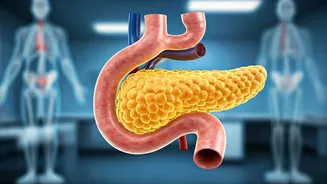
Pancreas: Vital Role
The pancreas is an essential organ in the human body, serving a dual purpose. It plays a significant role in both digestion and hormone regulation. Functioning
as an exocrine gland, the pancreas produces enzymes necessary for breaking down food in the small intestine. These enzymes, including amylase, lipase, and protease, are crucial for the efficient digestion of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins, respectively. Concurrently, the pancreas operates as an endocrine gland, producing vital hormones like insulin and glucagon. Insulin helps regulate blood sugar levels by facilitating glucose uptake by cells, while glucagon works in opposition to raise blood sugar when it drops too low. This complex interplay of digestive enzyme production and hormone regulation underscores the pancreas's importance in maintaining overall health and well-being. A compromised pancreas can lead to serious health problems, hence the importance of understanding its functions and the signals of potential distress.
Sign: Abdominal Pain
Persistent or recurring abdominal pain is a common indicator of pancreatic issues. The pain often manifests in the upper abdomen and can radiate to the back. This discomfort arises from the inflammation or irritation of the pancreas itself. This inflammation, or pancreatitis, can be triggered by various factors, including gallstones, alcohol abuse, or even certain medications. The pain may worsen after meals, as the pancreas is stimulated to release digestive enzymes, further irritating the inflamed organ. This pain can range from mild discomfort to severe, debilitating agony. The presence of such pain should not be overlooked, and it's essential to seek medical evaluation to determine the cause and receive appropriate treatment. Ignoring this sign can lead to chronic pancreatitis, increasing the risk of long-term complications and severe health impacts. Therefore, if you're experiencing unusual or persistent abdominal pain, consulting a healthcare professional is crucial for early detection and intervention.
Sign: Nausea, Vomiting
Nausea and vomiting are common symptoms associated with various pancreatic disorders. These symptoms often stem from the disruption of the digestive process due to pancreatic inflammation. When the pancreas is inflamed, the production and release of digestive enzymes can be affected, leading to improper food breakdown. This can, in turn, cause irritation in the digestive system, resulting in feelings of nausea and the physical act of vomiting. These symptoms may occur frequently or intermittently, depending on the severity of the pancreatic condition. In some cases, the vomiting may be severe and persistent, leading to dehydration and electrolyte imbalances. If nausea and vomiting are accompanied by abdominal pain, fever, or other concerning symptoms, medical attention should be sought promptly. These additional symptoms may indicate a more serious underlying problem that requires immediate diagnosis and treatment to prevent complications. Addressing these symptoms early is critical for managing discomfort and preventing long-term damage.
Sign: Jaundice
Jaundice, characterized by a yellowish discoloration of the skin and eyes, can be a warning sign of pancreatic problems. Jaundice occurs due to the buildup of bilirubin, a waste product produced during the breakdown of red blood cells. Normally, bilirubin is processed by the liver and excreted through bile. However, when the pancreas is diseased, such as in cases of pancreatic cancer or inflammation, it can obstruct the bile ducts. This obstruction prevents bile, including bilirubin, from flowing properly, leading to its accumulation in the bloodstream. Consequently, the excess bilirubin is deposited in tissues, causing the skin and whites of the eyes to turn yellow. Jaundice can also be accompanied by other symptoms, such as dark urine and pale-colored stools. The appearance of jaundice necessitates prompt medical evaluation because it can indicate a severe underlying health condition. The underlying cause needs to be identified to ensure proper treatment and prevent further complications. Any signs of jaundice warrant immediate medical attention.
Sign: Changes Stool
Changes in bowel habits, particularly the consistency, color, and frequency of stools, can indicate pancreatic dysfunction. The pancreas produces digestive enzymes necessary for breaking down food, including fats. When the pancreas is not functioning correctly, it may not produce sufficient amounts of these enzymes. This can result in malabsorption, which is the inability to digest and absorb nutrients from food, particularly fats. This malabsorption can lead to steatorrhea, a condition characterized by stools that are pale, bulky, greasy, and foul-smelling. These stools may also float due to their high-fat content. Additionally, changes in bowel frequency, such as diarrhea or constipation, may occur. The presence of changes in bowel habits combined with abdominal pain or other symptoms warrants a visit to your doctor. Such conditions, if left untreated, can lead to nutrient deficiencies and other health problems. Therefore, recognizing and addressing these signs early is crucial for maintaining good health.
Prevention Tips
Preventing pancreatic damage involves adopting healthy lifestyle habits and taking proactive steps to minimize risk factors. Limiting alcohol consumption is crucial because excessive alcohol use is a significant cause of pancreatitis. Maintaining a balanced diet low in saturated and processed fats can also help. High-fat diets can increase the risk of gallbladder disease, which can subsequently lead to pancreatitis. Regular exercise helps maintain a healthy weight and overall well-being. Keeping a healthy weight reduces the risk of many diseases, including those related to the pancreas. Staying hydrated and drinking plenty of water supports overall health and helps the digestive system function optimally. Recognizing and addressing any warning signs early, like those discussed earlier, is critical. Regular medical check-ups and screenings, especially for those with risk factors or a family history of pancreatic disease, are essential for early detection. Consulting a healthcare professional regarding any concerns and following their advice is vital to preserving pancreatic health.