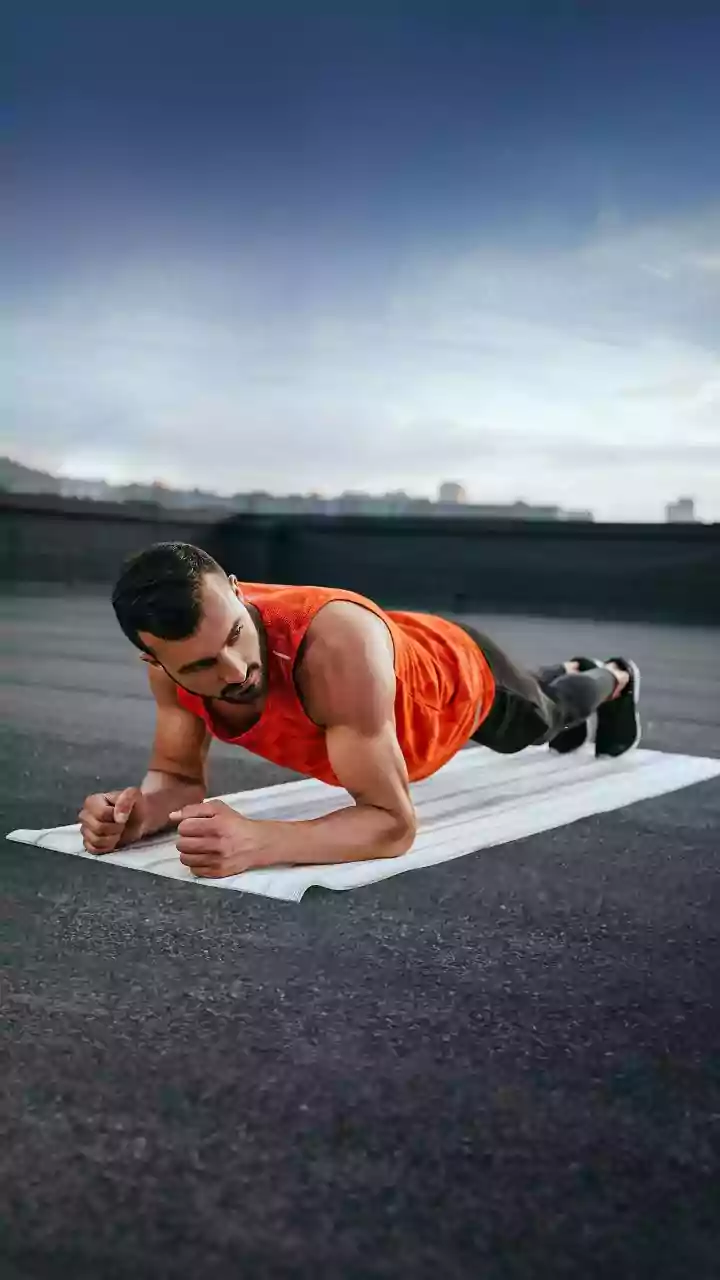
Embrace Strength Training
Strength training is a cornerstone of any anti-aging exercise regime, and it plays a vital role in maintaining muscle mass. As individuals age, they naturally
experience a decline in muscle mass, known as sarcopenia, which can lead to reduced mobility, increased risk of falls, and overall weakness. Incorporating strength training exercises, such as lifting weights or using resistance bands, combats this decline by stimulating muscle growth and strengthening existing muscles. This not only improves physical function but also boosts metabolism, making it easier to maintain a healthy weight. Regular strength training also supports bone density, reducing the risk of osteoporosis, a condition characterized by weak and brittle bones. Furthermore, strength training can improve cognitive function, mood, and overall quality of life. Start by choosing exercises that target all major muscle groups and gradually increase the weight or resistance as you get stronger. It's advisable to consult with a fitness professional or healthcare provider to develop a safe and effective strength training program tailored to your individual needs and abilities.
Cardio for Heart Health
Cardiovascular exercises are crucial for maintaining a healthy heart and overall cardiovascular system. Activities like brisk walking, jogging, cycling, or swimming improve heart health, increase blood flow, and lower blood pressure. Regular cardio exercise strengthens the heart muscle, making it more efficient at pumping blood throughout the body. This reduces the risk of heart disease, stroke, and other cardiovascular ailments, which become more prevalent with age. Cardio also enhances lung capacity and stamina, allowing you to perform daily activities with greater ease. Beyond physical benefits, cardio exercises can also release endorphins, which have mood-boosting effects and can help alleviate symptoms of depression and anxiety. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity cardio exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity exercise per week, spreading the activity throughout the week for optimal results. It is important to warm up before each workout and cool down afterward to prevent injuries and maximize the benefits.
Flexibility and Stretching
Flexibility and stretching exercises are often overlooked, but they play a significant role in maintaining mobility and preventing injuries as you age. As you get older, the body's flexibility naturally declines due to reduced production of lubricating fluids in the joints and the shortening of muscles and tendons. Regular stretching exercises, like yoga or Pilates, can improve your range of motion, reduce stiffness, and increase the elasticity of muscles and connective tissues. This can make everyday movements easier and reduce the risk of falls and injuries. Stretching also improves posture, relieves muscle tension, and enhances blood circulation. These exercises can also help in reducing the effects of arthritis. Incorporating stretching into your daily routine is simple. Hold each stretch for at least 30 seconds and focus on slow, controlled movements. Remember to breathe deeply throughout the stretches and listen to your body, never pushing yourself beyond a comfortable range of motion.
Balance Training is Key
Balance training is vital for preventing falls, which are a leading cause of injury among older adults. As individuals age, their balance tends to decline due to reduced muscle strength, changes in the inner ear, and diminished sensory feedback. Balance exercises help improve stability and coordination, reducing the risk of falls and related injuries like hip fractures. Simple balance exercises include standing on one leg, heel-to-toe walking, and using a balance board. These activities challenge your body's ability to maintain equilibrium, strengthening the muscles that support balance and improving your awareness of body position. Regular balance training can also improve your confidence in performing daily activities and help you maintain your independence. Incorporate balance exercises into your weekly routine, gradually increasing the difficulty as you become more comfortable. It is also beneficial to practice these exercises in different environments and on various surfaces to challenge your balance further and improve adaptability.
Mind-Body Connection
Mind-body exercises like yoga or Tai Chi are incredibly beneficial for healthy aging. These practices combine physical postures, controlled breathing, and meditation to improve both physical and mental health. They enhance flexibility, strength, balance, and coordination, while also reducing stress and improving mental clarity. Yoga and Tai Chi promote a sense of calm and well-being. Regular practice can lower blood pressure, improve sleep quality, and alleviate symptoms of anxiety and depression. They encourage mindfulness, helping you connect with your body and become more aware of your posture and movements. The gentle, low-impact nature of these exercises makes them suitable for people of all ages and fitness levels. Consider attending a class or following online tutorials to learn proper techniques and ensure safety. Mind-body practices can be a transformative addition to any exercise routine, offering holistic benefits that support both physical and mental well-being throughout the aging process.