Solar Maximum Anticipation
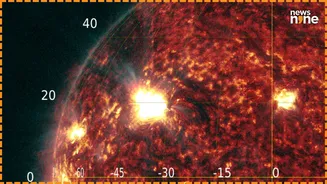
The primary reason for the increased aurora activity in 2026 is the solar maximum phase. The Sun goes through cycles of activity, and the solar maximum represents
the peak of these cycles. During solar maximum, the sun's magnetic field becomes highly unstable, resulting in a surge of solar flares and coronal mass ejections (CMEs). These events release massive amounts of energy and charged particles into space, which, when they collide with Earth's atmosphere, create auroras. Historically, solar maximums have produced some of the most spectacular displays of the Northern Lights, and 2026 is poised to follow suit, offering a prime opportunity to witness these celestial light shows.
Geomagnetic Storms Explained
The charged particles released by solar events travel through space and eventually interact with the Earth's magnetic field. This interaction can trigger geomagnetic storms, which are disturbances in Earth's magnetosphere. These storms are graded on a scale, with stronger storms resulting in more vibrant and widespread auroras. A G2 geomagnetic storm is mentioned, indicating a level of activity capable of producing impressive auroras. The intensity of these storms is crucial, as stronger storms reach lower latitudes, potentially making the Northern Lights visible from areas farther south than usual. This means that 2026 could provide a rare opportunity for people in various locations to witness the beauty of the aurora.
Impacts on Satellites
While the prospect of vibrant auroras is exciting, increased solar activity also poses challenges. Geomagnetic storms can impact technology, particularly satellites. The charged particles can interfere with the operation of satellites, potentially causing disruptions to communications, navigation systems, and other satellite-dependent services. The G2 storm watch illustrates the level of activity being monitored. Space weather forecasting is thus essential to protect these assets and to mitigate any potential damage or disruption. Scientists and engineers continuously monitor the sun and the Earth's magnetosphere to provide early warnings and minimize the risks associated with these events.
Best Viewing Conditions
Several factors influence the visibility of the Northern Lights. First, a clear, dark sky is essential. Light pollution from cities and towns can obscure the aurora, so venturing away from urban areas is recommended. Second, the location is crucial; the closer you are to the Arctic or Antarctic, the better your chances of seeing the aurora. However, during periods of heightened solar activity, such as during the 2026 solar maximum, auroras may be visible at lower latitudes. Finally, the timing is important. Auroras are typically most visible during the hours around midnight. Checking aurora forecasts and alerts can also increase your chances of witnessing this breathtaking phenomenon.
2026: A Unique Year
The confluence of factors makes 2026 a particularly promising year for witnessing the Northern Lights. This includes the solar maximum, potentially strong geomagnetic storms, and the possibility of auroras being visible at lower latitudes. Scientists and aurora enthusiasts are already preparing for the increased activity, with research and monitoring efforts underway to study and understand these celestial events. This heightened solar activity creates a unique window of opportunity to witness the splendor of the aurora, and the year is likely to be remembered as a high point in aurora-viewing experiences, providing a memorable sight for stargazers around the world.