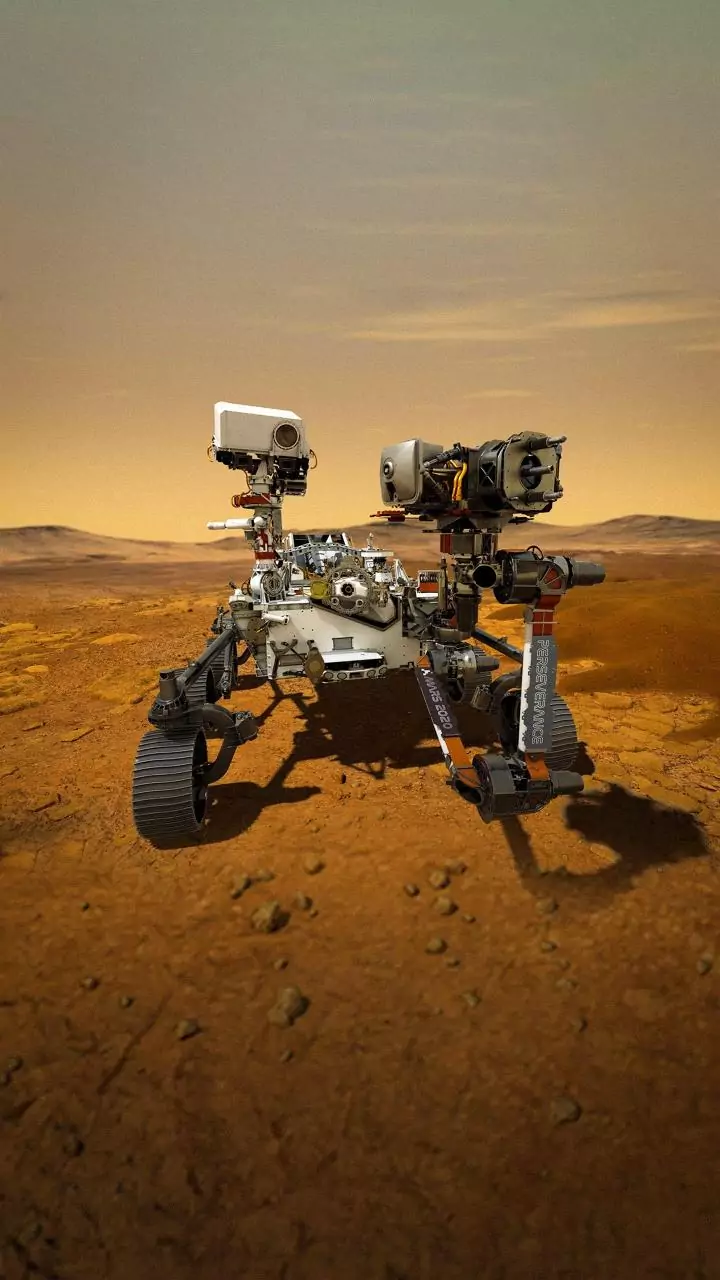
Mars Sample Return
The Mars Sample Return project is under significant scrutiny, with experts advocating for its prioritization. This mission is envisioned as a multi-stage
effort, aimed at collecting and returning samples from Mars to Earth. The project's main goal is to bring Martian materials back for comprehensive analysis. This approach allows scientists to use advanced laboratory techniques to study the samples, potentially uncovering clues about the planet's past, present, and the possibility of life. The focus is on the crucial importance of Mars Sample Return, which is considered a top priority.
Why the Urgency?
The urgency surrounding the Mars Sample Return mission is fueled by the desire to stay ahead in space exploration. Experts emphasize that bringing Martian samples back before other nations do, especially China, is a key strategic goal for the United States. This priority reflects the increasing global competition in space exploration. A successful Mars Sample Return mission could boost the United States' standing in the field, helping to secure its leadership. The initiative is not merely a scientific project, but a matter of national and global scientific prominence, driving the need for swift action.
Potential Scientific Gains
The potential scientific gains from analyzing Martian samples are enormous. Earth-based laboratories provide unparalleled capabilities for examining these materials in detail. Advanced analytical tools can be employed, offering insights into Mars' geological history, climate evolution, and the possible existence of past or present life. The samples could reveal crucial information about the planet's composition, the presence of water, and organic compounds. Studying these elements may provide answers about whether life ever existed on Mars. Discoveries made through studying returned samples can reshape scientific understanding of the Red Planet.
Challenges and Considerations
The Mars Sample Return mission faces numerous challenges. These include the technological complexity of collecting, securing, and transporting samples across interplanetary distances. There are also potential risks related to the contamination of Earth by any Martian microbes. Careful sterilization and containment measures are essential to prevent cross-contamination. Moreover, the project is expensive and requires significant funding, making it subject to debate and changing budgetary priorities. Despite these challenges, experts argue that the scientific benefits justify the investment, considering the unparalleled research opportunities the mission offers.