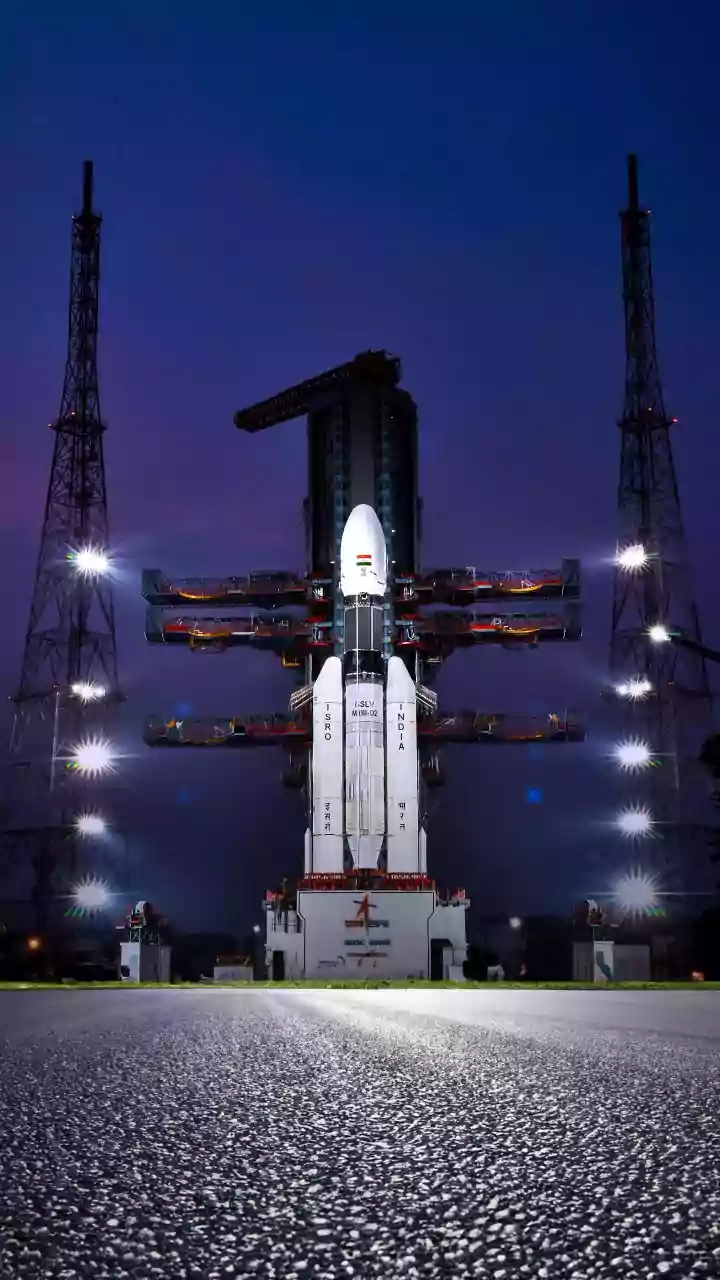
Third Stage Significance
The third stage is frequently the final push for an ISRO rocket to achieve its orbital goals. This stage often uses a cryogenic engine, which requires
liquid hydrogen and liquid oxygen – both stored at extremely low temperatures. The cryogenic engine burns these propellants, generating immense thrust to propel the payload into its predetermined orbit. The third stage's role is not just about power, however. It also needs to be incredibly precise, ensuring the satellite or spacecraft separates at the exact right moment and velocity to successfully enter its orbit. This precision is vital for the mission's long-term success, from communications satellites to scientific observation platforms. Any failure at this stage can be devastating, resulting in mission failure and financial setbacks.
Cryogenic Engine Hurdles
Cryogenic engines are known for their efficiency, but they present several challenges. One of the main challenges is the storage and management of liquid hydrogen and liquid oxygen. These propellants must be kept at exceptionally low temperatures, approximately -253 degrees Celsius for liquid hydrogen and -183 degrees Celsius for liquid oxygen. This is a crucial task since even minor temperature fluctuations can cause the propellants to boil off, which leads to a reduction in the engine's performance. Designing a reliable engine that can operate in these conditions requires sophisticated engineering to deal with the thermal management. Furthermore, the handling of such volatile substances carries significant risk. Leaks of hydrogen can lead to explosions, which necessitates highly rigorous safety protocols and design considerations.
Fuel Efficiency Concerns
The efficiency of the cryogenic engine is of paramount importance to the success of an ISRO mission. The specific impulse, or the efficiency with which a rocket engine converts propellant mass into thrust, is a critical factor. Engineers are constantly working on the designs of the engines to achieve higher specific impulse values. This involves optimizing the combustion process, reducing the weight of the engine components, and improving the fuel injection systems. Fuel efficiency is even more important in the third stage, where the rocket is already at a high altitude and velocity. Any inefficiency at this stage can compromise the ability of the rocket to reach the intended orbit and carry the desired payload. Therefore, innovation in engine design and propellant management is at the forefront of ISRO's efforts.
ISRO's Technological Approach
ISRO's engineers have adopted a multi-faceted approach to navigate these challenges. This includes continuous research and development in cryogenic engine technology. They are focusing on developing more robust and efficient engines that can withstand the extreme conditions of space. Moreover, ISRO is investing heavily in material sciences, seeking out lightweight and high-strength materials that can handle the cryogenic temperatures. Alongside technological upgrades, the agency places a great emphasis on rigorous testing and simulation. The engines undergo a wide range of tests to simulate the conditions of space, ensuring they are reliable and able to operate as designed. These simulations and tests are essential for detecting any problems before launch.
Future Mission Success
The third stage plays a vital role in ISRO's future space missions. The success in the design and management of the third stage directly impacts the success of the mission. For instance, the Chandrayaan and Gaganyaan missions rely heavily on the performance of the third stage to achieve their objectives. Future improvements in cryogenic technology will open doors to more ambitious and complex missions. By perfecting the third stage, ISRO not only increases the success rate of individual missions but also helps to contribute to advancements in space exploration, offering significant scientific and technological benefits for the country. The advancements in cryogenic engine technology directly correlate with India's increasing presence in the global space arena.