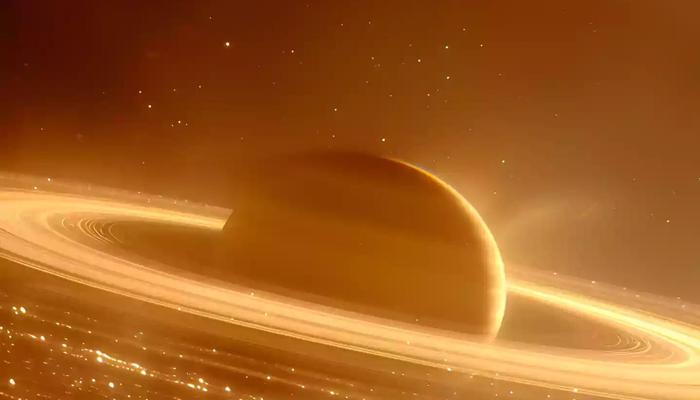
Unveiling the Enigma: Saturn's Mesmerizing Rings Explored. Dive into the mysteries of these celestial wonders!
Saturn, the sixth planet from the sun, is famous for its magnificent rings. These rings make
Saturn a unique and beautiful sight in our solar system, captivating astronomers and space enthusiasts alike.

Understanding these rings is a complex task, but scientists have made significant progress over the years using powerful telescopes and space missions. This article delves into the mysteries and wonders of Saturn's rings, exploring what we know about their composition, formation, and dynamics.
Saturn's rings: ice, rock, dust particles, wide, thin, water ice composition
Saturn's rings are not solid structures; instead, they are made up of countless particles of ice, rock, and dust. These particles range in size from tiny grains to large chunks several meters across.

The rings are incredibly wide, extending hundreds of thousands of kilometers from Saturn, but they are surprisingly thin, typically only a few meters thick. This makes them seem like a giant, flat disc surrounding the planet.
The composition of the rings is mostly water ice, which reflects sunlight brilliantly, giving them their bright and stunning appearance.
Saturn's rings: young debris from shattered moons or remnants of the solar system?
The origin of Saturn's rings is a topic of much debate among scientists. One leading theory suggests that the rings are relatively young, perhaps only a few hundred million years old. This theory proposes that the rings formed from the breakup of a moon or moons that ventured too close to Saturn.

Saturn's strong gravity could have torn these moons apart, scattering their icy debris into the ring system. Another theory suggests the rings could be remnants of the primordial solar system, material left over from the formation of Saturn itself.
More research and data are required to pin point the actual reason for the rings formation.
Saturn's rings diverse, gaps caused by moons, complex dynamics
The rings are not uniform; they are divided into several distinct rings, each with its own characteristics. These rings are separated by gaps, the most prominent of which is the Cassini Division.

The Cassini Division is a wide gap, easily visible through telescopes, caused by the gravitational influence of Saturn's moon Mimas. Other smaller gaps and ringlets are also present, created by the gravitational interactions of various moons orbiting near the rings.
The dynamics of the rings are complex, with particles constantly colliding and interacting with each other and with Saturn's moons.
Space missions reveal Saturn's rings' secrets
Several space missions have provided invaluable data about Saturn's rings. The Voyager missions in the 1980s gave us our first detailed look at the rings, revealing their complex structure and composition.
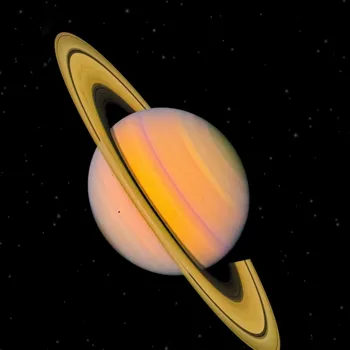
The Cassini spacecraft, which orbited Saturn from 2004 to 2017, provided even more detailed observations.
Cassini's instruments measured the size and distribution of ring particles, mapped the rings' gravitational field, and detected faint spokes, transient features that appear and disappear on the rings. These missions gave us a big leap in understanding the rings.
Mysteries of Saturn's rings, ongoing research for answers
Despite the advancements, mysteries still surround Saturn's rings. Scientists are still working to determining the rings' origin and age. It is also essential to understand the dynamics of the rings and how they interact with Saturn's moons.

Future missions and observations with advanced telescopes will play a key role in addressing these unanswered questions. The study of Saturn's rings continues to be a fascinating and rewarding field, promising new discoveries and insights into the formation and evolution of planetary systems.
AI Generated Content. Glance/InMobi shall have no liability for the content











