Dietary Adjustments Matter
A heart-healthy diet forms the cornerstone of cardiovascular wellness. Prioritize foods rich in essential nutrients while limiting those detrimental to heart health.
Embrace a diet abundant in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, as these provide crucial vitamins, minerals, and fiber. Integrate lean proteins, such as fish, poultry without skin, and beans, into your meals. These are less saturated fat-laden options than red meat. Control your intake of saturated and trans fats, frequently present in processed foods, fried items, and certain animal products. It is recommended to avoid excessive consumption of sodium, often hidden in processed foods and restaurant meals, as high sodium levels contribute to elevated blood pressure, a significant risk factor for heart disease. Instead, season your meals with herbs and spices to enhance flavor without adding salt. Incorporate foods containing omega-3 fatty acids, like fatty fish (salmon, mackerel), flaxseeds, and walnuts, which can help lower triglycerides and reduce inflammation. Be mindful of portion sizes to manage calorie intake and maintain a healthy weight, as excess weight strains the heart. Drink plenty of water to stay hydrated and support overall health.
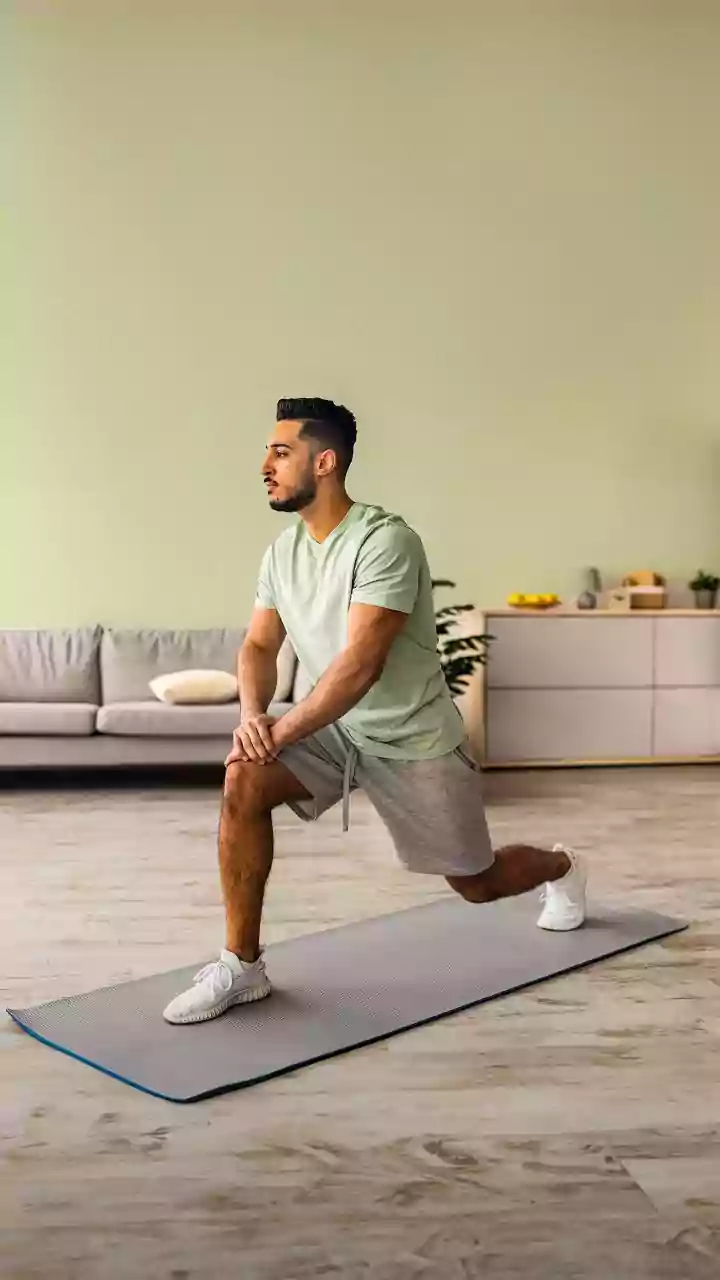
Embrace Regular Exercise
Regular physical activity significantly boosts heart health, offering multiple benefits that contribute to overall well-being. Engage in at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity exercise per week. Activities like brisk walking, jogging, swimming, or cycling effectively improve cardiovascular function. Exercise improves blood flow and reduces the risk of high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and type 2 diabetes, all of which are major risk factors for heart disease. Incorporate strength training exercises at least twice a week to build muscle and improve metabolism, which can further enhance cardiovascular health. Even small increases in daily activity can make a difference. Use stairs instead of elevators, walk during your lunch break, and park farther away from your destination to add extra steps to your day. Find activities that you enjoy to make exercise a sustainable part of your routine. Exercise is also an excellent stress reliever. Combine cardio with activities you enjoy such as dancing or team sports, and make it a social activity by exercising with friends or family. Ensure you warm up before each workout and cool down afterward to prevent injury and enhance performance.
Manage Stress Effectively
Stress significantly impacts heart health, making effective stress management essential for overall well-being. Prolonged stress can lead to increased blood pressure, inflammation, and other physiological changes that elevate the risk of heart disease. Integrate stress-reducing techniques into your daily routine. Practices like meditation, deep breathing exercises, and yoga can help calm the mind and body, reducing stress levels. Regular physical activity acts as a natural stress reliever, releasing endorphins that boost mood and reduce tension. Maintain a healthy work-life balance, avoiding overcommitment and burnout. Make time for hobbies and activities you enjoy to promote relaxation and mental well-being. Build a strong social support network. Connect with friends, family, and loved ones for emotional support, as social interaction helps buffer the effects of stress. If stress becomes overwhelming, seek professional help. Therapists and counselors can provide tools and strategies for managing stress effectively. Ensure you get enough sleep, as sleep deprivation can worsen stress levels. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night to support both physical and mental health. Practice mindfulness, focusing on the present moment, and letting go of worries about the past or future.
Monitor Your Health
Regular health check-ups and monitoring are critical for maintaining and improving heart health, enabling early detection and management of potential issues. Schedule regular visits with your healthcare provider, including check-ups and screenings. During these visits, your doctor will assess your blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and other key indicators of heart health. Be proactive and understand your family’s medical history, as a family history of heart disease can increase your risk. Provide your healthcare provider with detailed information to help them assess your individual risk factors. Understand your numbers, including your blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and blood sugar levels. Keep a record of these numbers and discuss any concerns with your doctor. Follow your healthcare provider’s recommendations for medication and lifestyle changes. Adhere to prescribed treatments and follow advice on diet, exercise, and stress management. Know the warning signs of a heart attack, such as chest pain, shortness of breath, and pain in the arm, jaw, or back. Seek immediate medical attention if you experience any of these symptoms. Use technology and apps to monitor your health, such as fitness trackers that monitor your activity levels and heart rate. Make lifestyle changes, such as quitting smoking, reducing alcohol consumption, and managing your weight. Keep an open line of communication with your healthcare provider to address concerns and ensure proactive care for your heart health.