Dangerous Everyday Habits
A top heart surgeon has identified five everyday habits that are particularly dangerous for heart health. These habits, often ingrained in daily routines,
can quietly damage the cardiovascular system over time. The goal is to raise awareness and help individuals take proactive steps to improve their heart health and overall well-being. This information highlights the significance of making informed lifestyle decisions to minimize heart-related risks. By understanding and addressing these habits, individuals can take crucial measures toward a healthier heart. This involves a commitment to adopting positive changes and seeking professional medical guidance when necessary. The long-term benefits include a reduced risk of heart disease and enhanced quality of life. Awareness of these habits enables individuals to proactively make choices that can extend their lives.
Poor Dietary Choices
One of the most dangerous habits is a diet high in processed foods, saturated fats, and excessive sodium. These dietary choices can contribute to high cholesterol, high blood pressure, and increased inflammation, all major risk factors for heart disease. Processed foods often contain high levels of sodium, which elevates blood pressure. Saturated fats, commonly found in red meat and fried foods, can raise LDL cholesterol levels, increasing the risk of plaque buildup in arteries. Adopting a heart-healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins is crucial. This helps to maintain a healthy weight, control cholesterol levels, and reduce inflammation. Limiting sodium intake by avoiding processed foods and using herbs and spices for flavor is essential. Choosing healthy fats like olive oil and avocados can also contribute to heart health. Making these dietary changes can significantly reduce the risk of heart disease and improve overall cardiovascular health. Consistent adherence to a balanced diet is key for long-term benefits.
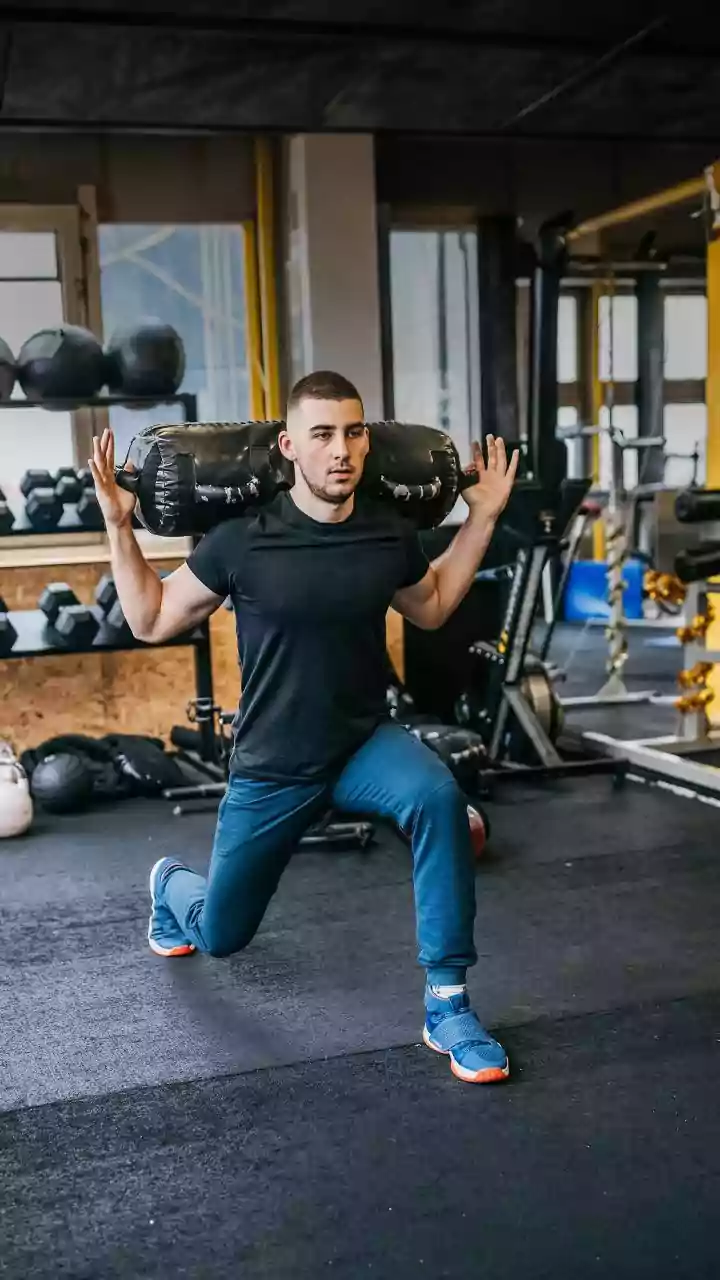
Lack of Exercise
Another significant risk factor is a lack of regular physical activity. Sedentary lifestyles contribute to weight gain, high cholesterol, and poor blood sugar control. All of these increase the likelihood of heart disease. Regular exercise, such as brisk walking, running, swimming, or cycling, strengthens the heart muscle, improves blood circulation, and helps maintain a healthy weight. The American Heart Association recommends at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity exercise per week. Incorporating exercise into your daily routine can be as simple as taking the stairs instead of the elevator, walking during lunch breaks, or joining a fitness class. Starting slowly and gradually increasing the intensity and duration of workouts is advisable. Regular physical activity not only benefits the heart but also improves overall mood and energy levels, contributing to a better quality of life. The cumulative effect of consistent exercise is a significant reduction in the risk of cardiovascular diseases.
Smoking and Tobacco
Smoking and the use of tobacco products are incredibly detrimental to heart health. Smoking damages blood vessels, increases blood pressure, and reduces the amount of oxygen that reaches the heart. This dramatically increases the risk of heart attack, stroke, and other cardiovascular diseases. Tobacco use in any form, including chewing tobacco and vaping, has similar harmful effects. Quitting smoking is one of the most effective steps a person can take to improve their heart health. Resources such as nicotine replacement therapy, counseling, and support groups can aid in the process. The benefits of quitting smoking are almost immediate, with reduced blood pressure and improved circulation. Within a year of quitting, the risk of heart disease decreases significantly. A smoke-free lifestyle protects not only the smoker but also those around them. Avoiding all forms of tobacco is crucial for preserving heart health.
Excessive Alcohol Consumption
While moderate alcohol consumption may have some benefits, excessive alcohol consumption can be extremely harmful to the heart. Heavy drinking can lead to high blood pressure, cardiomyopathy (weakening of the heart muscle), and irregular heartbeats. The recommended limit for moderate alcohol consumption is up to one drink per day for women and up to two drinks per day for men. Regularly exceeding these limits increases the risk of heart-related problems. If you consume alcohol, it's essential to do so in moderation. Monitor your intake and be aware of the potential risks. If you struggle with excessive alcohol consumption, seek help from healthcare professionals or support groups. Reducing or eliminating alcohol consumption can significantly improve heart health and reduce the risk of cardiovascular diseases. Awareness and moderation are key to protecting your heart from the adverse effects of alcohol.
Chronic Stress and Poor Sleep
Chronic stress and poor sleep patterns also significantly impact heart health. Prolonged stress can lead to high blood pressure, inflammation, and unhealthy lifestyle choices, such as overeating and reduced physical activity. Poor sleep disrupts the body's natural rhythms, increasing the risk of cardiovascular problems. Managing stress through techniques like meditation, yoga, or spending time in nature is beneficial. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night to allow the body to recover and function optimally. Creating a relaxing bedtime routine, avoiding caffeine and alcohol before bed, and ensuring a comfortable sleep environment can improve sleep quality. Addressing these issues can reduce the risk of heart disease and improve overall well-being. Consistent attention to stress management and sleep hygiene is a vital part of maintaining a healthy heart.