Muscle Power Revealed
The assertion that 'thick thighs save lives' isn't just a catchy phrase; it reflects the significant role of leg muscles in maintaining good health. Strong
thigh muscles are crucial for various bodily functions and provide several health benefits. They play an integral role in mobility, stability, and balance, reducing the risk of falls, especially as people age. Adequate leg strength also helps with everyday activities such as walking, climbing stairs, and carrying objects, improving overall quality of life. Furthermore, robust leg muscles can positively impact metabolic health by enhancing insulin sensitivity and promoting glucose uptake, which contributes to lower risks of type 2 diabetes. They contribute significantly to bone density, reducing the risk of osteoporosis and fractures.
Thigh Muscle Types
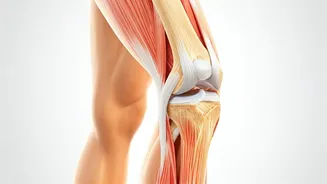
The human thigh is composed of several muscle groups, each contributing to different movements and functions. The quadriceps femoris, located at the front of the thigh, is one of the most prominent groups. It comprises four muscles: the rectus femoris, vastus lateralis, vastus medialis, and vastus intermedius. These muscles are essential for extending the knee and flexing the hip, enabling walking, running, and jumping. The hamstring muscles, at the back of the thigh, include the biceps femoris, semitendinosus, and semimembranosus. They are responsible for flexing the knee and extending the hip, assisting in activities like bending and lifting. Additionally, the adductor muscles, on the inner thigh, are essential for bringing the legs toward the midline of the body, aiding in balance and stability. Understanding the role of each muscle group is key to developing a comprehensive training program.
Boosting Leg Strength
Building strong leg muscles involves a combination of exercise and proper nutrition. Resistance training, using weights, resistance bands, or body weight, is crucial. Exercises such as squats, lunges, leg presses, and hamstring curls effectively target different thigh muscle groups. Proper form is paramount to avoid injuries and maximize effectiveness. Gradually increasing the weight or resistance as muscles get stronger is a fundamental principle of progressive overload. Incorporating a variety of exercises ensures that all muscles are engaged and that improvements continue over time. Consistency is key; aiming for at least two to three strength training sessions per week helps to see noticeable results. Along with resistance training, cardiovascular exercise such as running, cycling, or swimming also contributes to overall fitness and indirectly supports muscle development.