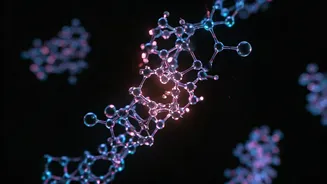
A Century-Old Rule
For over a hundred years, chemists have operated under a foundational rule governing the structure and behavior of molecules. This rule, deeply embedded
in chemical theory, has been a cornerstone of how scientists understand and predict molecular interactions. It dictates specific parameters for how atoms can bond and arrange themselves within a molecule, essentially defining the stable configurations molecules can assume. The rule has served as a reliable framework for synthesizing countless compounds and understanding their properties. However, like all scientific principles, it was not immune to challenge, and it seems this one has finally met its match. Scientists at UCLA set out to challenge this long-held convention, setting the stage for their remarkable discovery.
Challenging the Paradigm
The UCLA research team embarked on a mission to create a molecule that would directly contradict this established chemical rule. Their aim was not to simply tweak an existing compound but to build something that fundamentally violated the principle. This was a bold undertaking, requiring innovative experimental techniques and a deep understanding of molecular behavior. They meticulously planned their approach, using sophisticated tools to design and synthesize a molecule that would be unstable under the previously accepted rules. This required a creative and persistent effort, as the team had to anticipate and overcome numerous challenges that arose during the process. Their dedication and ingenuity led them to the successful creation of a molecule that defied the conventional wisdom of chemistry.
Molecular Marvel Unveiled
The culmination of their work was the creation of a novel molecule that defied the century-old rule. This molecule demonstrated a structural configuration that was previously deemed impossible, upending long-held assumptions about molecular stability and bonding. The team's achievement was not just a theoretical anomaly; it was a tangible demonstration that the established rules could be broken. The new molecule possessed properties that set it apart from others, opening up possibilities for new applications. This discovery sparked excitement within the scientific community, as it challenged the foundations of understanding, creating fresh approaches to designing and constructing molecules. The remarkable feat opened doors to a new understanding of molecular architecture and behavior.
Implications and Applications
This breakthrough from the UCLA chemists has significant implications that extend far beyond the laboratory. By demonstrating the possibility of creating molecules that violate established rules, the research broadens the possibilities in material science. The ability to design and synthesize unconventional molecules could lead to the development of new materials with unprecedented properties, like enhanced strength, flexibility, or unique electronic capabilities. Moreover, the findings may revolutionize drug development by enabling the creation of novel therapeutic agents. It creates new ways for chemists to target specific diseases with more precision and effectiveness. The research paves the way for a deeper understanding of molecular interactions, contributing to advancements across a wide range of scientific fields and industries.
Future Research Directions
The creation of this rule-breaking molecule signifies the beginning of a new chapter in molecular science, with researchers eager to explore its full potential. Future studies will likely focus on understanding the mechanisms behind the molecule's unique behavior, investigating its stability, and identifying potential applications. Scientists will undoubtedly delve into the broader implications of the findings, seeking to design additional unconventional molecules and explore how they interact with other substances. The researchers will attempt to refine the techniques they employed and search for any other molecular structures that defy currently accepted principles. This work could reveal new insights into the fundamental workings of chemical reactions and provide a powerful tool for designing customized molecules with specific functions, enhancing various fields, from electronics to medicine.