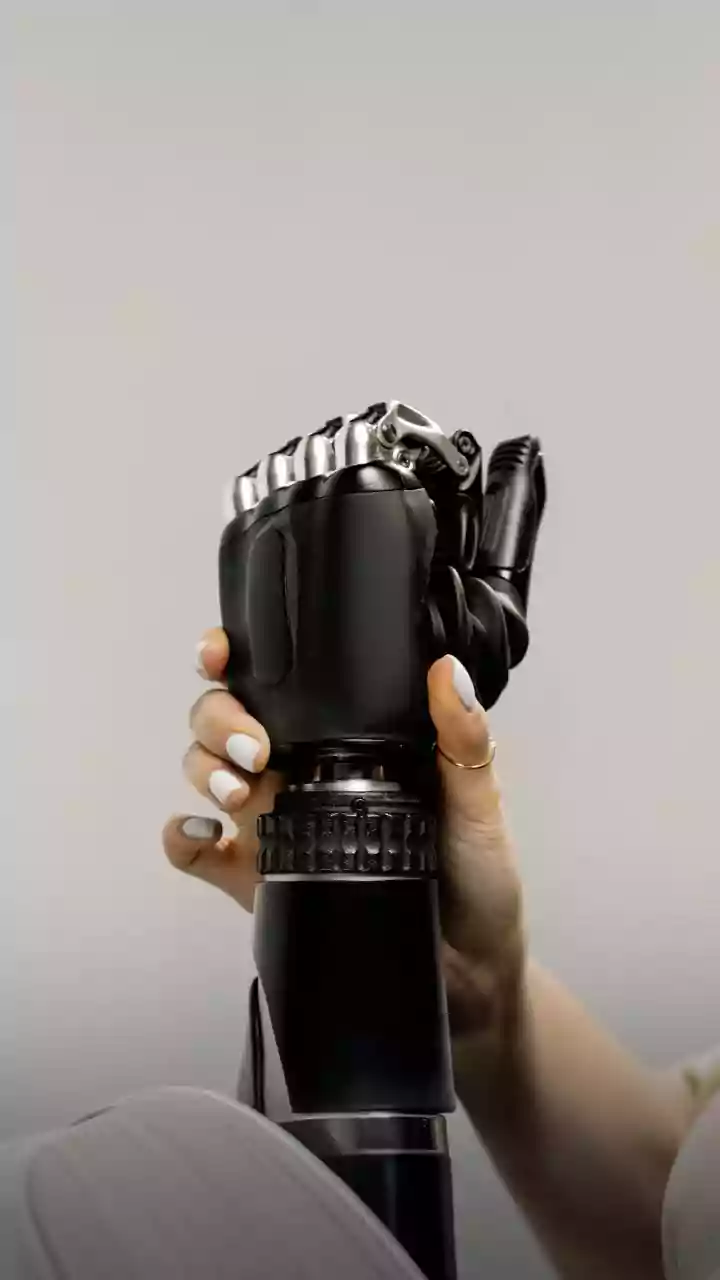
Mudras and Movement
The research focuses on the intricate hand gestures, or mudras, used in Indian classical dance. These mudras are not merely decorative; they are a complex
system of hand positions and movements that communicate specific meanings and emotions. The researchers found that these mudras could be translated into commands for robotic hands. The inherent precision and variety of mudras provide a rich vocabulary for controlling the intricate movements required for a robotic hand to perform various tasks. Through careful analysis and translation, each mudra is mapped to a set of actions, providing a nuanced and efficient method for robotic control. The effectiveness of this approach could potentially make the robotic hands more versatile and user-friendly.
Bridging the Gap
The key to this innovation lies in the ability to bridge the gap between human intent and robotic action. By using mudras, the system bypasses the need for complex programming or extensive training to control the robotic hands. The natural and intuitive nature of mudras allows for a more direct and immediate interaction with the robots. The study has shown that the system is able to interpret and execute these gestures with remarkable accuracy. This connection is especially crucial in fields such as prosthetics, where natural and fluid movement is essential for users' well-being. Additionally, this method can be applied to other areas where precision control is crucial. This advancement could transform how we approach robotics, making the robots easier to control and more adaptable.
Potential Applications
The implications of this research are wide-ranging. In healthcare, it could lead to the development of more sophisticated and natural-feeling prosthetic hands. Surgeons could control robotic tools with greater precision during delicate procedures, improving outcomes and reducing invasiveness. In manufacturing, robots could be taught to perform tasks that currently require human dexterity. Moreover, the entertainment industry could benefit from more expressive and lifelike robotic characters. The use of mudras could enhance human-robot interaction in various settings, leading to greater efficiency and collaboration. As this technology develops, it can improve the performance and increase the versatility of robots in various domains.
Future Directions
The next steps in this research include refining the translation of mudras into robotic movements and testing the system in a variety of real-world scenarios. Researchers are also exploring how to adapt the system to different types of robotic hands and how to integrate it with other control methods. The ultimate goal is to create a seamless and intuitive interface that allows users to control robots with the same ease and precision as they would use their own hands. Future developments could include adding different features to the system for enhanced utility, such as the ability to customize the system to individual needs. The continued research and development will lead to further improvements in robotics and the way we interact with technology.