EOS-N1's Mission
The EOS-N1 satellite was a crucial component of India's ambitious space exploration and Earth observation initiatives. Its primary purpose was to provide
high-resolution imagery and data for a variety of applications critical to national development and scientific research. These applications spanned diverse fields such as agriculture, where it could monitor crop health and yield; forestry, aiding in the assessment and management of forest resources; disaster management, offering real-time insights for flood, drought, and wildfire response; and urban planning, supporting the development and management of cities. Furthermore, the satellite was designed to contribute to climate change studies by tracking environmental parameters and to coastal zone monitoring, ensuring the effective management of marine resources and coastal ecosystems. The deployment of EOS-N1 was intended to bolster India's self-reliance in satellite technology and enhance its capabilities in remote sensing, providing invaluable data for informed decision-making across multiple sectors and furthering our understanding of our planet.
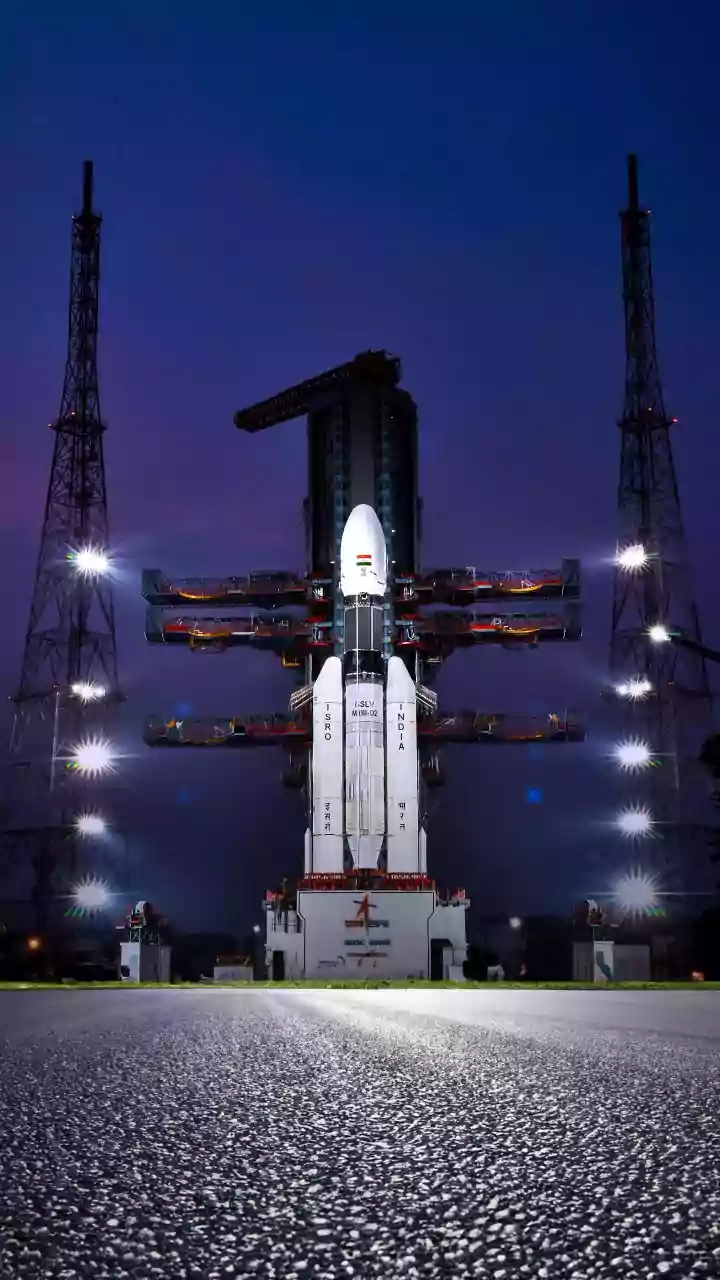
The PSLV Launch
The launch vehicle for the EOS-N1 satellite was the venerable Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV), often referred to as ISRO's 'workhorse'. The PSLV has a distinguished track record, having successfully deployed numerous satellites into various orbits for both national and international customers. Its reliability and versatility make it a cornerstone of India's launch capabilities. The mission designated as PSLV-C62 aimed to place EOS-N1 into its intended orbit with precision. Each PSLV mission is a culmination of extensive planning, rigorous testing, and the coordinated efforts of hundreds of scientists and engineers. The success of a PSLV launch signifies not just the delivery of a satellite but also a testament to the technological prowess and operational excellence of the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO). This particular launch was anticipated to further strengthen India's position in the global space arena by adding another advanced observation capability to its fleet.
Mission Anomaly Unfolds
Despite the meticulous preparations and the proven reliability of the PSLV, the EOS-N1 mission encountered an unforeseen anomaly during its ascent. The exact nature and timing of this anomaly led to the satellite not achieving its intended orbit. Such occurrences, while rare, are inherent risks in space missions. The causes can range from minor deviations in engine performance to complex system malfunctions. In the aftermath of such an event, ISRO's dedicated teams undertake a thorough investigation to pinpoint the root cause. This process involves analyzing telemetry data, reviewing launch procedures, and conducting detailed system diagnostics. Understanding the anomaly is critical for implementing corrective measures and ensuring the success of future missions. While the loss of a satellite represents a setback, the knowledge gained from such anomalies is invaluable for the continuous improvement and advancement of space technology and mission planning.