Here are today’s most important updates from the realm of Science and Space.
India’s Narmada Valley Carved Into Space History as NASA Honors It on Asteroid
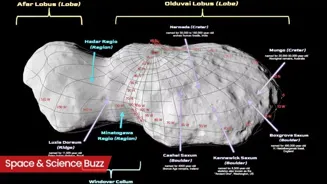
NASA’s Lucy mission has received a historic naming update from the International
Astronomical Union (IAU), which has approved official designations for surface features on the asteroid Donaldjohanson. One of the features has been named after India's Narmada. The small asteroid, located in the main belt between Mars and Jupiter, was visited by Lucy on April 20, 2025, during a successful flyby that served as a crucial rehearsal for the spacecraft’s main mission to Jupiter’s Trojan asteroids. Among the newly named regions is Narmada, honouring India’s Narmada Valley, where the fossilised remains of an ancient hominin, Homo erectus narmadensis, were discovered. The asteroid’s smaller lobe is called Afar Lobus, after Ethiopia’s Afar region, while the larger lobe is Olduvai Lobus, named for Tanzania’s Olduvai Gorge. The narrow connecting neck is Windover Collum, recalling Florida’s Windover Archaeological Site near NASA’s launch location.
From Orbit to Ocean: NASA’s Guardian Detects Tsunami Before Landfall

A powerful magnitude 8.8 earthquake struck off Russia’s Kamchatka Peninsula in late July, sending pressure waves through the upper atmosphere and triggering a tsunami that raced across the Pacific Ocean. A NASA technology spotted the ripples and warned 30 minutes before landfall. The event offered a real-world trial for Guardian (GNSS Upper Atmospheric Real-time Disaster Information and Alert Network), an experimental tsunami detection system under development at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California. The system, which had just deployed a new artificial intelligence component and messaging prototype, was put to the test against one of the strongest earthquakes ever recorded.
From Sun to Screen: AI Spots Solar Storms Before They Hit Earth

Scientists at NYU Abu Dhabi (NYUAD) have developed an artificial intelligence (AI) model that can forecast solar wind speeds up to four days in advance, significantly more accurately than current methods. Solar wind is a continuous stream of charged particles released by the Sun. When these particles speed up, they can cause "space weather" events that disrupt Earth's atmosphere and drag satellites out of orbit, damage their electrons, and interfere with power grids. The researchers trained their AI model using high-resolution ultraviolet (UV) images from NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory, combined with historical records of solar wind. Instead of analyzing text, like today's popular AI language models, the system analyzes images of the Sun to identify patterns linked to solar wind changes. The result is a 45 percent improvement in forecast accuracy compared to current operational models, and a 20 percent improvement over previous AI-based approaches.
Stroke Recovery Reimagined: Scientists Harness Stem Cells for Healing

Scientists in Zurich have shown that stem cell transplants can reverse stroke damage by regenerating neurons, restoring motor functions, and even repairing blood vessels. The breakthrough not only healed mice with stroke-related impairments but also suggested that treatments could soon be adapted for humans, marking a hopeful step toward tackling one of the world’s most devastating conditions. Its beneficial effects include regeneration of neurons and restoration of motor functions, marking a milestone in the treatment of brain disorders. Despite the encouraging results of the studies, the lead author warns that there is still work to be done. "We need to minimize risks and simplify a potential application in humans," he added.