Diabetes Diet Basics
A diabetes diet, at its essence, is a carefully planned approach to eating that assists in controlling blood sugar levels. It focuses on nutrient-rich
foods while minimizing those that can cause spikes in glucose. This dietary strategy emphasizes a balanced intake of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats, with a strong preference for whole, unprocessed foods. Portion control is a key element, ensuring that meals provide the necessary nutrition without overconsumption, thereby helping to maintain a healthy weight. The core concept revolves around making informed food choices to regulate blood sugar, contributing to overall health. It is about understanding how different foods affect the body and adopting dietary habits that support optimal health, preventing complications, and improving quality of life for individuals with diabetes.
Meal Planning Strategies
Effective meal planning is a cornerstone of diabetes management. It involves organizing meals and snacks ahead of time to ensure healthy food choices are readily available. Begin by consulting a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian to establish personalized dietary guidelines. Consider carb counting to monitor carbohydrate intake, as carbs have the most significant impact on blood sugar. Meal planning should also take into account the timing of meals and how they align with medication or insulin schedules. Preparing meals at home provides better control over ingredients and portion sizes. Maintaining a food journal to track food intake and blood sugar levels can help in understanding how different foods affect the body. Planning extends to grocery shopping, where choosing nutritious options is essential for staying on track with health goals, supporting stable blood sugar, and overall well-being.
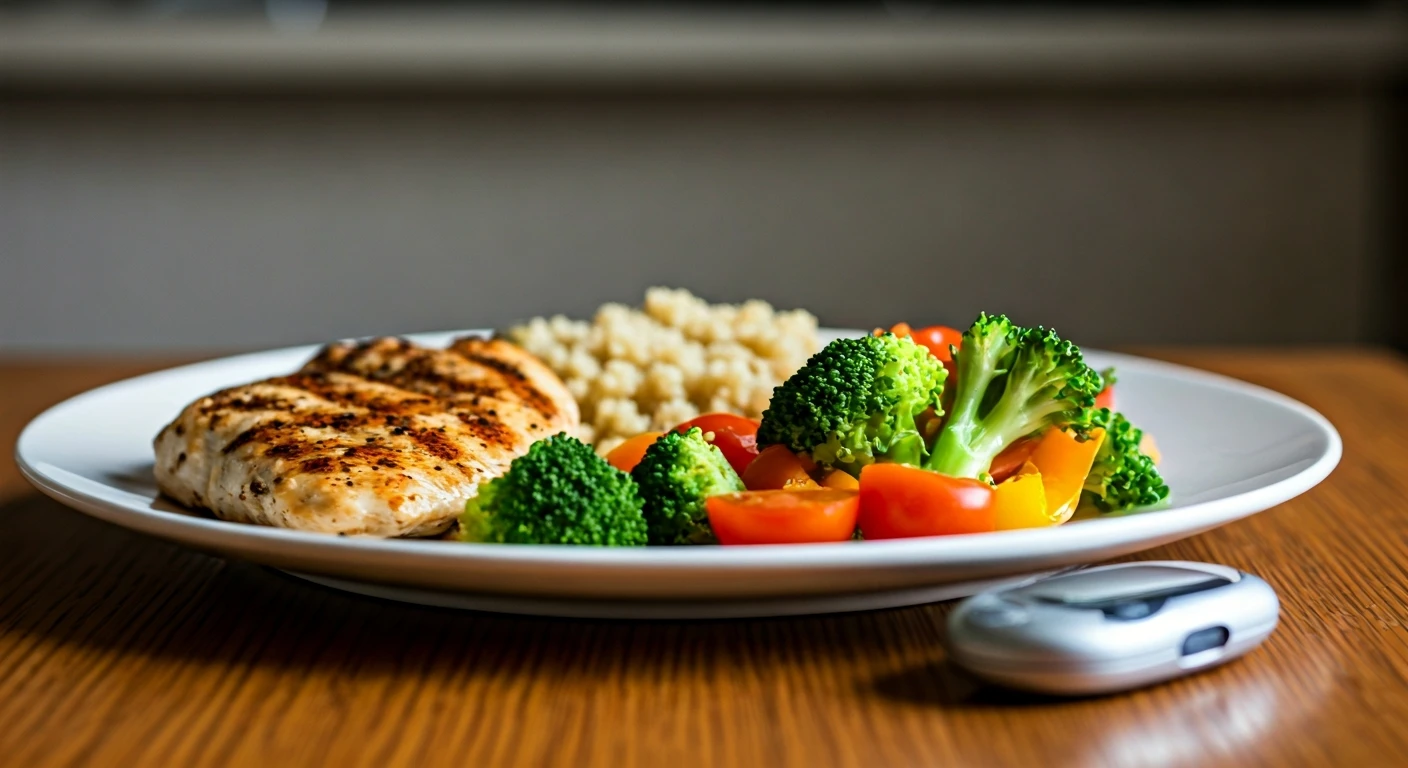
Food Choices and Guidelines
In managing diabetes, making the right food choices is fundamental. Focus on consuming nutrient-dense foods, including plenty of non-starchy vegetables such as leafy greens, broccoli, and peppers. Incorporate whole grains like brown rice and quinoa in moderation, paying attention to portion sizes. Opt for lean protein sources, such as fish, poultry, beans, and tofu. Healthy fats, including those found in avocados, nuts, and olive oil, are also essential. Limit processed foods, sugary drinks, and foods high in saturated and trans fats. Prioritize fiber-rich foods, which can help regulate blood sugar levels. When choosing fruits, it's essential to consider portion sizes and select those with a lower glycemic index. Regularly monitoring carbohydrate intake, choosing complex carbs over simple ones, and being mindful of fat intake are all critical to maintaining optimal blood sugar control and ensuring long-term health.
The Importance of Exercise
