New Delhi: The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) is developing LOX-Methane engines for induction into the next generation launch vehicles. The development
of the essential engine subsystems is progressing at the Liquid Propulsion Systems Centre (LPSC) of ISRO. A smaller scale test (sub-scale) test of these subsystems has commenced. Crucial to any cryogenic engine is an optimally designed thrust chamber with the injector head. For the first time, ISRO has conducted a hot test of the high-thrust thrust chamber of its developmental LOX-Methane engine with a single element injector. The test was conducted at the Thrust Chamber Test facility at the ISRO Propulsion Complex (IPRC) in Mahendragiri on 27 January, 2026.
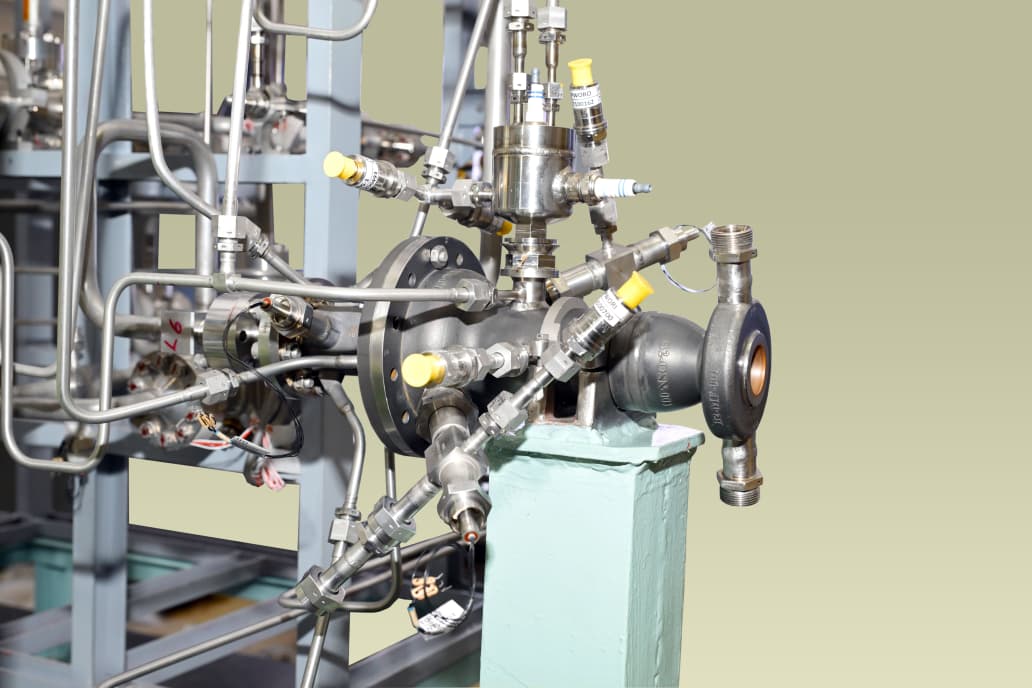
The 3D printed single-element Thrust chamber. (Image Credit: ISRO).
The sub-scale thrust chamber and the single element injector head were 3D printed, or realised through additive manufacturing. Ingition and flame sustenance inside the thrust chamber were achieved and the performance of all the systems were nominal. The test article will be further used to determine the optimal injector configuration through a series of additional hot tests. LOX-Methane engines offer several advantages over the hypergolic, cryogenic and solid fuels used by ISRO in its operational launch vehicles in terms of efficiency, reusability, safety, and mission flexibility. The SpaceX Raptor engines use LOX-Methane, and these engines are crucial for reusability.
LOX-Methane engine essential for ISRO’s future plans
ISRO’s Next Generation Launch Vehicle is presently imagined as a 100 metre tall rocket with a liftoff mass between 2,600 and 3,000 tons, with a diameter of 6.5 metres. The first stage uses a cluster of seven reusable and steerable LOX-Methane engines, with a pair of strapons of similar configuration. The second stage uses two LOX-Methane Engines, with the cryogenic upper stage using a pair of LOX-LH2 engines. This rocket is necessary to realise a number of aspirations of ISRO in the Space Domain, including assembling the Bharatiya Antariksh Station, and dispatching a crewed mission to the Moon.















