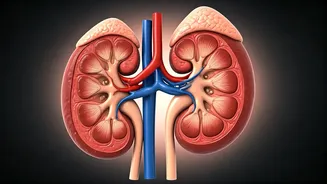
Avoiding Processed Foods
Processed foods, known for their convenience, can be silent saboteurs of kidney health. These items often harbor high levels of sodium, phosphorus, and
unhealthy fats, all of which can strain the kidneys. Sodium, for instance, leads to elevated blood pressure, a primary cause of kidney damage. Excessive phosphorus intake, particularly from additives, can disrupt the delicate balance within the body and contribute to kidney issues. Moreover, the added sugars and unhealthy fats in processed foods can contribute to obesity and diabetes, two significant risk factors for kidney disease. Therefore, minimizing the consumption of processed foods is a key dietary strategy for kidney protection. This includes a careful review of food labels and a preference for fresh, whole foods whenever possible.
Limiting High-Sodium Items
Sodium is another key area of focus for kidney health. The nutritionist emphasizes the necessity of curtailing the intake of high-sodium foods, as they directly impact blood pressure. High blood pressure, if left unchecked, can gradually damage the kidneys, diminishing their efficiency in filtering waste. This makes avoiding excessive sodium from dietary sources crucial. Common culprits include processed meats, canned soups, and salty snacks. The recommendation extends to the judicious use of table salt, suggesting the option of flavoring meals with herbs and spices instead. Being mindful of sodium content extends to restaurant meals and pre-packaged foods where sodium levels are often surprisingly high. By making conscious choices, individuals can substantially diminish the risk of kidney damage and uphold overall health.
Restricting Sugary Drinks
Sugary beverages are also a cause for concern when considering kidney health. Drinks loaded with sugar, like sodas, sweetened teas, and fruit juices with added sugar, can significantly raise blood sugar levels, increasing the chances of developing diabetes. Diabetes is a common factor in kidney disease. Regularly consuming these drinks is linked with weight gain and potential insulin resistance, intensifying the risk of kidney damage. The nutritionist's advice underlines the importance of switching to healthier choices such as water, unsweetened tea, or sparkling water, and these options assist in keeping the body hydrated and steer clear of unnecessary sugar intake. This change could also help limit the risk of kidney disease and maintain a healthier lifestyle.
Avoiding Excessive Alcohol
Alcohol is another factor that can impact kidney health. Overconsumption of alcohol can lead to dehydration, elevated blood pressure, and potential liver damage, all of which can indirectly affect kidney function. The kidneys work in tandem with the liver in the detoxification process, and overloading either organ with alcohol puts a strain on the entire system. While occasional, moderate alcohol consumption might not pose a serious threat for healthy individuals, regular and heavy drinking can escalate the risk of kidney disease. The recommendation usually involves adhering to recommended daily limits or completely abstaining, depending on individual health status. Being mindful of alcohol intake and its cumulative impact on overall health is critical for preventing kidney problems and maintaining overall well-being.
Reducing Red Meat Intake
Red meat consumption is also brought up for consideration. High protein diets, especially those heavily relying on red meat, can increase the workload on the kidneys. As the body metabolizes protein, it generates waste products that the kidneys have to filter out. Excessive intake might potentially overwork the kidneys, particularly in those with pre-existing kidney issues. Therefore, the nutritionist suggests moderation in red meat consumption and considering other protein sources, such as poultry, fish, beans, and lentils. This method not only eases the burden on the kidneys but also varies the diet, providing a wider spectrum of nutrients. These adjustments in dietary choices are vital for the health of the kidneys and promote overall wellness.
Limiting Caffeine Consumption
Lastly, the nutritionist offers insights into caffeine consumption. Excess caffeine, present in coffee, tea, and energy drinks, can increase blood pressure and, in some cases, can cause dehydration. While moderate caffeine intake is generally considered safe, excessive amounts can put additional stress on the kidneys. Caffeine can also interfere with certain medications and might affect sleep patterns, indirectly impacting health. The advice is to moderate the consumption of caffeinated beverages and keep a track of the body's reaction to caffeine. The alternative involves switching to decaffeinated versions or other hydrating options. Such approaches can help maintain optimal hydration and reduce any potential strain on the kidneys, contributing to better kidney health and overall wellness.