What is the story about?
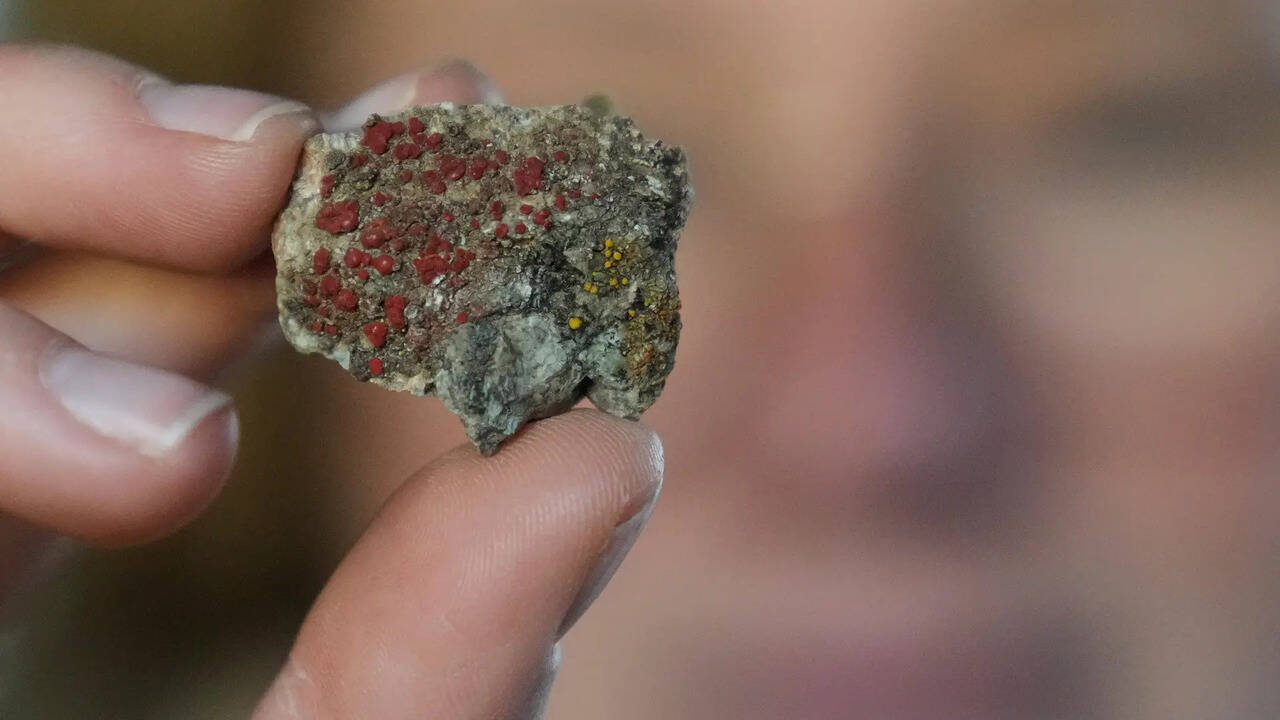
In Angwin, California, mycologist Jessica Allen searched for the elusive Manzanita butter clump, a rare yellow mushroom known to exist only along North
America's Western coastlines. This species was last spotted in Napa County two years ago, and Allen's expedition highlights the ongoing efforts to study and conserve fungi. Despite their vital role in ecosystems and contributions to the global economy, fungi have received limited attention in conservation initiatives. As climate change and habitat loss threaten their survival, scientists and citizen researchers are increasingly working to document and protect these essential organisms.
The Importance of Fungi
Fungi are neither plants nor animals but form a vast kingdom of life that includes yeasts, molds, lichens, and mushrooms. They play crucial roles as decomposers and connectors within ecosystems, providing food and nesting materials for numerous animals. Furthermore, fungi contribute significantly to human welfare, yielding medicines like penicillin and serving as a carbon storage medium.Despite estimates of approximately 2.5 million fungal species worldwide, only about 155,000 have been documented, which is a mere 6% of the believed total. Understanding these organisms' diversity is essential for effective conservation efforts.
Role of Citizen Scientists
Community involvement is vital in fungal conservation. Organizations like the California Lichen Society mobilize amateur researchers who often make significant discoveries and monitor rare species. These volunteers contribute to vital data collection that informs conservation strategies.During recent excursions, lichenologists and enthusiasts gathered to explore various habitats, demonstrating the excitement and curiosity that drives their research. The immersive experience often leads to unexpected findings and a deeper appreciation for these organisms.
Challenges in Fungal Conservation
Gregory Mueller, co-chair of the International Union for Conservation of Nature's fungal conservation committee, notes that the U.S. lags behind other regions in fungal conservation efforts. Currently, only two lichen species are federally protected, while various states are implementing their own measures.In addition to habitat loss, fungi face threats from climate change, invasive species, and overharvesting. For example, the quinine conk, an endangered mushroom in Europe, has suffered from excessive harvesting for its medicinal properties.
Ongoing Research and Future Directions
Mycologists like Nora Dunkirk are actively documenting vulnerable fungi species to support conservation efforts. Many fungi remain hidden beneath the surface, complicating research and conservation initiatives. Addressing these challenges requires enhanced awareness and community involvement.Past conservation efforts, such as the Northwest Forest Plan, highlight the interconnectedness of ecosystems. Protecting fungi is crucial not only for their survival but also for the health of entire forest ecosystems, as demonstrated by the case of the Northern spotted owl in the 1990s.