming increasingly important in our technologically advanced world.
Sun's magnetic field affects sunspots, solar flares, and CMEs
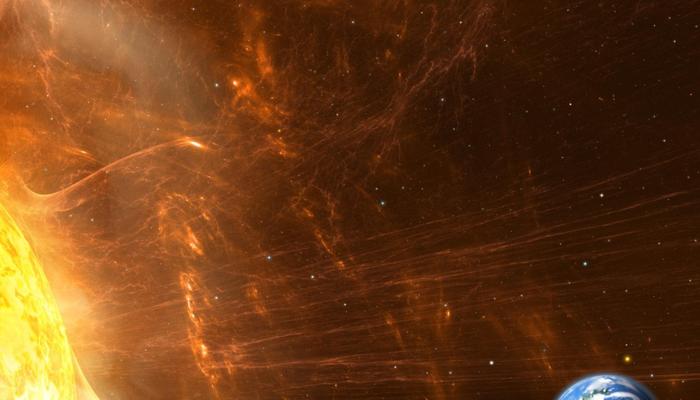
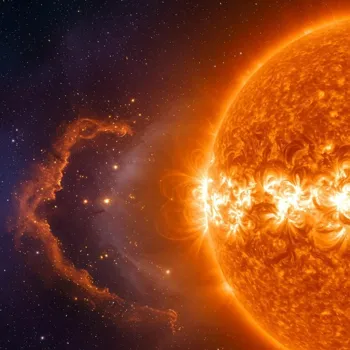
The sun’s activity is governed by its magnetic field, which goes through a roughly 11-year cycle. During this cycle, the number of sunspots—darker, cooler areas on the sun's surface—increases and decreases.

Sunspots are associated with strong magnetic activity, and their presence indicates a more active sun. When the sun is at its most active, it emits more solar flares and coronal mass ejections (CMEs).
These are powerful bursts of energy and charged particles that can travel through space and interact with Earth's magnetic field.
Solar cycle impacts technology, disrupts satellites, GPS, power grids
The solar cycle has significant impact on our technology. Satellites in orbit are vulnerable to the increased solar activity. Solar flares and CMEs can disrupt satellite communications, affect GPS accuracy, and even damage satellite electronics.

This can lead to interruptions in services many people rely on daily, such as navigation, weather forecasting, and television broadcasting. Power grids on Earth are also at risk, during the intense geomagnetic storms which leads to blackouts.
In 1989 caused in Quebec and caused outages for millions.
solar cycles impact weather patterns and climate long-term
While the exact link between solar cycles and weather is still a topic of ongoing research, there is evidence suggesting that solar variability can play a role.

Some studies indicate that changes in solar activity can influence atmospheric circulation patterns, potentially affecting regional temperatures and precipitation.
For example, some scientists believe that the Maunder Minimum, a period of very low sunspot activity in the 17th century, coincided with a colder period known as the "Little Ice Age" in Europe. These events highlight the potential for solar activity to have long-term effects on our climate.
Scientists study the sun's cycles to predict Earth impacts
Scientists are actively studying the sun and its cycles to better understand and predict its impact on Earth. Solar observatories, both on the ground and in space, constantly monitor the sun's activity, providing valuable data that helps us understand the complex processes driving the solar cycle.

Sophisticated computer models are being developed to forecast solar flares and CMEs, giving us more time to prepare for potential disruptions. This research is crucial for protecting our infrastructure and ensuring the continued operation of essential services.
Studying the sun's impact on Earth for preparedness
The sun's influence on Earth extends far beyond just providing light and warmth. Its cycles of activity can have significant consequences for our technology, weather, and climate.
By continuing to study the sun and improving our ability to predict its behavior, we can better prepare for the challenges and opportunities presented by our dynamic star. It’s important that we remember that space weather is a real concern and needs our attention. Let’s keep learning and adapting!
AI Generated Content. Glance/InMobi shall have no liability for the content


















