What's Happening?
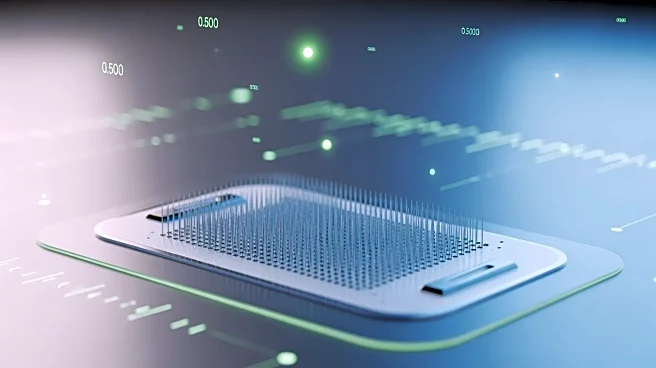
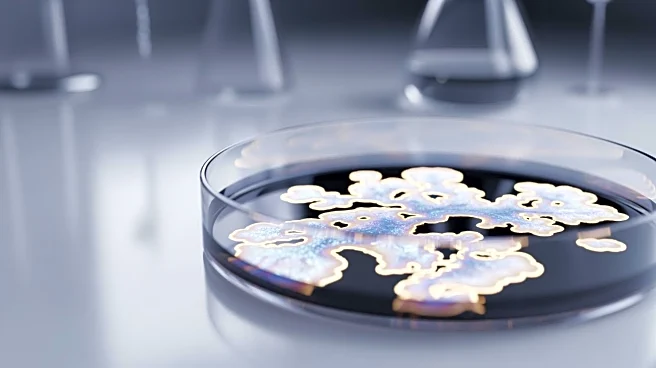
A new development in continuous glucose monitoring technology has emerged with the creation of a vertical graphene-coated core-shell microneedle sensor (VCMGS). This device is designed for real-time, continuous monitoring of glucose levels, offering a promising tool for diabetes diagnosis and management. The VCMGS features a hollow microneedle for skin penetration and a graphene-coated electrode for glucose detection. This design enhances the sensor's mechanical strength and stability, allowing for accurate and reliable glucose monitoring. The sensor's electrochemical properties are improved by the graphene coating, which increases sensitivity and reduces interference from other substances. The VCMGS has been tested in both in vitro and in vivo
settings, demonstrating its potential for effective glucose monitoring in real-world applications.
Why It's Important?
The development of the VCMGS represents a significant advancement in diabetes management technology. Continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) are crucial for individuals with diabetes, as they provide real-time data that can help manage blood sugar levels more effectively. The enhanced sensitivity and stability of the VCMGS could lead to more accurate glucose readings, reducing the risk of complications associated with diabetes. Additionally, the device's ability to monitor other biomarkers could expand its use beyond diabetes, potentially benefiting patients with various health conditions. This innovation could improve patient outcomes and reduce healthcare costs by enabling better disease management and early detection of health issues.
What's Next?
The next steps for the VCMGS include further testing and refinement to ensure its reliability and accuracy in diverse settings. Clinical trials may be conducted to validate its effectiveness in human subjects, which could lead to regulatory approval and commercialization. The integration of this technology into healthcare systems could transform diabetes management, offering patients a more convenient and effective way to monitor their health. Additionally, the potential to track other biomarkers could open new avenues for research and application in various medical fields.
Beyond the Headlines
The VCMGS not only promises to enhance diabetes management but also raises important considerations regarding accessibility and affordability. Ensuring that this technology is available to a wide range of patients, including those in low-resource settings, will be crucial. Moreover, the ethical implications of continuous health monitoring, such as data privacy and patient autonomy, will need to be addressed as this technology becomes more widespread. The development of the VCMGS could also spur further innovation in wearable health technology, leading to new solutions for chronic disease management.