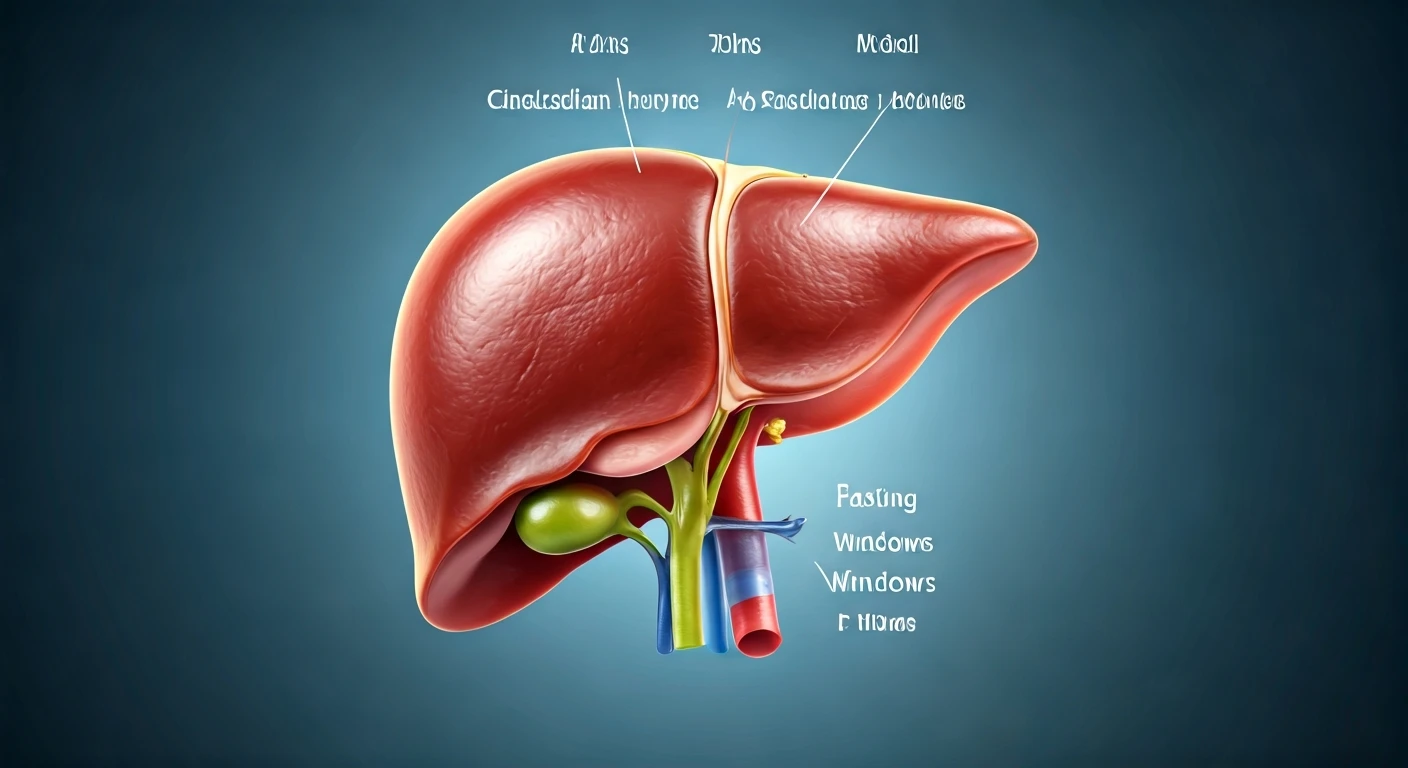
MASLD: An Overview
Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD) is emerging as a significant health challenge in India. This condition is characterized
by an excessive buildup of fat in the liver, often linked to lifestyle factors. MASLD's progression involves stages, starting with simple steatosis (fatty liver) and potentially leading to more severe conditions like steatohepatitis (MASH), fibrosis, cirrhosis, and even liver cancer. Understanding these stages is critical for early detection and intervention. Risk factors for MASLD include obesity, type 2 diabetes, insulin resistance, and metabolic syndrome. A combination of factors, such as unhealthy eating habits, lack of physical activity, and genetic predisposition, can contribute to the development of MASLD. Early diagnosis is key, offering opportunities to reverse or slow disease progression through lifestyle modifications. The prevalence of MASLD is rising in India, underscoring the urgency for awareness, screening, and effective management strategies among the population. Regular check-ups and adopting a healthy lifestyle are essential to mitigate the risk and impact of this condition.
Diagnosis and Screening
Effective screening and diagnosis are crucial in managing MASLD. Initial screening often involves a comprehensive medical history review, physical examination, and blood tests to evaluate liver function. Elevated liver enzymes, such as alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST), can indicate liver damage. Imaging techniques, like ultrasound, are commonly used to detect fatty liver. More advanced methods, such as transient elastography (FibroScan) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), are used to assess liver stiffness and fibrosis, which can help determine the severity of the disease. In some instances, a liver biopsy may be performed to assess the extent of liver damage more accurately. Regular monitoring and follow-up are essential for individuals diagnosed with MASLD. These screenings help track disease progression and assess the effectiveness of interventions. Early diagnosis provides the best opportunity to intervene with lifestyle changes and reduce the risk of advanced liver disease. Recognizing and utilizing these diagnostic tools is essential for maintaining liver health and preventing severe complications associated with MASLD.
