Unveiling 10 Physics Discoveries That Altered Our World. Dive into the transformative impact of these breakthroughs!
Physics, the study of matter, energy, and their interactions, has shaped our world in profound
ways. From the smallest particles to the vast expanse of the cosmos, physics unravels the fundamental laws that govern everything.
Over centuries, brilliant minds have made groundbreaking discoveries that have not only expanded our understanding of the universe but also revolutionized technology and daily life. Let's explore ten such remarkable discoveries in physics that have left an indelible mark on our world.
The story of physics is woven with threads of curiosity, ingenuity, and relentless pursuit of knowledge. Each discovery, a testament to human intellect, has paved the way for further exploration and innovation, leading to a world that would be unrecognizable to our ancestors.
From the ability to harness electricity to the development of life-saving medical technologies, physics has constantly redefined the boundaries of what's possible.
These discoveries not only improved our quality of life but also provided a deeper understanding of our place in the vast cosmos, inspiring awe and wonder.
Newton's Laws of Motion and Universal Gravitation:
Sir Isaac Newton's laws of motion, formulated in the 17th century, laid the foundation for classical mechanics. These three laws describe how objects move and interact with each other.
The first law, the law of inertia, states that an object at rest stays at rest, and an object in motion stays in motion with the same speed and in the same direction unless acted upon by a force.
The second law relates force, mass, and acceleration (F=ma), explaining how force affects an object's motion. The third law states that for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction.
Coupled with his law of universal gravitation, which describes the attractive force between any two objects with mass, Newton provided a comprehensive framework for understanding the movements of celestial bodies and objects on Earth.
Newton's ideas revolutionized astronomy, allowing for accurate predictions of planetary orbits. It also enabled engineering marvels like bridges and buildings. His laws are still fundamental, providing the base to designing most technologies.
They form building block, still providing answers to basic questions.
Electromagnetism:
The 19th century witnessed a revolution in physics with the unification of electricity and magnetism. Scientists like Michael Faraday and James Clerk Maxwell demonstrated that these seemingly distinct forces were actually linked.
Faraday's work on electromagnetic induction showed that a changing magnetic field could create an electric current. Maxwell built upon this work, developing a set of equations that described the behavior of electromagnetic fields.
Maxwell's equations predicted the existence of electromagnetic waves, which travel at the speed of light.
This groundbreaking discovery led to the understanding of light as an electromagnetic wave and paved the way for the development of radio communication, television, and countless other technologies that rely on electromagnetic radiation. It's hard to imagine a world without communication devices.
Electromagnetic field brought this reality today.
The Discovery of Radioactivity:
In 1896, Henri Becquerel stumbled upon radioactivity while investigating uranium salts. He found that these salts emitted radiation that could penetrate materials even in the absence of external excitation.

Marie and Pierre Curie further investigated this phenomenon, discovering new radioactive elements like polonium and radium. Their work revolutionized the world.
The discovery of radioactivity opened the door to nuclear physics and nuclear medicine.
Radioactive isotopes are used in various applications, from cancer treatment to carbon dating. This also paved the way to use nuclear energy for power generation. However, radiation is potentially harmful and dangerous.
Quantum Mechanics:
At the beginning of the 20th century, classical physics failed to explain certain phenomena like blackbody radiation and the photoelectric effect. Max Planck, Albert Einstein, and others developed quantum mechanics, a revolutionary theory that redefined our understanding of the subatomic world.
Quantum mechanics revealed that energy is not continuous but rather exists in discrete packets called quanta.
The theory also introduced the concept of wave-particle duality, which states that particles like electrons can behave as both waves and particles.
Quantum mechanics has had a monumental impact on technology, leading to the development of lasers, transistors, and semiconductors, which are the foundation of modern electronics. Quantum computers are a reality because of theory.
Einstein's Theory of Relativity:
Albert Einstein's theory of relativity, comprising special relativity and general relativity, revolutionized our understanding of space, time, gravity, and the universe.
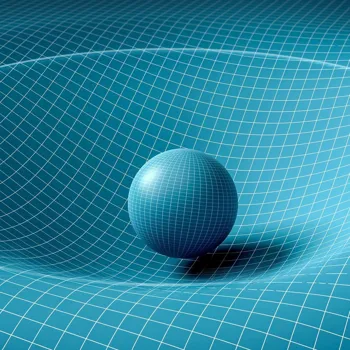
Special relativity, published in 1905, introduced the concept of spacetime and stated that the speed of light is constant for all observers. It also revealed the famous equation E=mc², which demonstrates the equivalence of mass and energy.
General relativity, published in 1915, describes gravity as a curvature of spacetime caused by mass and energy. Einstein's theories have had profound implications for astrophysics, cosmology, and technology.
They are essential for the functioning of GPS satellites, which rely on relativistic corrections to provide accurate positioning. They are also essential in astrophysics to understand the behavior of the galaxy.
Nuclear Fission:
In 1938, Otto Hahn and Fritz Strassmann discovered nuclear fission, the splitting of an atom's nucleus into two or more smaller nuclei. This process releases an immense amount of energy.
This discovery led to the development of nuclear weapons during World War II and the subsequent use of nuclear energy for power generation. Though controversial, nuclear fission has provided a powerful energy source.
Nuclear Energy is a way to generate large amounts of electricity.
Nuclear medicine uses radioactive materials to diagnose and treat several diseases.
The Transistor:
Invented in 1947 at Bell Laboratories, the transistor is a tiny semiconductor device that can amplify or switch electronic signals and electrical power. The invention of the transistor replaced bulky vacuum tubes, leading to the miniaturization of electronics.
Transistors are the building blocks of modern computers, smartphones, and countless other electronic devices.
Transistors are reliable, small in size and affordable. Integrated circuits (ICs) are the miniaturized electronic circuits containing transistors. Transisitor replaced vaccum tube which were heavy, prone to errors, and used a lot of energy
The Laser:
The laser (Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation) is a device that emits a highly focused and coherent beam of light. The first laser was built in 1960 by Theodore Maiman.
Lasers have revolutionized various fields, including medicine, telecommunications, manufacturing, and entertainment. They are used in surgery, optical fibers, barcode scanners, and laser pointers.
Laser has many use case in the modern technology world.
Lasers have medical, communication and entertaiment world. Lasers helped to enhance the world.
The Standard Model of Particle Physics:
The Standard Model is a theoretical framework that describes the fundamental particles and forces that govern the universe. It includes quarks, leptons, and bosons, which interact through the strong, weak, and electromagnetic forces.
The Higgs boson, a key particle in the Standard Model, was discovered in 2012 at the Large Hadron Collider. The Standard Model can accurately describe the behavior of matter at the subatomic level.
Gravitational Waves:
In 2015, the Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory (LIGO) detected gravitational waves, ripples in spacetime predicted by Einstein's theory of general relativity.

This discovery confirmed a key prediction of Einstein's theory and opened a new window into the universe, allowing us to study black holes and other extreme astrophysical events. This allows us to study more about our universe. This provided another reason to think and do research.
These ten discoveries represent only a fraction of the remarkable achievements in physics that have transformed our world. As scientists continue to unravel the mysteries of the universe, we can expect even more groundbreaking discoveries that will shape our future in ways we can only imagine.
Every element of technology needs the support of physics to bring it into reality.
Physics, at its core, is about understanding the fundamental nature of reality. It’s about asking big question and seeking answer with the help of experience.
As we continue to explore the universe, we can expect new discoveries to shape the world. The constant pursuit of knowledge promises a future filled with technological and scientific marvels.
AI Generated Content. Glance/InMobi shall have no liability for the content










