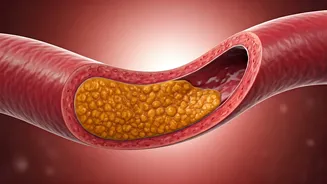
Artery Plaque Explained
Artery plaque, also known as atherosclerosis, is a significant health concern. It occurs when substances like cholesterol, fat, calcium, and other materials
accumulate in the inner walls of the arteries. Over time, these substances form plaque, which hardens and narrows the arteries, a process called atherosclerosis. This buildup restricts blood flow to the heart and other vital organs, leading to various health complications. The process often starts early in life, and risk factors such as high cholesterol, high blood pressure, smoking, and diabetes can accelerate plaque formation. This article will help to understand the causes, the symptoms and possible ways to tackle it for a better life.
Diet and Heart Health
Dietary choices significantly impact artery health. Consuming a diet rich in saturated and trans fats can raise LDL (bad) cholesterol levels, which contribute to plaque buildup. It’s important to prioritize foods that promote heart health. Embrace a diet filled with fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins to get the most benefits. Incorporating sources of omega-3 fatty acids, such as fatty fish, into your diet can help reduce inflammation and lower the risk of heart disease. Regular consumption of fiber-rich foods, like oats and legumes, can help lower cholesterol levels. Be mindful of portion sizes and avoid excessive intake of processed foods, sugary drinks, and red meats, as these can increase plaque formation.
Exercise's Crucial Role
Regular physical activity is another cornerstone of artery plaque prevention. Exercise helps maintain a healthy weight, lowers blood pressure, and improves cholesterol levels. It also enhances the body's ability to use insulin, reducing the risk of type 2 diabetes, a major risk factor for heart disease. The recommended amount of exercise is generally at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity exercise each week. This could include activities like brisk walking, jogging, cycling, or swimming. In addition to aerobic exercise, incorporate strength training exercises at least two days a week to help build muscle mass and further improve overall cardiovascular health. It's beneficial to consult with a healthcare professional to create a safe and effective exercise plan.
Lifestyle Risk Factors
Several lifestyle choices impact artery plaque formation. Smoking, for instance, significantly increases the risk of heart disease by damaging blood vessels and raising blood pressure. Quitting smoking is one of the most effective steps to improve cardiovascular health. Excessive alcohol consumption can also negatively affect heart health, increasing blood pressure and triglyceride levels. If you drink alcohol, do so in moderation, which means up to one drink a day for women and up to two drinks a day for men. Managing stress is also crucial. Chronic stress can contribute to high blood pressure and other risk factors for heart disease. Practicing stress-reducing techniques, such as meditation, yoga, or spending time in nature, can be beneficial.
Medical Check-Ups
Regular medical check-ups play a crucial role in artery plaque prevention. Routine screenings, such as blood pressure checks and cholesterol tests, can help detect early signs of heart disease. It's important to discuss your individual risk factors with your healthcare provider. Your doctor might recommend additional tests like a coronary calcium scan or a stress test to assess the health of your arteries. If any abnormalities are detected, the healthcare provider will develop a tailored treatment plan, which may include lifestyle modifications, medication, or other interventions. Following your doctor's advice and attending all scheduled appointments is very important to ensure ongoing management and maintenance of your heart health.