Oats: The Champion
Oats are a powerhouse when it comes to lowering cholesterol, thanks to their high soluble fiber content. This fiber helps to reduce the absorption of cholesterol into
your bloodstream. Consuming just one and a half cups of cooked oatmeal daily can lower your total cholesterol by 5% to 8%. Beyond oatmeal, other oat-based options such as oat bran and certain ready-to-eat cereals made with oats can also provide these benefits. To make this change in diet, include oats as a staple in your breakfast, mixing it with fruits, nuts, or seeds for added flavor and nutritional value. Remember that consistently consuming oats helps maintain healthy cholesterol levels, which is crucial for overall cardiovascular health. The soluble fiber in oats acts like a sponge, soaking up cholesterol as it moves through your digestive system, reducing the amount that gets absorbed into your body.
Beans: The Fiber King
Beans, the humble legumes, are excellent sources of soluble fiber, which plays a pivotal role in reducing cholesterol levels. Whether it's kidney beans, navy beans, or lentils, beans are a versatile and affordable addition to any diet. Research shows that eating just half a cup of cooked beans daily can lower LDL (bad) cholesterol by up to 10%. Beans also contain resistant starch, a type of fiber that the body doesn't fully digest, aiding in weight management and improved blood sugar control, which indirectly helps manage cholesterol. You can incorporate beans into your meals easily, adding them to soups, salads, or even using them as a base for vegetarian burgers or tacos. Consistent consumption of beans contributes to a heart-healthy diet, providing essential nutrients and promoting overall well-being. Beans are also a great source of protein, making them an excellent choice for anyone looking to increase their protein intake.
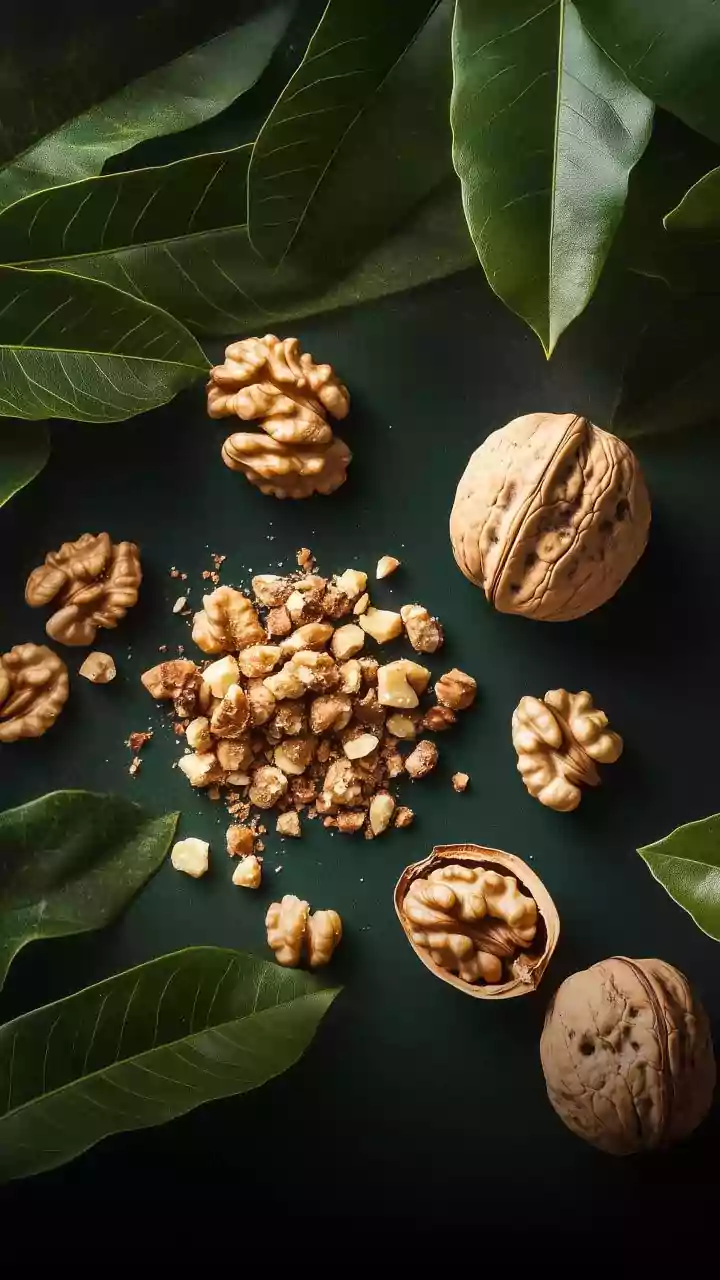
Nuts: Heart-Healthy Snack
Nuts, particularly almonds, walnuts, and pecans, are rich in unsaturated fats, fiber, and plant sterols, which all contribute to lowering cholesterol levels. Regular consumption of nuts can improve the lipid profile, reducing LDL cholesterol. A handful of nuts, about 1.5 ounces, per day can be beneficial. They also provide essential nutrients such as vitamin E, magnesium, and potassium, supporting heart health. Include nuts as snacks, add them to your salads, or incorporate them into your breakfast cereals. Be mindful of portion sizes, as nuts are calorie-dense. Look for unsalted varieties to avoid excessive sodium intake. Adding nuts to your daily diet supports cardiovascular health and can be part of a broader cholesterol-lowering strategy. They also make a satisfying and convenient snack that can help you avoid less healthy options.
Fruits: Nature's Boost
Fruits, especially those high in soluble fiber, such as apples, grapes, strawberries, and citrus fruits, significantly contribute to lowering cholesterol. Pectin, a type of soluble fiber found in these fruits, helps reduce LDL cholesterol levels. A serving of these fruits daily can make a noticeable difference in cholesterol management. Citrus fruits are particularly beneficial due to their high vitamin C content, an antioxidant that supports overall health. Eat fruits whole to maximize fiber intake, and incorporate them into your smoothies, salads, or as a dessert option. Aim for a variety of colorful fruits to get a range of nutrients. Consistent fruit intake supports heart health and promotes a balanced diet, crucial for effectively managing cholesterol levels. Fruit consumption is also associated with improved blood pressure control and reduced risk of chronic diseases.
Vegetable Oils: Healthy Fats
Using vegetable oils instead of saturated fats, such as those found in butter or lard, is a key step towards lowering cholesterol levels. Oils like olive oil, canola oil, and sunflower oil are rich in monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats, which can help reduce LDL cholesterol. When cooking, opt for these healthier oils, using them for sautéing, baking, or as a dressing. Olive oil, in particular, has been linked to numerous health benefits due to its high antioxidant content. Replace unhealthy fats in your diet with vegetable oils, as this is a proactive step towards cardiovascular health. Using these oils supports a balanced diet, contributing to a better lipid profile, and may also reduce the risk of heart disease. Remember to choose cold-pressed or extra virgin options for the most nutritional value.