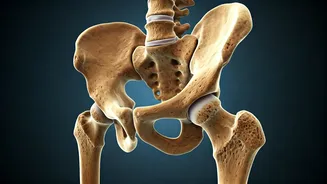
Bone Density Problems
A primary signal of calcium deficiency is bone health deterioration. Calcium is the building block of bones, so inadequate levels directly impact bone density.
Women might notice increased fracture risk, especially in wrists, hips, and spine. Over time, this can lead to osteoporosis, making bones brittle and susceptible to breaks from minor incidents. Regular bone density tests, in conjunction with calcium-rich diet and exercise, are crucial to mitigate this risk and maintain robust skeletal health.
Muscle Cramps & Spasms
Calcium plays a pivotal role in muscle contraction and relaxation. Insufficient calcium can lead to frequent muscle cramps, particularly in the legs and feet. These cramps often occur at night or during physical activity. Additionally, muscle spasms and twitching may become more noticeable. Ensuring adequate calcium intake, alongside magnesium and potassium, can help regulate muscle function and alleviate these uncomfortable symptoms. If cramps persist, consulting a healthcare professional is advisable.
Dental Health Issues
The health of your teeth mirrors your calcium levels. Calcium is essential for strong teeth and enamel. A lack of calcium can lead to increased tooth decay, gum disease, and weakened tooth structure. Women with calcium deficiency may experience more cavities and a higher susceptibility to dental problems. Regular dental check-ups and a calcium-rich diet, as well as proper oral hygiene practices, are essential to maintain healthy teeth and prevent dental complications associated with calcium insufficiency.
Nail Fragility & Weakness
Brittle and easily breakable nails can also indicate calcium deficiency. Calcium contributes to nail strength and structure. When calcium levels are low, nails may become thin, weak, and prone to splitting or peeling. Women may also experience slower nail growth. Enhancing calcium intake through dietary sources or supplements, while simultaneously maintaining adequate hydration and avoiding harsh chemicals, can contribute to healthier and more resilient nails.
Skin Problems & Dryness
Calcium plays a role in skin health and the regulation of cell turnover. Calcium deficiency can manifest as dry, itchy skin and even conditions like eczema or psoriasis. The skin may also be more prone to inflammation and sensitivity. Maintaining adequate calcium levels, in conjunction with proper hydration, moisturizing routines, and sun protection, can help support healthy skin. If skin issues persist, consulting a dermatologist can help identify any underlying conditions.
Fatigue & Exhaustion
Calcium impacts energy levels and overall well-being. Insufficient calcium may contribute to feelings of fatigue, exhaustion, and generalized weakness. Women may feel consistently tired, even after adequate rest. Calcium aids in energy production within cells. Incorporating calcium-rich foods, ensuring a balanced diet, and addressing other possible underlying causes of fatigue, such as iron deficiency or sleep disorders, are all steps to improve overall energy levels.
Emotional Changes & Mood
Calcium plays a role in nerve function and may affect mood regulation. Low calcium levels can be linked to irritability, anxiety, and even depression. Women may experience mood swings and difficulty managing stress. Adequate calcium intake supports the proper function of the nervous system. Moreover, consider additional lifestyle adjustments, such as regular exercise and stress-reduction techniques, to support emotional well-being.
Insomnia & Sleep Issues
Calcium plays a role in sleep regulation, as it helps the brain use tryptophan to make melatonin. Melatonin regulates sleep cycles. Calcium deficiency may contribute to insomnia or difficulty sleeping. Women might experience restless nights or struggle to fall asleep. Ensuring sufficient calcium intake can improve sleep quality. Consider establishing a relaxing bedtime routine and limiting screen time before bed to support healthy sleep patterns.
Menstrual Cycle Irregularities
Calcium contributes to hormonal balance, impacting the menstrual cycle. Low calcium levels can potentially lead to irregular periods, heavier bleeding, or increased premenstrual symptoms. Women may experience more intense cramps or bloating. Adequate calcium intake, along with maintaining a healthy diet and regular exercise, can assist in regulating the menstrual cycle. If cycle irregularities persist, it is crucial to consult a healthcare professional.
Slow Wound Healing
Calcium is involved in blood clotting and the healing process. Insufficient calcium may impede the body's ability to heal wounds effectively. Women might notice that cuts and bruises take longer to heal. Ensuring adequate calcium intake supports overall wound healing. Maintaining good nutrition and addressing any underlying health conditions are also vital for promoting efficient healing. If slow wound healing persists, seeking medical advice is recommended.