Unraveling Gravity's Cosmic Dance: Indian Perspective - Explore how gravity sculpts our Universe with Indian astronomers
From the smallest grain of sand to the largest galaxy cluster, gravity is the invisible
force that shapes the Universe we see. It's not just about things falling down; it's the cosmic architect, responsible for building the grand structures that dot the night sky.
Indian astronomers and astrophysicists have been contributing significantly to our understanding of gravity's role, both through theoretical work and observational projects.
This article delves into the fascinating world of gravitational influence on cosmic structure formation, highlighting some key insights relevant to the Indian scientific community and the general public.
Gravity shapes the universe, from galaxies to dark matter
Gravity, a fundamental force of nature, governs the interaction between any two objects with mass. The more massive the objects, the stronger the gravitational pull between them.
It's this force that keeps our feet firmly on the ground, the planets orbiting the Sun, and the stars clustered together in galaxies. But its influence extends far beyond our immediate surroundings.
On the largest scales, gravity sculpts the distribution of matter in the Universe, creating the cosmic web.
Indian scientists are actively involved in simulating the behavior of gravity in these complex environments, using powerful supercomputers like the facility at the Inter-University Centre for Astronomy and Astrophysics (IUCAA) in Pune.
They develop sophisticated models to understand how tiny density fluctuations in the early Universe, amplified by gravity over billions of years, led to the formation of galaxies, clusters, and vast voids.
This work is crucial for testing our understanding of the Big Bang theory and the nature of dark matter and dark energy.
The ongoing observations obtained from ground based observatories in India like Giant Metrewave Radio Telescope (GMRT) and Himalayan Chandra Telescope (HCT) combined with the data from space based observatories like AstroSat offer a unique opportunity to validate theoretical conclusions along side these simulations.
The story of cosmic structure formation after the Big Bang
The story of cosmic structure formation begins shortly after the Big Bang. The early Universe was remarkably uniform, but not perfectly so. Tiny variations in density existed, like ripples in a vast ocean. These initial fluctuations acted as seeds for gravitational growth.

Regions slightly denser than average began to attract more matter due to their stronger gravitational pull. As more matter accumulated, the gravitational force intensified, pulling in even more material.
This process, known as gravitational instability, continued over vast stretches of time, amplifying the initial density fluctuations.
In regions where the density was significantly higher than average, gravity eventually overcame the expansion of the Universe, causing matter to collapse and form structures such as galaxies and galaxy clusters.
The less dense regions, on the other hand, became vast cosmic voids, almost devoid of matter. It's fascinating to consider that the seeds of these colossal structures were sown in the extremely early Universe, a testament to the enduring power of gravity.
Indian cosmologists are currently working on tracing back these seeds and linking them to what they observe now, by using the aforementioned facilities.
Galaxies, gravity's influence, black holes, mergers, Indian research
Galaxies, the building blocks of the cosmic web, are themselves products of gravity's influence. Within galaxies, gravity holds stars, gas, and dust together, creating swirling disks and elliptical shapes.

Supermassive black holes, lurking at the centers of most galaxies, exert an incredibly strong gravitational pull, influencing the motion of stars and gas in their vicinity. The process of galaxy mergers, where two or more galaxies collide and merge into a larger system, is also driven by gravity.
These mergers can trigger intense bursts of star formation and dramatically alter the shapes of galaxies.
The study of galaxy formation and evolution is a major focus of astronomical research in India, with scientists using a combination of observational data and computer simulations to unravel the complex physical processes involved.
Some of the oldest discovered galaxies have been detected by Indian facilities, that provide vital insights into the formation of earliest galaxies.
This has opened new avenues for research on galactic evolution and has motivated scientists to look for newer, advanced tools and techniques for further investigation.
Galaxy clusters reveal cosmic mysteries, AstroSat aids research
Clusters of galaxies, the largest gravitationally bound structures in the Universe, are collections of hundreds or even thousands of galaxies held together by their mutual gravitational attraction.
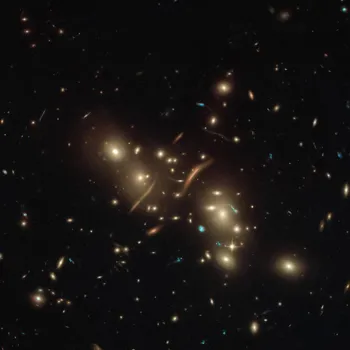
These clusters are embedded in vast halos of dark matter, an invisible substance that makes up the majority of the matter in the Universe. The hot gas within galaxy clusters emits X-rays, providing a valuable tool for studying their properties and the distribution of dark matter.
The Indian space-based observatory AstroSat has made significant contributions to the study of galaxy clusters, particularly through its X-ray imaging and spectroscopic capabilities.
By analyzing the X-ray emission from these clusters, scientists can measure their mass, temperature, and composition, providing insights into the evolution of the cosmic web.
Mapping them offers crucial tests of cosmological models and helps constrain the parameters of dark energy, this is a hot topic in modern Indian research.
Gravity shapes cosmic web; Indian astronomers study for universe insights
Beyond galaxies and clusters, gravity also plays a crucial role in the large-scale distribution of matter in the Universe. The cosmic web, with its interconnected network of filaments, sheets, and voids, is a direct consequence of gravitational instability.
The distribution of galaxies and clusters within the cosmic web provides valuable information about the initial conditions of the Universe and the nature of dark matter and dark energy. Indian astronomers are involved in large-scale surveys of galaxies to map the cosmic web in greater detail.
These surveys, combined with theoretical modeling, are helping to refine our understanding of the Universe's evolution and its ultimate fate. They offer a unique chance to validate fundamental cosmological parameters and improve existing models.
Dark matter shapes cosmic structures, Indian scientists explore detection methods
Dark matter, an enigmatic substance that interacts with ordinary matter only through gravity, plays a crucial role in shaping cosmic structures. Dark matter provides the gravitational scaffolding upon which galaxies and clusters of galaxies form.

Without dark matter, the gravity of ordinary matter alone would not be sufficient to form the structures we observe today.
Indian scientists are actively involved in the search for dark matter, both through direct detection experiments and through indirect methods that look for the products of dark matter annihilation or decay.
The ongoing studies and work provides information about dark matter distribution via gravitational lensing effects on background sources which has given new insights on the dark matter in the galaxies.
Indian scientists leading gravity research in cosmic structures
The study of gravity's role in shaping cosmic structures is a vibrant and exciting field of research. The Indian scientific community is making significant contributions to this field, through theoretical modeling, observational studies, and the development of new technologies.

As we continue to probe the depths of the Universe, with increasingly powerful telescopes and sophisticated computer simulations, we will undoubtedly gain a deeper understanding of gravity's enduring influence on the cosmos.
The journey to uncover the secrets of gravity is a continuous one, and Indian scientists are poised to play a leading role in this quest.
AI Generated Content. Glance/InMobi shall have no liability for the content