Eating Habits Matter
Dietary habits play a vital role in both the development and management of MASLD. A balanced diet, rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins, is crucial. Limiting the intake of processed foods, sugary drinks, and saturated fats is essential to reduce the buildup of fat in the liver. Portion control and mindful eating practices contribute to weight management, which directly impacts liver health. Incorporating dietary changes into daily routines can significantly improve liver function and overall health. Furthermore, increasing the intake of fiber through foods like oats, beans, and vegetables is beneficial for reducing liver fat. Considering the role of carbohydrates, complex carbohydrates are preferable over simple sugars. Prioritizing foods that are high in antioxidants, such as berries and green leafy vegetables, is also helpful. These can combat oxidative stress, which is often associated with MASLD. Implementing these dietary changes, while challenging, is a significant first step towards improving liver health and reducing MASLD risk.
Sleep and Liver Health
Sleep patterns have a significant impact on liver health, making it an essential consideration in the management of MASLD. Adequate, quality sleep supports metabolic processes, and disruptions in sleep can negatively impact liver function. Sleep deprivation and irregular sleep schedules can lead to insulin resistance, increased inflammation, and weight gain, all of which contribute to MASLD. It is crucial to establish a consistent sleep schedule and ensure enough hours of sleep nightly. Aiming for 7-9 hours of sleep per night can help regulate metabolic functions and support liver health. Addressing sleep disorders, such as sleep apnea, is vital, as this can affect liver function. Improving sleep hygiene can involve creating a relaxing bedtime routine, avoiding caffeine and alcohol before bed, and making the sleeping environment conducive to rest. Prioritizing sleep is not only beneficial for liver health but also enhances overall well-being. By integrating healthy sleep habits, individuals can support their liver function and enhance their overall health outcomes, which is particularly beneficial when managing MASLD.
Fasting and MASLD
Intermittent fasting (IF) is another lifestyle factor that can significantly affect MASLD. IF involves cycling between periods of eating and voluntary fasting on a regular schedule. Various IF methods, such as time-restricted eating (TRE) and alternate-day fasting (ADF), have shown promise in improving liver health. IF can lead to weight loss, reduce insulin resistance, and decrease liver fat. It improves metabolic parameters, which are often compromised in MASLD patients. When considering IF, it is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional to ensure it is appropriate and safe. They can determine if fasting is suitable based on individual health conditions and needs. Implementing IF should be a gradual process, starting with shorter fasting periods and gradually increasing the duration as tolerated. It’s also crucial to focus on nutrient-dense foods during the eating windows to ensure overall health and adequate nutrition. Combining intermittent fasting with other lifestyle modifications, such as regular exercise and a healthy diet, can boost its effectiveness in managing MASLD and supporting liver health.
Activity for the Liver
Regular physical activity plays a crucial role in managing MASLD. Exercise helps in weight management, which is critical for reducing liver fat accumulation. Physical activity improves insulin sensitivity, reducing the risk of further liver damage. Both aerobic exercise, such as brisk walking and jogging, and strength training can benefit liver health. Aiming for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity activity per week is recommended. Strength training exercises, performed at least twice a week, can increase muscle mass and improve metabolic function. Integrating physical activity into daily routines can be as simple as taking the stairs, walking during breaks, or joining a fitness class. The combination of regular exercise with healthy eating habits can amplify the benefits for liver health. Maintaining a consistent exercise routine is crucial for sustaining the positive effects on liver function. Consulting with a healthcare provider can help in creating a personalized exercise plan that aligns with individual health needs and limitations.
Treatment and Management
Managing MASLD often involves a multi-faceted approach. Lifestyle modifications, including dietary changes, regular exercise, and maintaining healthy sleep patterns, form the foundation of treatment. Weight management is crucial as it reduces liver fat and improves liver function. In some cases, medication may be prescribed to address specific issues such as insulin resistance or elevated liver enzymes. Regular monitoring is essential to track disease progression and response to treatment. Periodic check-ups, including liver function tests and imaging, are crucial. Seeking advice from healthcare professionals, including hepatologists, can guide treatment plans. They can provide comprehensive care and support tailored to individual needs. Following medical advice and maintaining a healthy lifestyle are essential to improving liver health and preventing the progression of MASLD. It's crucial to adopt a holistic approach, incorporating both medical interventions and lifestyle adjustments, for optimal results.
Taking Action Now
Taking proactive steps is vital for managing MASLD and improving overall health. The first step involves assessing current health habits, including diet, physical activity levels, and sleep patterns. Identifying areas for improvement is crucial. Setting realistic goals, such as increasing physical activity or adopting a healthier diet, is essential. Making gradual changes over time is a sustainable approach. Consider consulting with healthcare professionals, including doctors and dietitians, for personalized advice and support. Educating oneself about MASLD and its risk factors is vital. Staying informed about the latest research and treatment options empowers individuals to make informed decisions. Creating a support system, which can include friends, family, or support groups, can help with staying motivated and adherent to health goals. By taking these actions, individuals can effectively manage MASLD and improve their liver health. Making health a priority will ensure a proactive approach towards well-being.