Weight Gain's Hidden Threats
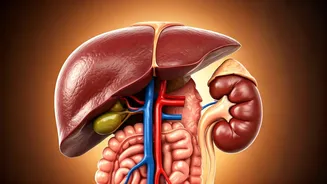
Weight gain, often dismissed as a cosmetic issue, carries significant health risks that extend far beyond aesthetics. Recent research underscores the insidious
ways extra pounds can negatively impact internal organs such as the liver, kidneys, and gut. These organs are crucial for overall health. The liver, essential for detoxification and metabolism, can suffer from fat accumulation, potentially leading to non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). This condition can, in turn, progress to more severe liver damage. The kidneys, vital for filtering waste and regulating fluid balance, face increased strain with excess weight, raising the risk of chronic kidney disease. Furthermore, the gut microbiome, which is critical for digestion and immune function, can be disrupted by weight gain. This disruption affects nutrient absorption and increases the risk of inflammation and metabolic disorders, underscoring the necessity to take action. Ignoring these internal effects can have substantial repercussions on overall health.
Metabolism and BMI's Limits
The effects of extra weight on your metabolism are complex and often underestimated. Metabolism, the process by which your body converts food and drink into energy, is significantly influenced by weight. An increase in body weight can slow down metabolism, making it harder to lose weight and maintain a healthy body composition. This metabolic slowdown occurs partly because fat tissue is less metabolically active than muscle tissue. Body Mass Index (BMI) is commonly used to assess whether a person has a healthy weight. BMI is calculated based on height and weight. However, it's not the complete picture because it doesn't account for factors like muscle mass, body composition, or the distribution of fat. A person with a high BMI might appear to be overweight, but if they have a lot of muscle, they might be healthy. Conversely, someone with a normal BMI could still have health problems if they have a high percentage of body fat. The limitations of BMI emphasize the need to consider other health indicators when assessing overall health.
Diabetes and Heart Disease
Weight gain drastically elevates the risk of both diabetes and heart disease, two of the leading causes of illness and death globally. The mechanisms that link excess weight to these diseases are well-understood. For instance, excess weight leads to insulin resistance, a condition where cells fail to respond to insulin, which helps regulate blood sugar levels. This can lead to chronically elevated blood sugar, and eventually, type 2 diabetes. Furthermore, extra weight often causes a rise in blood pressure and harmful cholesterol levels, which are critical risk factors for heart disease. High blood pressure strains the heart and blood vessels, while elevated cholesterol can lead to the buildup of plaque in arteries, causing blockages that can trigger heart attacks or strokes. Moreover, weight gain can create a state of chronic inflammation in the body. This inflammation contributes to the development and progression of both diabetes and heart disease. Being aware of these relationships is a good way to stay healthy.
Protecting Your Organs
Protecting your vital organs from the harmful effects of weight gain involves a series of lifestyle changes. One of the most important steps is adopting a balanced diet. This focuses on whole, unprocessed foods like fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains. Limiting processed foods, sugary drinks, and unhealthy fats can greatly reduce the risks associated with weight gain. Regular physical activity is another critical factor. Exercise helps maintain a healthy weight, boosts metabolism, improves insulin sensitivity, and reduces inflammation. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity exercise per week, combined with strength training. Getting enough sleep, managing stress levels, and staying hydrated are essential. Chronic stress can lead to overeating and weight gain. Adequate sleep and hydration support overall health and optimal bodily functions. Regular check-ups with healthcare professionals also help monitor health and catch any potential problems early. By making these changes, you can strengthen your body.