What's Happening?
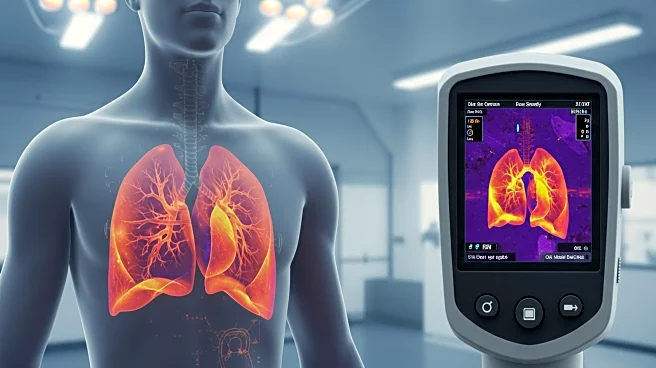
A study conducted at the First Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou Medical University evaluated the effectiveness of infrared thermal imaging technology in diagnosing pulmonary infections in emergency settings. The research involved 200 patients, with 108 diagnosed with pulmonary infections and 92 without. Infrared thermography was used alongside traditional X-ray examinations to assess lung infections. The study found that infected patients exhibited localized hyperthermia in the lung areas, contrasting with the homogeneous temperature distribution in non-infected patients. The infrared imaging provided a visual representation of temperature variations, aiding in the identification of infection sites.
Why It's Important?
The use of infrared thermal imaging in diagnosing pulmonary infections could revolutionize emergency medical practices by providing a non-invasive, rapid diagnostic tool. This technology offers potential benefits in improving diagnostic accuracy and speed, which are critical in emergency settings. It could reduce reliance on X-rays, minimizing radiation exposure for patients. The ability to quickly identify infection sites can lead to more timely and targeted treatments, potentially improving patient outcomes and reducing healthcare costs. This advancement may also enhance diagnostic capabilities in resource-limited settings where traditional imaging equipment is scarce.
What's Next?
Further research and validation studies are necessary to establish infrared thermal imaging as a standard diagnostic tool for pulmonary infections. The technology's integration into clinical practice will require training for medical personnel and adjustments in hospital protocols. Regulatory approval and standardization of equipment specifications are essential steps before widespread adoption. Additionally, exploring the application of this technology in other types of infections or medical conditions could expand its utility in healthcare.
Beyond the Headlines
The adoption of infrared thermal imaging technology raises ethical considerations regarding patient privacy and data security, as thermal images could potentially reveal sensitive information. There is also a need to address potential disparities in access to advanced diagnostic technologies, ensuring equitable healthcare delivery across different regions and populations.