Mission's Core Purpose
The primary objective of the TRACERS mission is to explore the interaction between Earth's magnetic field and the solar wind. The solar wind, a stream
of charged particles emanating from the sun, constantly bombards the Earth. Earth's magnetic field, or magnetosphere, acts as a protective shield, deflecting most of this solar wind. However, the interaction isn't simple; it's a dynamic and complex process. TRACERS seeks to understand how the solar wind affects Earth's magnetosphere and how energy and particles are transferred during these interactions. This knowledge is crucial for understanding space weather, which can disrupt communication systems, affect satellites, and pose hazards to astronauts.
Launch and Deployment
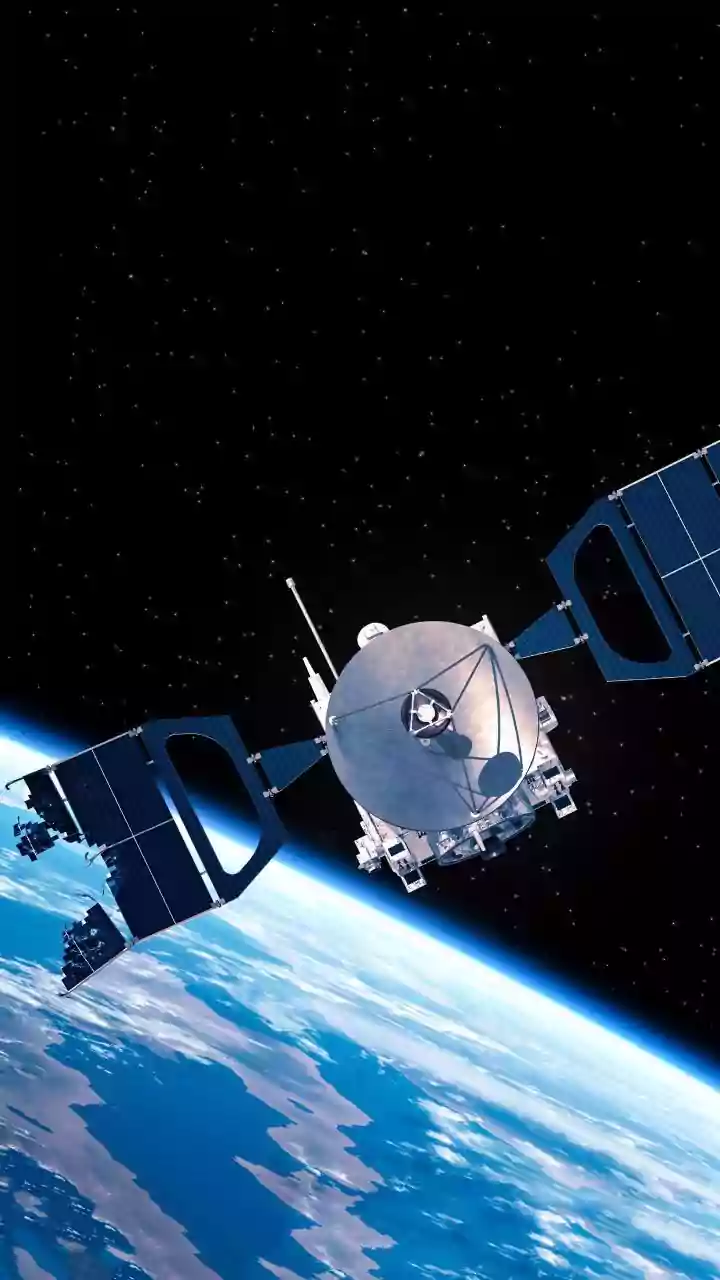
The TRACERS mission embarked on its journey thanks to a successful launch. The mission involves two satellites designed to work in tandem. The deployment of these satellites was carefully planned to ensure optimal data collection. The mission utilizes the SmallSat Rideshare Program, which provides a cost-effective way to launch small satellites. The spacecraft were launched as a secondary payload, demonstrating the flexibility and efficiency of this program. The deployment phase involved precise maneuvers and careful monitoring of the satellites' systems to ensure they were operating correctly. This successful launch marked the beginning of a significant scientific undertaking for NASA, promising to yield valuable data about Earth’s space environment.
Scientific Instruments
The TRACERS satellites are equipped with cutting-edge instruments to measure various aspects of the Earth's magnetic field and the solar wind. The instruments on board include magnetometers, which measure the strength and direction of magnetic fields; and particle detectors, which measure the number, energy, and type of particles present. These instruments work together to create a comprehensive picture of the interactions between the solar wind and Earth’s magnetosphere. The data collected by these instruments will be transmitted back to Earth for analysis by scientists. The sophisticated technology enables the detailed tracking of the dynamic processes in space, giving insights into energy transfer and particle movement. The combined capabilities of the instruments ensure a complete picture of the complex interactions, enabling scientists to make groundbreaking discoveries.
Expected Outcomes
The TRACERS mission is expected to deliver vital insights into the behavior of Earth's magnetosphere. It aims to reveal how the solar wind interacts with our planet's magnetic field, how energy is transferred during these interactions, and how particles are accelerated and transported within the magnetosphere. This data will greatly enhance our understanding of space weather and its effects on our planet. Furthermore, the information could improve space weather models, helping scientists predict and mitigate the impacts of space weather events. The mission results could also lead to advancements in satellite technology and communication systems, making them more resilient to space weather disruptions. The anticipated outcomes of TRACERS are poised to have far-reaching implications, influencing everything from satellite operations to long-term space exploration.
Implications and Future
The discoveries made by TRACERS will have numerous implications for various fields. A better understanding of space weather could lead to improved forecasts, allowing for better protection of satellites, communication networks, and astronauts. The mission data can also help improve the designs of spacecraft to withstand the challenges of the space environment. The information gleaned may also provide insights into planetary magnetospheres. Furthermore, the success of the TRACERS mission represents a significant step in space exploration. It emphasizes the importance of understanding the interactions between the Sun and our planet and contributes to the ongoing efforts to explore and understand the universe. The mission's findings will pave the way for future space missions and enhance our understanding of the universe around us.