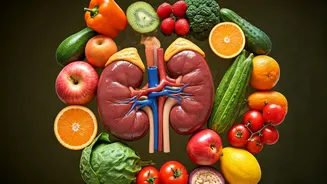
Understanding Kidney Health
Kidneys are vital organs, crucial for filtering waste and toxins from the blood. They maintain fluid balance, regulate blood pressure, and produce hormones.
Proper kidney function is critical for overall health. A nutritionist's insights on dietary choices can significantly impact kidney health. The food we consume directly affects kidney function, so making informed choices is crucial. This helps prevent kidney damage and supports the kidneys' role in maintaining the body's balance.
Avoiding Processed Foods
Processed foods are often high in sodium, phosphorus, and other additives that can strain the kidneys. Sodium leads to increased blood pressure, which can damage the kidneys over time. Excessive phosphorus can disrupt the balance of minerals, potentially harming kidney health. Artificial ingredients and preservatives in processed foods further add to the kidneys' workload. Opting for fresh, whole foods reduces the burden on your kidneys and helps them function more effectively. Minimizing processed food intake is a foundational step in maintaining kidney health.
Limiting High-Sodium Foods
High-sodium foods, like canned soups, processed meats, and salty snacks, contribute to high blood pressure. High blood pressure is a significant risk factor for kidney disease. Consuming excessive sodium forces the kidneys to work harder to maintain fluid balance. This can lead to kidney damage. A nutritionist avoids these foods to manage blood pressure effectively and protect kidney function. Reading food labels carefully and choosing low-sodium options helps reduce sodium intake. This proactive step helps to maintain optimal kidney health.
Reducing Red Meat Intake
High consumption of red meat can strain the kidneys because of its high protein content. When the body metabolizes protein, it produces waste products that the kidneys must filter. Excessive protein intake can overload the kidneys. Furthermore, red meat often contains high levels of saturated fats, which can contribute to other health problems, indirectly affecting kidney health. By limiting red meat intake, the nutritionist helps reduce the burden on their kidneys, promoting long-term health. Choosing lean protein sources can be a better strategy.
Avoiding Sugary Drinks
Sugary drinks such as sodas, sweetened juices, and energy drinks are often high in added sugars, contributing to weight gain and diabetes, which are risk factors for kidney disease. Excess sugar can cause inflammation, placing extra stress on the kidneys. Regular consumption of these beverages increases the likelihood of developing kidney-related issues. The nutritionist avoids these drinks to keep blood sugar levels stable, reducing the risk of kidney problems. Opting for water, unsweetened tea, or other healthier alternatives supports overall kidney and metabolic health.
Limiting Alcohol Consumption
Excessive alcohol consumption can damage the kidneys and impair their ability to filter blood. Alcohol can lead to dehydration and disrupt the normal function of kidney cells. Chronic alcohol use increases the risk of kidney disease and other health issues. Limiting alcohol consumption is crucial for maintaining kidney health. Moderate alcohol intake is often recommended, but abstaining altogether is best for those with existing kidney problems. A nutritionist’s avoidance of excessive alcohol supports overall well-being and kidney function.
Caffeine in Moderation
While not directly harmful in moderation, excessive caffeine intake can affect blood pressure and potentially strain the kidneys. Caffeine is a diuretic and can lead to dehydration if not balanced with sufficient fluid intake. The nutritionist likely monitors caffeine consumption to ensure hydration and kidney function. Consuming caffeine in moderate amounts may not pose a significant risk, but excessive intake could lead to problems. Staying hydrated and being mindful of caffeine's impact on blood pressure is vital for maintaining kidney health.