What's Happening?
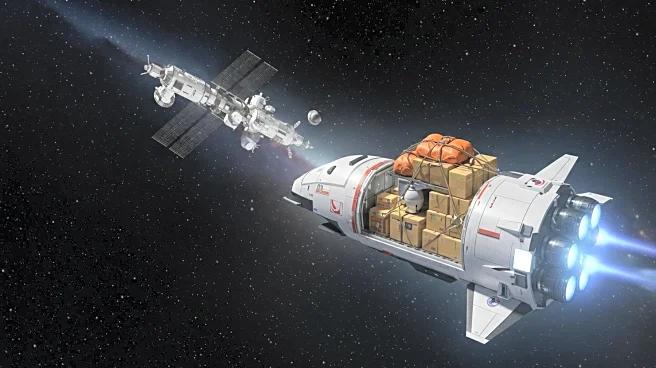
SpaceX's Falcon 9 rocket launched the Dragon spacecraft from Cape Canaveral, Florida, early Sunday morning. The spacecraft is en route to the International Space Station (ISS) and is expected to dock at approximately 7:30 a.m. ET on Monday. This marks the third flight for the Dragon spacecraft and the 33rd resupply mission by SpaceX to the ISS. The mission, conducted under NASA contracts, includes over 5,000 pounds of supplies and more than 50 research projects. Among the scientific materials are components for 3D printing medical implants, bio-printed liver tissue for studying blood vessel development in microgravity, and supplies for printing 3D metal cubes in space. Additionally, bone-forming stem cells are being sent to study bone loss prevention, with potential applications for reducing bone loss in patients on Earth.
Why It's Important?
The resupply mission is crucial for ongoing scientific research and technological advancements aboard the ISS. The experiments conducted in microgravity can lead to breakthroughs in medical treatments, such as the development of functional organs for transplantation. The mission also supports future space exploration, including NASA's Artemis missions to the Moon and potential astronaut missions to Mars. The supplies sent, including food items like tortillas, are essential for the daily operations and well-being of the ISS crew. The mission highlights the importance of international collaboration and continuous innovation in space exploration, benefiting both space missions and terrestrial applications.
What's Next?
Following the docking of the Dragon spacecraft, the ISS will receive a boost in its orbit through thruster firings. This maneuver is necessary to counteract the drag caused by the thin atmosphere at the station's altitude of approximately 250 miles above Earth. The ongoing research and experiments will continue to provide valuable insights into space exploration and potential applications on Earth. The success of this mission may lead to further advancements in space technology and international cooperation in scientific endeavors.