Exploring the Universe: Hubble Telescope's Top 10 Discoveries will leave you in awe! Dive into the cosmic wonders
The Hubble Space Telescope, launched way back in 1990, has been a game-changer for astronomy.
Imagine a giant eye in the sky, untouched by the Earth's blurry atmosphere! It has given us images and data that have transformed our understanding of the universe.

It’s like having a VIP seat to the grand cosmic show. Let's take a look at ten of the most amazing discoveries made possible by this incredible machine.
Pinpointing the Age of the Universe
Before Hubble, the age of the universe was a big debate. Scientists were throwing around numbers that differed by billions of years! Hubble helped to narrow down this age by precisely measuring the rate at which the universe is expanding, known as the Hubble Constant.

By observing distant Cepheid variable stars in other galaxies, Hubble allowed astronomers to calculate distances accurately. This brought the estimated age of the universe to around 13.8 billion years.
Knowing how old the universe is, it gives us a better timeline for how everything came to be, from the Big Bang to the formation of galaxies and stars. It's like finally figuring out when the party started.
Confirming the Existence of Supermassive Black Holes
Black holes were once theoretical objects that scientists thought existed. Hubble provided visual proof. By observing galaxies with active galactic nuclei, which are super bright centres, Hubble detected gas and stars whirling around at incredible speeds.

The only explanation for this was the presence of supermassive black holes at the centres of these galaxies. These black holes have masses millions or even billions of times that of our Sun!
Hubble's data not only confirmed their existence but also helped astronomers understand how these giants influence the evolution of galaxies. These monsters gobble everything up, even light!
Witnessing the Birth and Death of Stars
Hubble has captured breathtaking images of stellar nurseries, regions where new stars are born. These images show clouds of gas and dust collapsing under gravity to form new stars.

Hubble has also observed the death throes of stars, capturing images of planetary nebulae, the colourful shells of gas that are ejected by dying stars. These nebulae are like cosmic butterflies, beautiful and transient. Looking at these images, you get a sense of the full life cycle of a star.
Discovering Proto-planetary Disks
These protoplanetary disks are swirling disks of gas and dust orbiting young stars. These disks are where planets eventually form. Hubble has given us images of these disks around distant stars, providing direct evidence that planets form from these disks.

Observing these protosolar systems using Hubble helps us learn how our solar system and all of the planets came to be!
Unveiling the Structure of Galaxies
Before Hubble, our understanding of galaxy shapes and structures was limited. Hubble's sharp images revealed the intricate details of spiral galaxies, like our own Milky Way, and elliptical galaxies.

It has also shown us how galaxies collide and merge, forming even bigger and more complex structures. Hubble's observations have helped us understand the diversity of galaxies in the universe.
Deep Field Images
These images are like looking through a keyhole at the deepest parts of the universe. Hubble pointed at a seemingly empty patch of sky for days at end, collecting faint light. These revealed thousands of galaxies, most of which were never seen before.

These deep field images have provided clues about the evolution of galaxies and the early universe. They are a powerful reminder that the universe is much bigger and far more amazing than we can ever imagine
Hubble has acted like a time machine, capturing light that has taken billions of years to reach us from the depths of space.
Hubble is a telescope that orbits just outside Earth's atmosphere. This alone gave a distinct advantage over ground telescopes. Imagine gazing from the outside!
Hubble’s data is used for many years, not just for the current year. And, the data is used by many astronomers.
Mapping Dark Matter
Dark matter is the mysterious substance that makes up most of the matter in the universe, but we can't see it directly. Hubble has helped astronomers map the distribution of dark matter by observing how it bends light from distant galaxies, a phenomenon known as gravitational lensing.
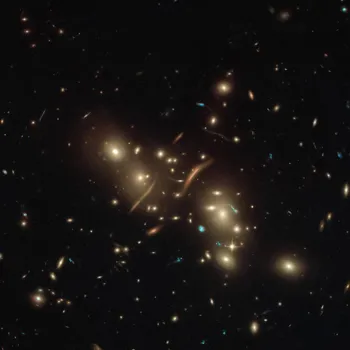
These maps reveal the underlying structure of the universe. This gives scientists more clues to unravel the question what dark matter even is.
Studying the Atmospheres of Exoplanets
Exoplanets are planets that orbit stars other than our Sun. Hubble can study the atmospheres of exoplanets when they pass in front of their host stars. By analyzing the starlight that passes through the exoplanet's atmosphere, Hubble can identify the elements and compounds present.
This data helps scientists determine whether an exoplanet could be habitable.
Tracking Comet Shoemaker-Levy 9's Impact on Jupiter
In 1994, Hubble captured the dramatic impact of Comet Shoemaker-Levy 9 on Jupiter. The comet broke apart into fragments that collided with the giant planet, creating huge plumes of debris in Jupiter's atmosphere.

This event provided valuable insights into Jupiter's atmosphere and the frequency of impacts in our solar system. This was an amazing look at how dangerous the solar system can be, and how often bigger solar systems will impact its planets.
Providing High-Resolution Images of Planets in Our Solar System
While Hubble is mostly used to study distant objects, it has also provided stunning images of planets in our solar system. These images have revealed details about the atmospheres and surfaces of planets like Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, and Uranus, helping scientists understand them.

To even know these planets exist in our solar system, is a massive wonder in history.
Hubble & James Webb telescopes expand universe perception
These are just a few of the many amazing discoveries made by the Hubble Space Telescope. It has broadened our perception of the universe. And with new telescopes coming online, like the James Webb Space Telescope, we can expect even more amazing discoveries in the coming years.














