Trump's Greenland Interest
The genesis of this discussion stems from Donald Trump's interest in acquiring Greenland, an island predominantly covered by ice. His initial suggestion
to purchase Greenland was met with a mixture of amusement and concern. While the Danish government quickly dismissed the idea, the implications of such a move reverberated across the globe. Trump’s interest, potentially driven by strategic advantages and resource considerations, ignited a debate about sovereignty, international relations, and the island's future. His comments about the potential for acquiring Greenland highlight the ongoing discussions about geopolitical power and the evolving dynamics of international relations. The former president's perspective brought Greenland to the forefront of global attention, sparking discussions on its importance and strategic significance.
Geopolitical Significance
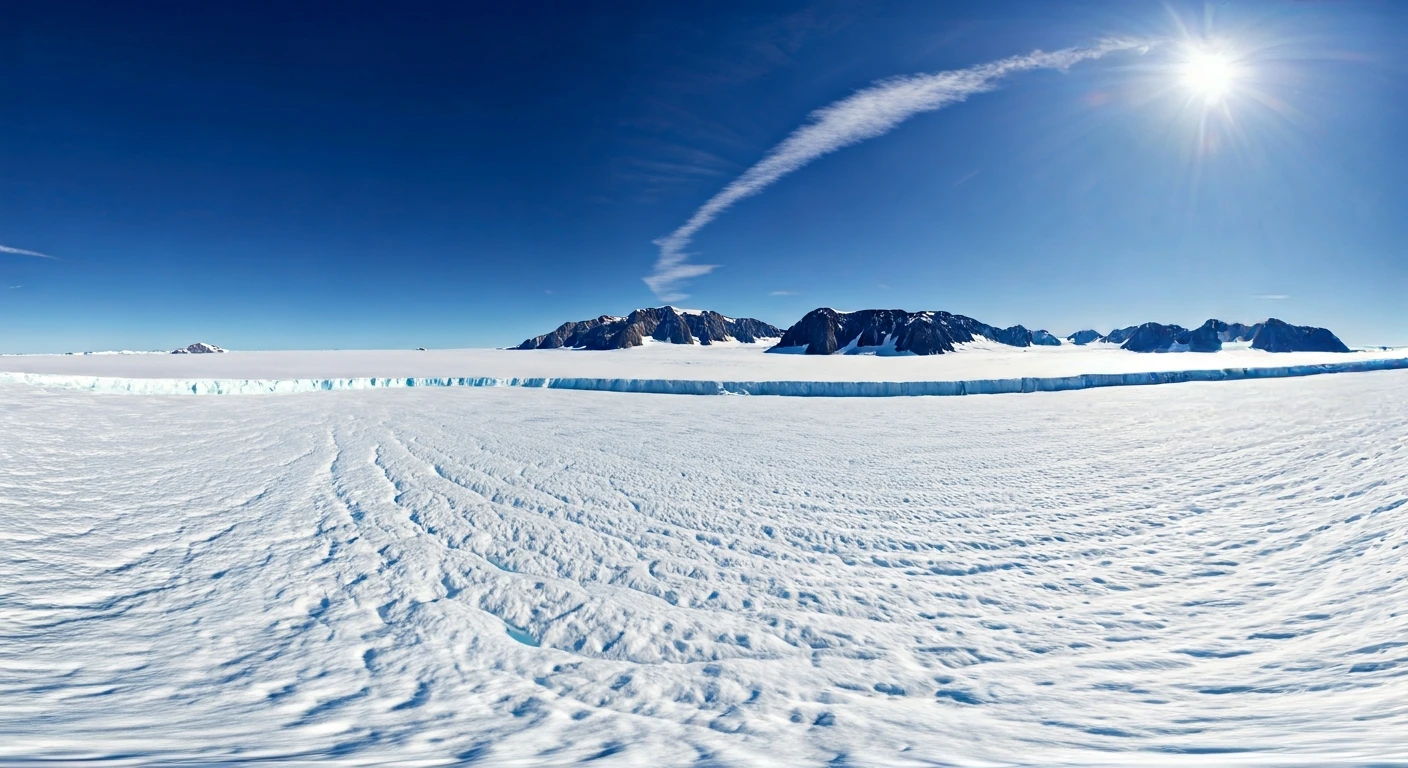
Greenland's strategic location in the Arctic is crucial. It sits between North America, Europe, and Russia, making it a critical point for defense and surveillance. The island's position allows for monitoring of potential threats and control over key shipping routes. Any nation controlling Greenland gains a considerable advantage in the region. The US, which already has a military base there, has long recognized Greenland's strategic importance. This interest extends to its potential role in future Arctic conflicts. The interplay of geopolitical strategy, resource control, and climate change is evident in the interest surrounding Greenland. Its significance is magnified in an era defined by evolving global power dynamics and heightened competition for strategic advantage. Control over the island translates into influence over the Arctic, impacting security, commerce, and scientific research.
Why Greenland 'Green'?
Despite covering about 80% of its landmass with thick ice, Greenland is called ‘Green’land. The historical explanation stems from Norse explorer Erik the Red, who sought to attract settlers. By calling the island 'Greenland,' he aimed to portray it as a hospitable and appealing destination. This deceptive marketing strategy worked, as Norse settlements thrived for several centuries. Even today, the name remains, albeit a misnomer given the reality of the vast ice sheet. This illustrates how perception and branding can shape understanding, even when they diverge from reality. While the name has endured, the harsh environment presents challenges. Climate change accelerates ice melt, dramatically reshaping the landscape. The warming trends are also uncovering a landscape that could be 'greener,' as it begins to reveal areas that were once hidden beneath the ice.
Reactions and Responses
Upon Trump's suggestion of acquiring Greenland, there was a swift reaction. The Danish government, which governs Greenland, quickly dismissed the proposal. Greenlandic political parties also voiced their disapproval, asserting their self-determination and desire to maintain their existing relationship with Denmark. The responses showed a strong desire to protect Greenland's sovereignty and preserve its unique culture and identity. The island's citizens expressed concerns regarding their future and the potential impact of outside influence. Moreover, the discussions highlighted the importance of indigenous rights and the need for respectful engagement in international affairs. Trump's proposal led to a renewed focus on the historical relationship between Greenland, Denmark, and the US, bringing questions of self-governance and geopolitical strategies to the forefront.
Strategic Resources
Greenland is rich in untapped resources. Its soil contains valuable minerals, including rare earth elements crucial for modern technology. With the ice melting due to climate change, access to these resources becomes increasingly feasible. Greenland's potential has drawn international interest. The prospect of resource extraction presents both opportunities and challenges. While it could boost the island's economy, it also raises environmental concerns and sparks debates about sustainable development. The competition for these resources adds another layer of complexity to the region's geopolitical dynamics. The focus on resources adds depth to discussions about the long-term impact of climate change on the Arctic region. The potential for resource extraction also impacts the interests of the various stakeholders involved, including governments, corporations, and indigenous communities.