Strike: The Basics
The bank strike that took place on January 27, 2026, significantly affected banking operations across India. The primary reason for the strike was employee
protest, though the exact demands weren't given in the context. The impact of the strike varied; some banks faced complete shutdowns, while others managed to keep some services running, with the specific details depending on the bank and its individual arrangements. Customers and businesses experienced interruptions to regular banking activities such as cash transactions, cheque clearances, and other crucial financial operations. The strike highlighted the importance of a smooth-functioning banking system and demonstrated the potential for significant disruption during periods of industrial action. It is essential to consider such information for anyone relying on these services, especially businesses, which depend heavily on the financial support of banks for their functioning.
Services Disrupted
During the bank strike on January 27, 2026, several essential banking services were disrupted. These included, but were not limited to, cash withdrawals and deposits, which are vital for daily transactions. Cheque clearances, a significant method for fund transfers, faced delays, affecting both individuals and businesses. The strike impacted online banking services to varying degrees, with some banks experiencing complete outages or reduced functionality, while others continued to operate partially. Moreover, other financial services, like loan processing, might have been put on hold, creating further inconvenience for customers awaiting approvals and disbursements. The degree of disruption depended on how each bank handled the strike, with some banks preparing contingencies to minimize the impact of the strike. This disruption emphasized the banking system's dependence on smooth operations for economic activity and the potential implications of employee actions.
Affected Banks Overview
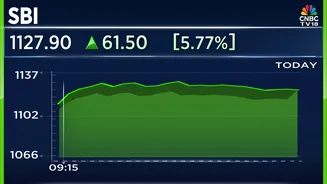
Not all banks were affected equally by the January 27, 2026 strike. Some banks, such as the State Bank of India (SBI), may have announced their response, informing customers about possible service disruptions and the steps they were taking to mitigate the impact. It's important to remember that some banks continued to offer a variety of services to customers, thereby showing their preparation for dealing with these situations. Certain banks were closed, while others managed to stay open. Specific updates on which banks were closed, or open, were provided by different sources. Customers should consult with their respective banks for the most recent and precise updates. This variance among banks underscores the need for people to rely on information, especially during periods of industrial unrest.
Strike's Main Reasons
The main reasons behind the bank strike on January 27, 2026, stemmed from employee protests, though the specific details of these demands were not available in the given context. Such industrial actions are typically prompted by a variety of concerns, which may include pay, working conditions, job security, or policy disagreements. These disputes between bank employees and management can arise from multiple issues that reflect the evolving needs and expectations of bank staff. The strike's main cause highlights the importance of maintaining proper communication between the employees and the management. Employee unions play a crucial role in representing their members’ needs and negotiating with bank management to resolve issues and reach acceptable solutions. Understanding the primary reason for a strike gives insights into the wider issues that can affect the financial services sector and customer experience.
What Continued Working?
Despite the bank strike on January 27, 2026, certain banking services continued to operate or were available to customers through other channels. ATMs remained functional for cash withdrawals and, in some cases, deposits, providing people with crucial access to funds, although availability might vary based on the bank. Online banking platforms and mobile apps enabled customers to conduct financial transactions remotely, ensuring continuity for services such as fund transfers and bill payments. Certain banks made specific arrangements to keep crucial services open, while some branches may have had a limited staff on-site. Therefore, despite the disruptions caused by the strike, customers still had access to some banking services, which provided them with a way to manage their financial activities during a challenging period. The continuous service availability revealed banks' efforts to minimize customer inconvenience, which are critical during industrial actions.