Unlocking the Truth About Fats: Distinguishing Healthy vs. Unhealthy Fats. Dive deeper into the myths and facts to make informed choices for a healthier lifestyle
For years, fats have been demonized as
the villains of our diet, blamed for everything from weight gain to heart problems. But the truth, as always, is more nuanced. Not all fats are created equal.
In fact, some fats are essential for our health, playing crucial roles in everything from cell function to hormone production. It's time we busted some common myths and got the facts straight about healthy and unhealthy fats, so you can make informed choices for a healthier you.
One of the biggest misconceptions is that all fat makes you fat. This simply isn't true. While consuming excess calories, regardless of the source (fats, carbohydrates, or proteins), can lead to weight gain, fats themselves aren't inherently fattening.
Healthy fats, like those found in nuts, seeds, and avocados, can actually help you feel full and satisfied, potentially aiding in weight management. The type of fat you consume matters far more than the total amount. Focus more on the quality of fat you are consuming.
Then, there's the myth that fat clogs your arteries. This is a partial truth, applicable mainly to unhealthy fats. Saturated and trans fats, often found in processed foods, can raise LDL (bad) cholesterol levels, increasing the risk of heart disease.
However, unsaturated fats, like monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats, can actually help lower LDL cholesterol and raise HDL (good) cholesterol, protecting your heart health.
Unveiling the Good Guys: Healthy Fats
Let's shine a spotlight on the fats that deserve a place on your plate.
These healthy fats are essential for various bodily functions and contribute to overall well-being.
Monounsaturated Fats (MUFAs)
These fats are found in foods like olive oil, avocados, almonds, and cashews. MUFAs can improve cholesterol levels, reduce the risk of heart disease and help control blood sugar. Using olive oil for cooking and adding avocados to your salad are great ways to incorporate MUFAs into your diet.

Polyunsaturated Fats (PUFAs)
PUFAs include omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids, which are crucial for brain function, reducing inflammation, and supporting heart health. Omega-3s are found in flaxseeds, chia seeds, walnuts, and leafy green vegetables.
Omega-6s are present in vegetable oils like sunflower oil and corn oil, but it's important to consume them in moderation as an excess can promote inflammation.
The Omega-3 Advantage
Omega-3 fatty acids, particularly EPA and DHA, are vital for brain health, eye health, and reducing inflammation. Since our bodies can't produce them efficiently, we need to obtain them through our diet.
Incorporating flaxseeds, chia seeds, walnuts and leafy green vegetables into your meals can significantly boost your omega-3 intake.
The Not-So-Good Guys: Unhealthy Fats
Now, let's turn our attention to the fats that should be limited in your diet. These unhealthy fats can negatively impact your health, increasing the risk of various diseases.
Saturated Fats
Found mainly in animal products like ghee and butter, saturated fats can raise LDL cholesterol levels, increasing the risk of heart disease. While it's not necessary to eliminate saturated fats entirely, it's best to consume them in moderation.
Choose lean protein sources and opt for lower-fat dairy products.
Trans Fats
Trans fats are the real villains. Often created artificially in processed foods to extend shelf life, trans fats raise LDL cholesterol and lower HDL cholesterol, significantly increasing the risk of heart disease. Trans fats are commonly found in baked goods, fried foods, and processed snacks.
Always check the ingredient list and avoid products containing "partially hydrogenated oils."
Decoding Food Labels: A Guide to Healthy Choices
Navigating the world of fats can be confusing, but understanding food labels can empower you to make healthier choices.
Total Fat
Pay attention to the total fat content per serving. However, don't just focus on the number; look at the types of fat.
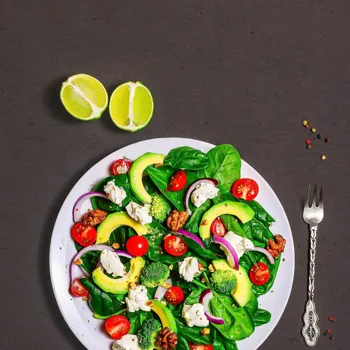
Saturated Fat
Limit your intake of saturated fat. Aim for a diet low in saturated fat.
Trans Fat
Avoid trans fats completely. Look for products with "0g trans fat" and check the ingredient list for "partially hydrogenated oils."
Unsaturated Fats
Prioritize foods rich in monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats.

Incorporating Healthy Fats into Your Diet: Simple Steps
Adding healthy fats to your diet is easier than you think. Here are some simple strategies:
Snack on Nuts and Seeds
Keep a mix of almonds, walnuts, and pumpkin seeds on hand for a healthy snack.

Add Avocado
Incorporate avocado slices into your salads, sandwiches, or simply enjoy them with a sprinkle of salt and pepper.
Flaxseeds and Chia Seeds
Sprinkle flaxseeds or chia seeds into your smoothies, yogurt, or oatmeal.

Busting Common Myths: Separating Fact from Fiction
Let's address some common misconceptions about fats:
Myth: All fat is bad for you.
Fact: Unsaturated fats are essential for health.
Myth: Eating fat makes you fat.
Fact: Excess calories cause weight gain, not necessarily fat alone.
Myth: Saturated fat is always unhealthy.
Fact: Moderation is key. Some saturated fats are less harmful than others.
Myth: You should avoid all fat to lose weight.
Fact: Healthy fats can aid in weight management by promoting satiety.
The Bottom Line: Embrace Healthy Fats, Limit Unhealthy Fats
Fats are an essential part of a healthy diet. By understanding the difference between healthy and unhealthy fats and making informed choices, you can reap the numerous benefits of healthy fats while minimizing the risks associated with unhealthy fats.
Embrace monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats, limit saturated fats, and avoid trans fats altogether. Your heart, brain, and overall health will thank you.
The journey to understanding fats is a continuous learning process so that you can make decisions for a healthier way of life.
The myth that fat makes you gain weight is a common one. People believe that eating fatty foods will directly lead to weight gain. However, this is overly simplistic.
Weight gain occurs when you consume more calories than your body burns, regardless of whether those calories come from fats, carbohydrates, or proteins. Healthy fats, when consumed in moderation, can actually help with weight management.
Fats contribute to feelings of fullness, which can help you eat less overall. Focus on portion control.
Many people think that all saturated fats are bad for you and should be avoided entirely.
While it's true that excessive consumption of saturated fats can raise LDL (bad) cholesterol levels, increasing the risk of heart disease, these fats also have important role in the human body.
Saturated fats can be a part of a balanced diet, particularly from quality whole food sources, consumed in moderation. A good approach is to enjoy saturated fats as part of a diverse diet, prioritizing unsaturated fats.
There is the misconception that avoids all fats which is the effective way of losing weight. While reducing your total calorie intake is generally necessary for weight loss, eliminating fats entirely can be counterproductive.
Fats play important roles in hormone production, nutrient absorption, and cell function. Depriving your body of fats can lead to nutrient deficiencies and other health problems. Including healthy fats in your diet can also help you feel more satisfied, reducing cravings for unhealthy foods.
AI Generated Content. Glance/InMobi shall have no liability for the content