Regular physical activity plays a critical role in diabetes management. Exercise helps improve insulin sensitivity, enabling the body to use insulin more effectively, leading to better blood sugar control. Engaging in activities like brisk walking, cycling, or swimming can significantly benefit people with diabetes. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week, and spread it throughout the week. Incorporate both aerobic and strength-training exercises for comprehensive health benefits. Before starting any exercise program, consulting with a healthcare provider is essential, especially if you have pre-existing health conditions. Monitor your blood sugar levels before, during, and after exercise to understand how your body responds and make adjustments as needed. Consistency and adapting the exercise to your abilities and health status are keys to reaping the rewards, reducing the risk of complications, and improving overall health for individuals with diabetes.
Monitoring Blood Glucose
Regular monitoring of blood glucose levels is a crucial component of diabetes care. It gives individuals a clear understanding of how their bodies respond to food, exercise, and medication. Using a blood glucose meter or a continuous glucose monitor (CGM) helps in tracking these levels. The frequency of testing depends on the type of diabetes, treatment plan, and individual needs; consult with your doctor for specific recommendations. Record blood glucose readings, noting the time and any relevant factors, such as meals or exercise. This information allows healthcare providers to assess how well the treatment plan is working and make necessary adjustments. Learning to interpret the readings and understand trends allows for proactive management and helps in preventing or managing potential complications. It is a proactive step, enabling individuals to take control of their health, providing insights that support informed decision-making and promote overall well-being and a better quality of life.
Lifestyle Adjustments
Integrating lifestyle adjustments is vital for effectively managing diabetes. Besides diet and exercise, stress management is significant. Stress can elevate blood sugar levels; techniques such as meditation, deep breathing, or yoga can help alleviate this. Adequate sleep is another key factor. Aim for 7-8 hours of quality sleep each night, as sleep deprivation can affect blood sugar control. Staying hydrated is also essential; drinking enough water supports various bodily functions, including glucose metabolism. Avoid smoking and limit alcohol consumption, as both can negatively impact blood sugar levels and overall health. Regularly consult healthcare professionals, including your doctor and a registered dietitian, for guidance and support. Staying informed, adhering to medical advice, and making consistent lifestyle adjustments contribute to achieving better blood sugar control, improving quality of life, and reducing the likelihood of complications.