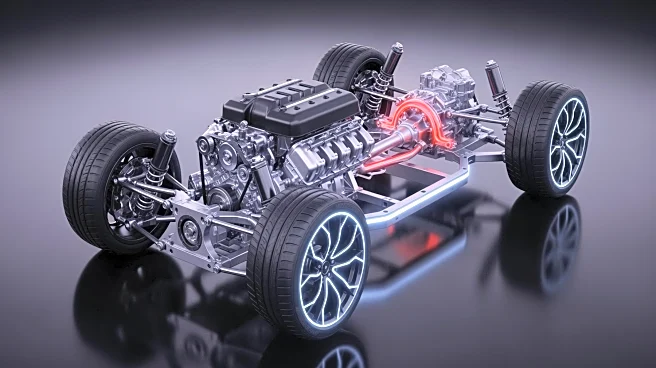
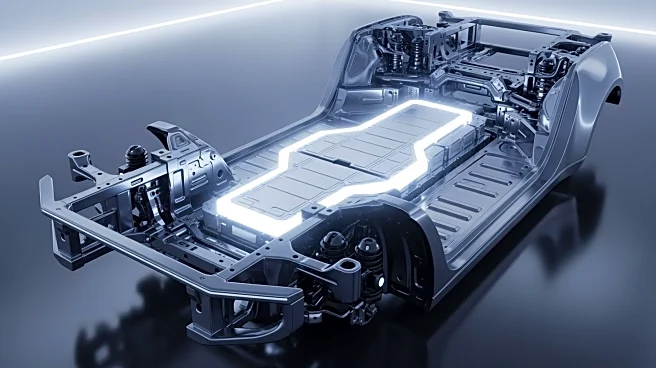
The mid-engine, four-wheel-drive (M4) layout is a fascinating aspect of automotive design that combines the placement of the engine in the middle of the vehicle with the capability to drive all four wheels. This configuration is often associated with sports and racing cars, offering a unique balance of performance and handling. By placing the engine between the front and rear axles, the M4 layout provides distinct advantages in terms of weight distribution
and traction, making it a preferred choice for high-performance vehicles.
The Mechanics of the M4 Layout
In the M4 layout, the internal combustion engine is strategically positioned in the middle of the vehicle, between both axles. This placement is crucial as it allows the engine's center of gravity to lie between the front and rear axles, enhancing the vehicle's balance and handling. The power generated by the engine is transmitted through a shaft to a central differential, which then distributes power to both the front and rear axles. This setup is particularly beneficial for sports cars and racing vehicles, where precise handling and stability are paramount.
The center differential in many four-wheel-drive cars is similar to that found in two-wheel-drive vehicles, allowing torque to be distributed to both drive axles while permitting them to spin at different speeds. This feature significantly improves cornering on high-grip surfaces like tarmac. However, unlike the differentials on the drive axles, which provide equal torque to both wheels, the center differential in an M4 layout often has a bias towards one set of drive wheels, depending on the car's application.
Advantages of the Mid-Engine Placement
One of the primary benefits of the mid-engine placement is the improved handling balance it offers. Since the engine is the heaviest component of a car, positioning it between the axles helps achieve a more even weight distribution. This balance is further enhanced when the engine is located behind the passenger compartment, as it pushes down on the rear wheels, increasing grip and allowing more torque to be applied before wheelspin occurs.
Additionally, the mid-engine placement allows for a more aerodynamic design. With the engine not located at the front, the vehicle can be designed with a reduced frontal area, minimizing air resistance and improving overall aerodynamic efficiency. This design consideration is particularly important for high-speed sports cars, where aerodynamics play a crucial role in performance.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite its advantages, the M4 layout is not without its challenges. The complexity and cost of manufacturing such a system can be higher compared to traditional layouts. Additionally, the mid-engine placement often results in limited passenger and cargo space, as the engine and transmission occupy a significant portion of the vehicle's interior.
Moreover, the variable handling characteristics of a four-wheel-drive system can present challenges during high-speed cornering. A vehicle may exhibit understeer when entering a corner and then transition to oversteer midway through, requiring skilled handling to maintain control. Despite these challenges, the M4 layout remains a popular choice for high-performance vehicles, offering a unique blend of power, balance, and handling that is hard to match.