Early Warning Signs
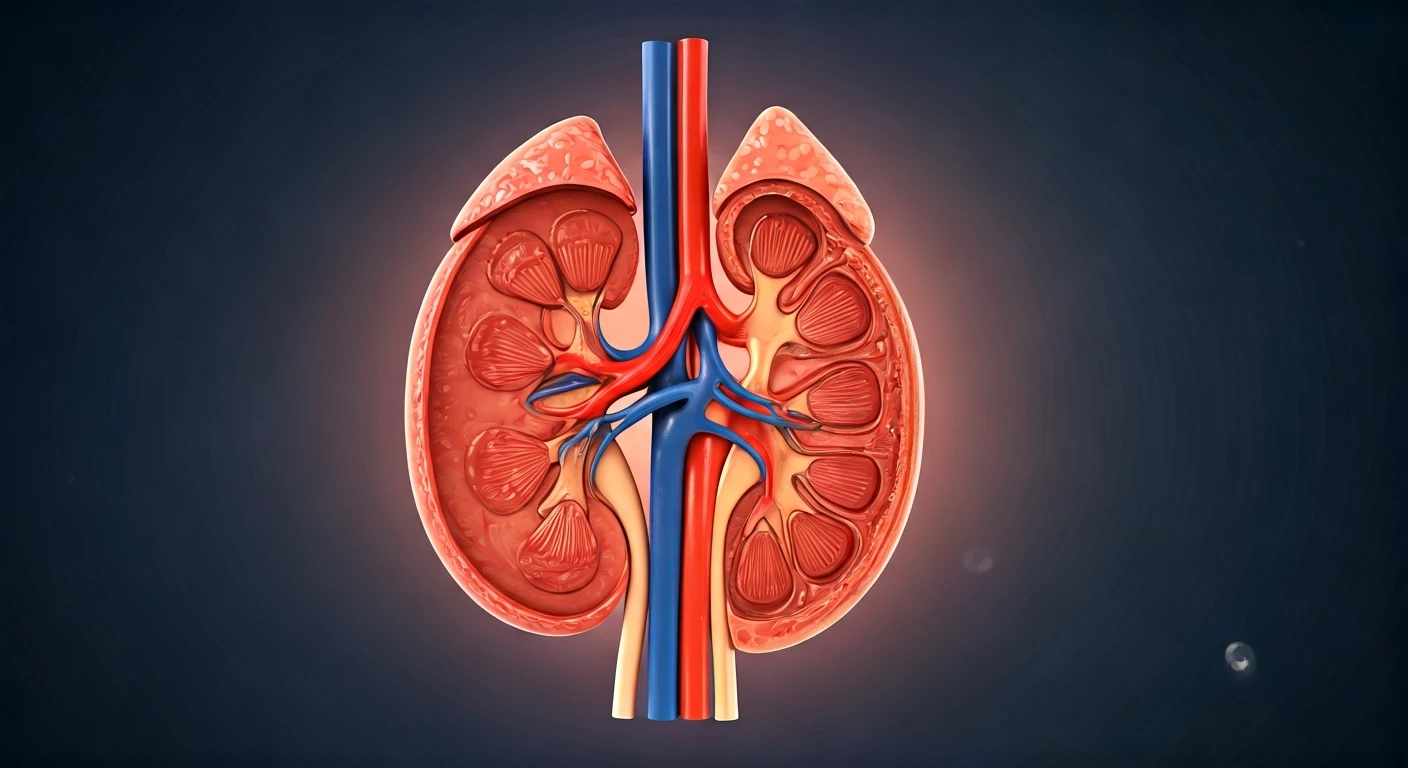
Detecting kidney issues early is crucial for effective treatment. One of the initial signs may be swelling, particularly in the legs, ankles, or feet.
This occurs because the kidneys are unable to effectively remove excess fluid. Another symptom could be changes in urination patterns, like increased frequency, especially at night, or producing less urine than usual. Additionally, you may notice changes in urine appearance, such as it being foamy or discolored. Fatigue, or feeling tired and lacking energy, is also a common indicator. Furthermore, persistent high blood pressure that is difficult to control can be another warning signal. Individuals with diabetes should routinely monitor these symptoms and report them to their healthcare providers for proper evaluation and management. Early intervention can significantly impact the progression of the disease.
Advanced Symptoms Unveiled
As kidney failure progresses, the symptoms often become more pronounced and varied. A significant issue is the accumulation of waste products in the blood, leading to nausea, vomiting, and loss of appetite. Skin changes can manifest, with dryness, itchiness, and altered skin pigmentation, stemming from the body's inability to filter toxins. Breathing difficulties, potentially caused by fluid buildup in the lungs, are also common. Another severe symptom can be the appearance of metallic taste in the mouth. These more advanced signs signify a serious decline in kidney function and necessitate immediate medical care. Furthermore, cognitive changes such as difficulty concentrating and confusion can occur, further indicating the severity of the condition. It’s important to remember that such advanced symptoms often require immediate medical intervention.
Diabetes’ Impact Explained
Diabetes, particularly when poorly managed, significantly damages the kidneys over time. High blood sugar levels injure the tiny blood vessels in the kidneys, which eventually impairs their ability to filter waste. This damage, known as diabetic nephropathy, gradually leads to kidney failure. The longer a person has diabetes and the less controlled their blood sugar is, the greater the risk. Moreover, high blood pressure, often linked to diabetes, further compounds kidney damage. Proper management of diabetes is essential to prevent nephropathy. This includes maintaining healthy blood sugar levels, regular check-ups, and potentially the use of medications to protect the kidneys. A proactive approach is key to preserving kidney health.
Importance of Testing
Regular kidney function tests are vital for diabetics. These tests help detect kidney problems early, allowing for timely intervention. Common tests include urine tests to check for protein, which indicates kidney damage, and blood tests to measure creatinine and estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR). Creatinine levels can measure the waste products in your blood. The eGFR provides an estimate of how well the kidneys are filtering. These tests are usually part of a routine checkup for those with diabetes. More frequent testing may be required if there are indications of kidney trouble or if blood sugar levels aren’t controlled adequately. Proactive testing is an investment in long-term health, as it allows for early identification and control of any potential kidney-related issues.
Preventive Measures Outlined
Several lifestyle changes can help protect kidney health for people with diabetes. Strict blood sugar control is the most important step, which involves diet, exercise, and medication as needed. Maintaining healthy blood pressure is also critical, and often requires dietary modifications (such as reducing sodium intake), regular exercise, and medication if prescribed by a doctor. Regular physical activity supports overall health, and may indirectly improve kidney function, as well. Staying hydrated is also very important, as drinking enough water helps the kidneys filter waste more efficiently. Limiting alcohol consumption, and avoiding smoking, are other steps that can help. Regular check-ups and following the doctor's advice are essential for the ongoing management of kidney health and early intervention when required.