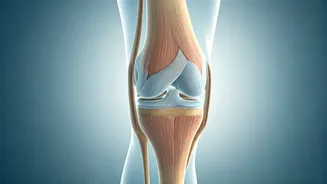
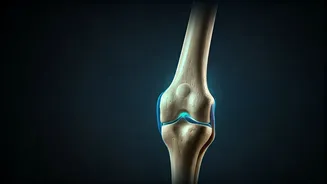
Understanding Knee Health
Knee health is vital for maintaining an active lifestyle and overall well-being. The knee joint, a complex structure, is susceptible to wear and tear due
to age, activity level, and underlying health conditions. Understanding the mechanics of the knee, including the role of cartilage, ligaments, and muscles, is the first step toward proactive care. Recognizing early warning signs such as pain, swelling, or stiffness can lead to timely intervention and prevent further deterioration. Moreover, understanding risk factors like obesity, previous injuries, and genetics helps individuals make informed decisions about lifestyle and preventative measures to protect their knees.
Exercise and Strengthening
Regular exercise and strengthening exercises are cornerstones of knee care. Focused exercises help to fortify the muscles that support the knee, reducing stress on the joint itself. Exercises such as quadriceps strengthening (leg extensions), hamstring curls, and calf raises can be beneficial. Low-impact activities like swimming, cycling, and walking are also excellent choices, promoting cardiovascular health without placing excessive strain on the knees. Consistency is crucial; aim for regular exercise sessions, gradually increasing the intensity and duration. Remember to listen to your body and modify exercises as needed to avoid pain or discomfort, consulting with a physical therapist or healthcare provider to develop a tailored exercise plan suited to your individual needs and capabilities.
Dietary Considerations
Dietary choices play a significant role in both joint health and overall well-being. Consuming a balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods can help reduce pain and swelling in the knees. Include foods abundant in omega-3 fatty acids (found in fish like salmon and flaxseeds), antioxidants (found in colorful fruits and vegetables), and vitamin D. Conversely, it is wise to limit processed foods, sugary drinks, and excessive saturated fats, as they can contribute to inflammation. Maintaining a healthy weight is also vital, as excess weight places additional stress on the knees. Consider consulting a nutritionist or registered dietician for personalized dietary advice tailored to your specific needs and health conditions to maximize the positive impact of your diet on your knee health.
Pain Management Strategies
Managing knee pain is crucial for improving quality of life and facilitating continued activity. Over-the-counter pain relievers such as ibuprofen or naproxen can provide temporary relief. However, always follow dosage instructions and consult with a doctor if you experience persistent pain. Heat and cold therapy can also alleviate pain and swelling; applying ice packs during acute flare-ups and using heat to relax muscles. Physical therapy, involving specialized exercises and manual techniques, can strengthen muscles, improve range of motion, and reduce pain. For some, injections such as corticosteroids or hyaluronic acid may be considered under medical supervision. It is important to address pain promptly to prevent it from becoming chronic.
Lifestyle Modifications
Making lifestyle changes can significantly impact knee health and reduce the risk of joint replacement. Choose low-impact activities like swimming or cycling over high-impact exercises. Modify activities to minimize stress on your knees; for example, proper form during exercise, using assistive devices such as walking sticks, and avoiding prolonged periods of standing or kneeling. Wearing supportive footwear and using shoe inserts can provide additional stability and shock absorption. Maintaining good posture and practicing proper body mechanics during daily activities can also help reduce strain on your knees. Small changes in your routine, such as taking breaks to stretch or altering your work setup, can make a difference.
When to Seek Help
Recognizing when to seek medical attention is vital for the effective management of knee problems. Consult a doctor if you experience persistent pain, swelling, stiffness, or instability in your knee. If pain worsens despite conservative treatments, consult a doctor. Other warning signs include difficulty bearing weight, a limited range of motion, or a popping or locking sensation. Prompt diagnosis can help guide proper treatment and can help prevent further damage. Early intervention can preserve joint health, and a doctor can provide a comprehensive evaluation, including imaging tests like X-rays or MRIs, to determine the underlying cause of your knee problems. Following the doctor's advice and staying proactive can enhance your long-term knee health.