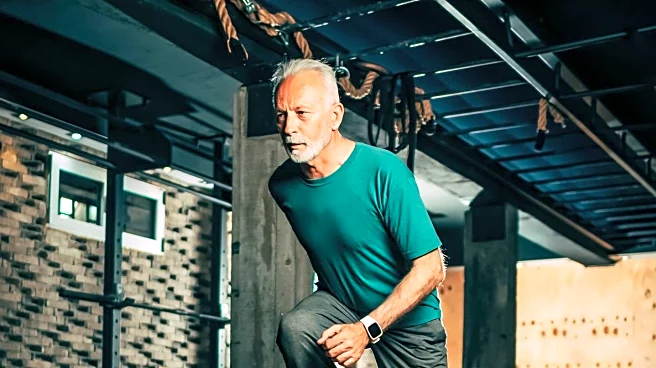What's Happening?
As individuals reach the age of 65, they enter what medical professionals refer to as the 'third age,' a period marked by gradual physiological, metabolic, and cognitive changes. Despite these changes,
experts emphasize that this stage should not be seen as a decline but as an opportunity for preventive measures to maintain independence. Regular strength training and balance exercises are recommended to combat muscle loss and improve cardiovascular health. Additionally, proper nutrition and medication management are crucial to prevent falls and other health issues. The focus is on maintaining functional ability rather than just chronological age, with early detection and intervention being key to reversing conditions like frailty and sarcopenia.
Why It's Important?
The transition into the 'third age' is significant as it represents a critical period for implementing preventive health strategies. With age, the body's ability to handle stressors diminishes, making older adults more susceptible to falls, confusion, and hospitalization. By focusing on strength training, nutrition, and medication management, individuals can maintain their independence and quality of life. This approach not only benefits the individuals but also reduces healthcare costs associated with age-related health issues. The emphasis on early intervention and prevention can lead to better health outcomes and a more active lifestyle for older adults.
What's Next?
Moving forward, healthcare providers are likely to continue promoting preventive measures for those entering the 'third age.' This includes comprehensive health reviews, updating vaccinations, and addressing fall risks at home. There may also be an increased focus on social engagement and mental health to combat loneliness and depression, which are common in older adults. As the population ages, there will be a growing need for policies and programs that support healthy aging and independence.