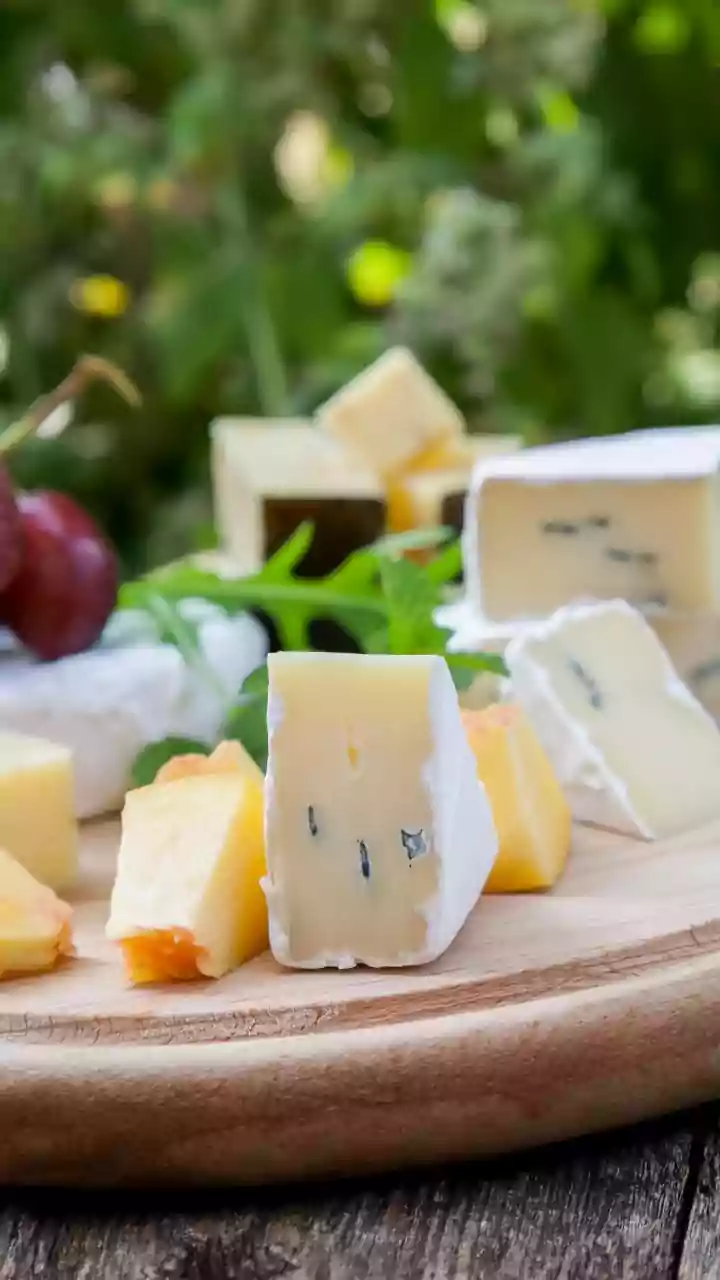
The Nutrient Powerhouse
Full-fat dairy products are packed with vital nutrients not found in the same abundance in lower-fat alternatives. They’re excellent sources of fat-soluble
vitamins, including A, D, E, and K, which are absorbed more efficiently when consumed with fat. Calcium, critical for bone strength, and phosphorus, which is involved in various bodily functions, are also abundant. Moreover, whole-fat dairy offers a good source of protein, crucial for building and maintaining tissues and muscles. They also provide conjugated linoleic acid (CLA), a fatty acid associated with several health benefits. These products often have undergone less processing than their lower-fat counterparts, which can sometimes lead to the loss of beneficial elements.
The Matrix Effect
The 'food matrix effect' refers to how nutrients in food work together to provide benefits to your health. These interactions boost absorption and utilization. For example, fat supports the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins. The combined effect is more beneficial. Fats in dairy also contribute to feeling full, which may help manage weight, as they take longer to digest. Embracing the whole food matrix means opting for the complete nutritional profile. This allows the body to benefit from the natural design of food.
Whole Diet Matters
A balanced diet involves consuming a variety of foods in appropriate proportions, ensuring you receive a wide range of nutrients. Dairy, including whole-fat varieties, can fit well into such a diet, contributing to protein, calcium, and vitamin intake. However, a balanced diet includes other elements like fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains. Understanding the role of each food group is essential for creating a personalized eating plan. A registered dietitian or nutritionist can provide tailored advice for a healthy and balanced diet.
Moderation is Key
The key to enjoying the advantages of whole-fat dairy is moderation. While certain foods, like whole-fat dairy, can be helpful, excessive consumption can diminish the benefits. It is important to be mindful of portion sizes and to include these foods as part of a varied, balanced diet. It’s also crucial to listen to your body. Consider how different foods affect you, noting any digestive or energy level changes. Consider your lifestyle and activity levels. A mindful approach allows you to savor the taste and gain the nutritional benefits while minimizing any potential downsides.
The Study's Findings
Scientific research shows that whole-fat dairy consumption is not always linked to negative health outcomes and can, in certain cases, offer benefits. The focus of research has evolved from viewing fats as harmful to understanding the role of different fats in the body. Some studies indicate that the saturated fats in dairy might not negatively impact cardiovascular health as much as previously thought. There’s also evidence that unique fatty acids in dairy, such as CLA, may offer anti-inflammatory properties. However, it's important to stay informed about the latest research findings. Staying informed helps to make educated decisions for health and well-being.