Understanding the Luteal Phase
The luteal phase, which typically spans days 15 to 28 of the menstrual cycle, is a crucial period. Following ovulation, the body prepares for either a potential
pregnancy or the start of a new menstrual cycle. This phase is dominated by the hormone progesterone, which thickens the uterine lining to support implantation of a fertilized egg. However, if fertilization doesn't occur, progesterone levels decline, triggering menstruation. During this phase, various changes occur, including potential bloating, mood swings, and changes in metabolism. Knowing what to eat can help ease these effects and help the body.
Prioritizing Whole Foods
During the luteal phase, focusing on whole, unprocessed foods is key. These foods provide essential nutrients, which is crucial for hormonal balance and overall well-being. Incorporate a variety of colorful fruits and vegetables, such as berries, spinach, and sweet potatoes. These provide antioxidants that combat inflammation, which can be heightened during this phase. Include lean proteins like chicken, fish, or lentils to support cell repair and hormone production. Healthy fats from sources like avocados, nuts, and olive oil can aid hormone regulation and keep you feeling satiated. Remember to drink plenty of water to stay hydrated and support bodily functions.
Embracing Nutrient-Rich Choices
Specific nutrients are particularly beneficial during the luteal phase. Magnesium, found in foods like dark chocolate, nuts, and leafy greens, can help alleviate premenstrual symptoms like cramps and mood swings. Fiber-rich foods such as whole grains, fruits, and vegetables can assist with digestion and stabilize blood sugar levels, helping to manage energy levels. Iron, found in red meat, spinach, and beans, is essential to replace the iron lost during menstruation. Incorporate foods rich in B vitamins, such as eggs and fortified cereals, to support energy production and nervous system function. Consider a well-rounded diet with these nutrient-dense choices to effectively support your body.
Managing Cravings and Bloating
The luteal phase can bring increased cravings and potential bloating. To manage these, focus on balancing your meals with protein, healthy fats, and complex carbohydrates. This helps to stabilize blood sugar and reduce cravings. Limit processed foods, sugary drinks, and excessive salt, as these can worsen bloating and inflammation. Staying hydrated is also essential; drink plenty of water and herbal teas to support digestion and reduce water retention. Include potassium-rich foods like bananas and sweet potatoes to counteract sodium's effects and reduce bloating. By carefully choosing foods, you can mitigate these common issues.
Sample Meal Ideas
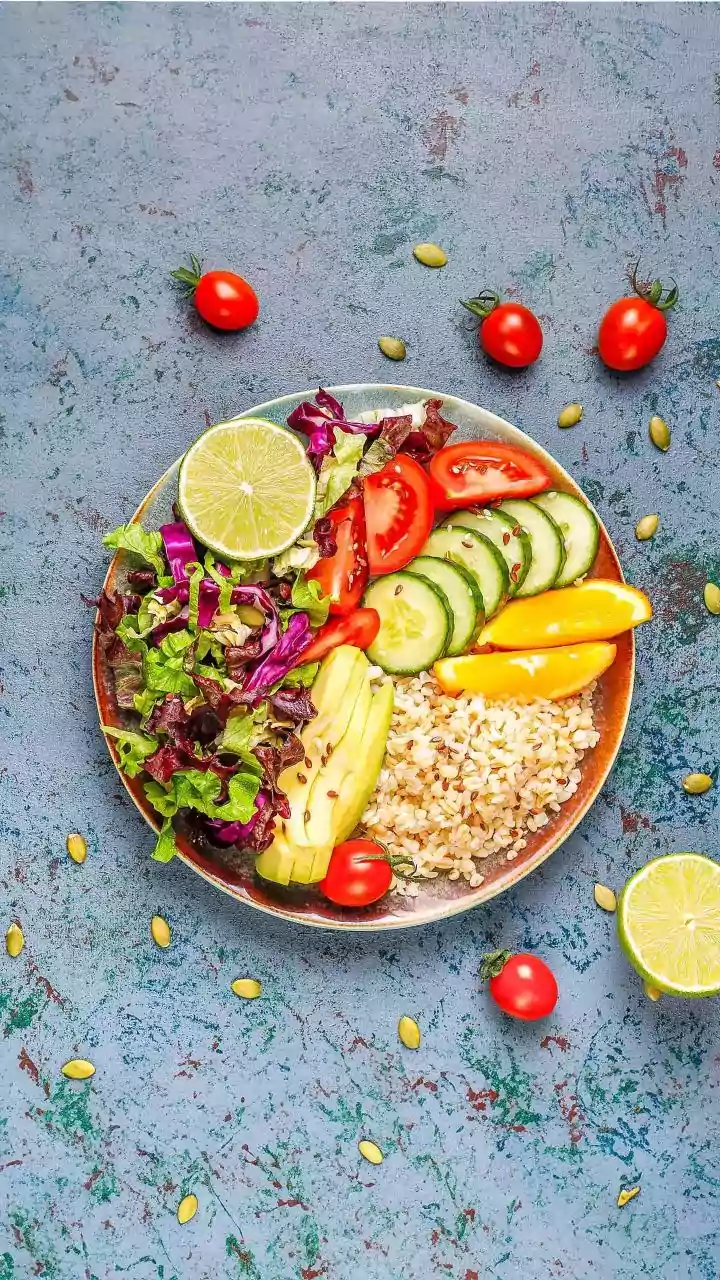
Planning meals ahead can support your nutritional goals. Start your day with a breakfast of oatmeal with berries, nuts, and seeds. Lunch could be a salad with grilled chicken, avocado, and a variety of vegetables. For dinner, consider a lean protein like baked salmon with roasted sweet potatoes and steamed broccoli. Snacking on a handful of almonds or a piece of fruit between meals can keep you satiated and prevent unhealthy cravings. Aim for a balanced plate at each meal and listen to your body's hunger and fullness cues. Tailoring your diet to these options can help you feel your best.