Unveiling the Great Attractor: A Cosmic Mystery Pulling Galaxies! Delve into the hidden universe forces
The universe, as we see it twinkling above us every night, may seem like a calm and orderly place.
But looks can be deceiving! Beyond what our eyes can perceive through even the most powerful telescopes, lies a cosmic mystery – the Great Attractor.

This isn't some kind of super-powered alien with a galactic lasso, but rather, a region in space with a gravitational pull so immense, it's tugging at galaxies millions of light-years away, including our own Milky Way.
It has baffled scientists for about a decade, and the details about it are something that has amazed researchers.
The mystery of the Great Attractor in space exploration
Imagine the universe as a giant, slightly uneven, trampoline. If you place a bunch of marbles (representing galaxies) on the trampoline, they'll naturally roll towards the lowest point. The Great Attractor is essentially one of these deeply curved low points.

It resides in the direction of the constellations Centaurus and Hydra, but it's hidden behind something called the Zone of Avoidance. This zone is a region of the sky obscured by the dust and gas of our own Milky Way galaxy.
Think of it like trying to spot a hidden treasure buried behind a huge sand dune. It makes observing and understanding the Great Attractor incredibly difficult. What exactly is creating this monstrous gravitational pull? That's the million-dollar question!
Scientists believe it could be a massive supercluster of galaxies, a concentration of dark matter, or perhaps something even more exotic that we haven't yet imagined. However, research is being done to discover the cause or reason behind it.
Astronomers overcome Zone of Avoidance using diverse wavelengths for deeper galaxy exploration
The main problem with studying the Great Attractor is, as said before, the Zone of Avoidance. This region of our sky, heavily populated with stars, gas, and dust in our own galaxy, obscures our view of what lies beyond. It’s like trying to look through a thick fog – you can only see so far.

However, astronomers are clever folks and have found ways around this obstacle. They employ techniques that use different wavelengths of light, such as infrared and X-rays, which can penetrate the dust and gas more easily.
By using these special "eyes," they can peer deeper into the Zone of Avoidance and get a clearer picture of the galaxies and structures lurking behind it. Even with these advanced technologies, it's still like piecing together a giant cosmic puzzle with many of the pieces missing.
The process has been long. And it requires immense amounts of work.
The Great Attractor linked to Laniakea Supercluster, but mystery persists
One of the leading theories about the Great Attractor is that it's home to a supercluster of galaxies called the Laniakea Supercluster. A supercluster is a collection of galaxy clusters, which themselves are collections of galaxies.
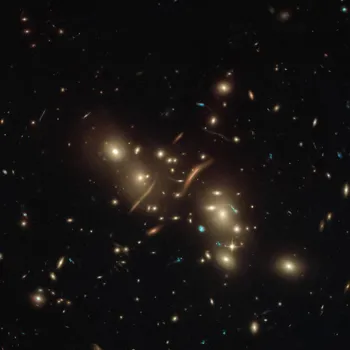
Think of it like this: galaxies form groups, groups form clusters, and clusters form superclusters. Laniakea is a vast structure, spanning over 500 million light-years, and contains the Milky Way along with approximately 100,000 other galaxies!
This would result in a humongous amount of mass packed into a relatively small space. However, the mass of Laniakea alone doesn't seem to be enough to account for all the gravitational pull attributed to the Great Attractor.
That's where the mystery deepens and the hunt for other contributing factors continues. The actual cause is still not known.
Dark matter's gravitational effects remain a mystery in the universe
Another potential ingredient in this cosmic recipe is something called dark matter. We can't see dark matter directly, because it doesn't interact with light. However, we know it's there because of its gravitational effects on other objects in the universe.

Dark matter is thought to make up a significant portion of the universe's mass, much more than the visible matter we can see in stars and galaxies.
If a large concentration of dark matter were located in the region of the Great Attractor, it could certainly contribute to its powerful gravitational pull. Figuring out how much dark matter is present and how it's distributed is like trying to weigh an invisible object.
Scientists are using various techniques, such as gravitational lensing (where the gravity of a massive object bends light from more distant objects), to map the distribution of dark matter in this region of space. It is yet to be discovered.
Understanding the Great Attractor reveals cosmic structure mysteries
So, what's the significance of all this cosmic tug-of-war? Understanding the Great Attractor helps us better understand the large-scale structure of the universe. It gives us clues about how galaxies form, how they move, and how they interact with each other over vast cosmic distances.

It also challenges our understanding of gravity and the distribution of matter in the universe.
As we continue to explore this hidden region of space and refine our theories, we are getting closer to unraveling one of the universe's biggest mysteries and gaining a deeper appreciation for the complex and interconnected nature of the cosmos. It may take a while, but research is being done.
AI Generated Content. Glance/InMobi shall have no liability for the content














