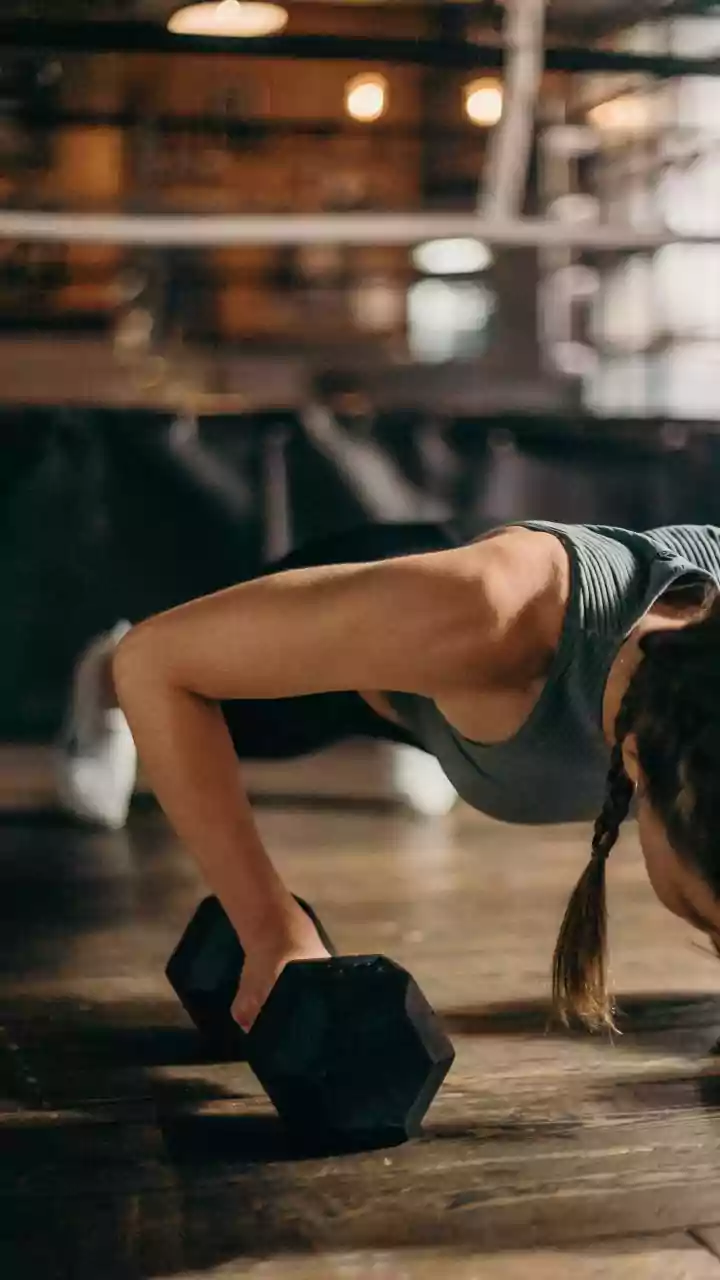Global Wellness Foundations
At the heart of global health lies the consistent pursuit of wellness. This universal concept involves a harmonious interplay between physical, mental,
and social well-being. Across cultures, the emphasis on basic health principles such as adequate nutrition, regular physical activity, and sufficient rest remains constant. The specifics, however, often differ. Dietary habits, for instance, are deeply embedded in cultural traditions, with cuisines around the world reflecting regional ingredients and preferences. Similarly, attitudes towards physical exercise vary, ranging from structured gym routines to communal sports or outdoor activities. Moreover, mental health awareness is gaining traction globally, with increased recognition of the need for stress management and emotional support.
Nutrition: A Global View
Nutrition plays a pivotal role in maintaining health, and its importance is recognized worldwide. Eating a balanced diet that meets the body's nutritional needs is a fundamental health practice. Across different regions, dietary habits vary considerably due to factors like climate, agricultural practices, and cultural preferences. For instance, diets in Asian countries often feature rice and vegetables as staples, while Mediterranean diets emphasize olive oil, fruits, and vegetables. In contrast, many Western diets might include a higher proportion of processed foods and red meat. Despite these variances, the basic nutritional requirements remain consistent: adequate intake of proteins, carbohydrates, healthy fats, vitamins, and minerals. Understanding the nutritional value of different foods and adopting sustainable eating habits are key to improving global health outcomes.
Physical Activity Worldwide
Physical activity is a cornerstone of good health, and its importance is universal. Regular exercise offers multiple benefits, including improved cardiovascular health, weight management, and enhanced mental well-being. Physical activity levels, however, fluctuate significantly worldwide, often depending on lifestyle, resources, and cultural norms. Some regions emphasize structured exercise, with gyms and fitness centers being commonplace. Others favor outdoor activities such as walking, cycling, or team sports. Moreover, the accessibility of recreational spaces and infrastructure, such as parks and walking trails, can significantly affect activity levels. Regardless of the form, consistent physical activity remains critical for preventing chronic diseases and promoting longevity. Cultural perspectives also influence how exercise is viewed, with some societies integrating it seamlessly into daily routines while others view it as a separate activity.
Mental Well-being Matters
Mental health is an increasingly recognized aspect of overall well-being, and its importance is becoming more widely acknowledged across the globe. Mental health includes emotional, psychological, and social well-being. It affects how we think, feel, and act as we cope with life. Factors such as stress, social support, and access to mental health services greatly impact mental health status. In numerous societies, mental health is being destigmatized, leading to greater openness in discussing mental health challenges and an increase in the availability of mental health services. Culturally sensitive approaches that address the specific needs and challenges of different populations are vital. Education and awareness programs can improve mental well-being by providing individuals with coping mechanisms for managing stress and promoting positive mental health practices.
Healthcare Systems Globally
Healthcare systems globally display significant diversity. These systems are typically structured to provide medical care, preventive services, and public health interventions. The availability and quality of healthcare vary widely, influenced by factors like economic resources, infrastructure, and governmental policies. Some nations have universal healthcare systems that provide access to care for all citizens, while others rely on a mix of public and private healthcare options. Furthermore, the focus of healthcare systems can differ. Some prioritize preventive care, emphasizing public health initiatives and early detection of diseases. Others may focus more on treating acute illnesses and managing chronic conditions. Understanding the nuances of global healthcare systems is vital for improving health outcomes and promoting health equity worldwide.
Preventive Health Measures
Preventive health measures are a cornerstone of maintaining good health and preventing diseases. These measures include practices that help individuals stay healthy and prevent the onset of illness. Vaccination programs, which protect against infectious diseases, are a critical component of preventive care. Regular check-ups, screenings, and health education are also vital. Screening for conditions such as cancer, heart disease, and diabetes can allow for early detection and treatment, significantly improving outcomes. Healthy lifestyle choices, including a balanced diet and regular exercise, also act as preventive measures. Public health initiatives, such as promoting clean water and sanitation, play a key role in preventing the spread of infectious diseases. Implementing and maintaining effective preventive health measures contributes to longer, healthier lives across cultures.