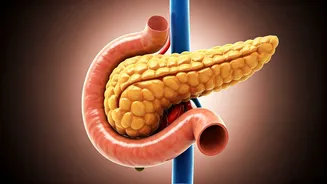
Dietary Modifications
The cornerstone of reversing pre-diabetes lies in making smart dietary choices. Starting with what you eat daily can have a huge impact. Focus on a diet rich
in whole, unprocessed foods such as fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins, while minimizing the intake of sugary drinks and refined carbohydrates. Prioritize whole grains over white bread and pasta, and limit consumption of processed foods, which are often high in added sugars and unhealthy fats. Controlling portion sizes is another key factor; be mindful of how much you are consuming at each meal. It is beneficial to consult a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian who can create a customized meal plan to cater to your specific needs and preferences, maximizing your progress towards managing blood sugar levels and improving overall health.
Regular Physical Activity
Regular exercise is critical for managing pre-diabetes, making it one of the most effective interventions. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise each week, such as brisk walking, cycling, or swimming. Additionally, incorporating strength training exercises at least twice a week can help build muscle mass. As muscles use glucose for energy, building more muscle helps to lower blood sugar levels, even when you are at rest. Consider activities you enjoy, such as dancing, gardening, or playing sports to keep yourself motivated. Prioritizing regular physical activity helps improve insulin sensitivity, aiding your body in utilizing insulin more effectively and managing blood sugar levels.
Achieving Weight Loss
Excess weight, particularly around the abdomen, is a significant risk factor for pre-diabetes. Even a modest reduction in body weight can significantly improve insulin sensitivity and glucose levels. Aim for a gradual and sustainable weight loss, typically about 5% to 10% of your body weight, which can have a considerable impact on your health. Combine a balanced diet with regular exercise to create a calorie deficit and achieve weight loss goals. Focus on making lifestyle changes that you can sustain over the long term, rather than relying on crash diets or quick fixes. Remember that consistent efforts will bring the most lasting improvements in your overall health.
Stress Management Techniques
Chronic stress can disrupt blood sugar levels, making it challenging to manage pre-diabetes effectively. Practicing stress-reducing techniques is vital for overall health. Incorporate stress-reducing activities into your daily routine, such as deep breathing exercises, meditation, or yoga. Spending time in nature, pursuing hobbies you enjoy, and connecting with friends and family can also help. Ensuring adequate sleep is also crucial, as sleep deprivation can heighten stress levels and negatively affect blood sugar control. Consider mindfulness-based stress reduction programs or other relaxation techniques to help manage stress effectively and stabilize blood sugar levels.
Sufficient Sleep Patterns
Adequate sleep is often overlooked, but it significantly influences blood sugar regulation. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night to optimize your health. Poor sleep is linked to insulin resistance, which hinders the body's ability to utilize insulin, potentially elevating blood sugar levels. Establish a consistent sleep schedule by going to bed and waking up at the same time each day, including weekends, to regulate your body’s natural sleep-wake cycle. Create a relaxing bedtime routine, such as taking a warm bath, reading, or listening to calming music, to unwind before sleep. Ensure your bedroom is conducive to sleep: dark, quiet, and cool. Prioritizing good sleep supports overall metabolic health and aids in effectively managing pre-diabetes.
Regular Blood Sugar Monitoring
Monitoring blood sugar levels regularly provides valuable insight into how different foods, activities, and lifestyle factors impact your glucose levels. Use a blood glucose meter to check your blood sugar at different times of the day, such as before meals, after meals, and before bed. This practice enables you to identify patterns and make informed decisions about your diet and lifestyle. Track your readings and share them with your healthcare provider; this collaborative approach ensures tailored adjustments to your treatment plan. Regular monitoring allows for early detection of any fluctuations in blood sugar levels and promotes proactive management of pre-diabetes.
Stay Hydrated Always
Staying well-hydrated can have a positive impact on blood sugar management. Drinking enough water helps the kidneys flush out excess sugar through urine, thus maintaining healthy blood glucose levels. Aim to drink water throughout the day and avoid sugary drinks, such as soda and juices. Monitor your urine color; light yellow indicates proper hydration. It's important to be mindful of how much water you're taking in with other beverages, like caffeinated drinks, which can dehydrate the body. Staying hydrated supports various bodily functions and contributes to your overall well-being, making it an important factor in your pre-diabetes management plan.












![[WATCH] T20 World Cup 2026: Gautam Gambhir hosts dinner for Team India players ahead of Namibia clash](https://g-mob.glance-cdn.com/public/fc/image/7gXS1xdhs5Q0.webp)

