The Omega-3 Deficiency
The significant lack of Omega-3 fatty acids in many people's diets is a concerning issue. Research indicates that a staggering 3 out of 4 individuals do
not receive an adequate amount of these vital nutrients. This deficiency underscores a widespread problem linked to dietary habits and food choices. Omega-3s are essential fats, meaning the body cannot produce them and requires them from the diet. The deficiency is linked to various health challenges, highlighting the importance of understanding the sources and functions of Omega-3 fatty acids. By identifying this gap, people can take proactive measures to improve their diet and address potential health risks. Focusing on Omega-3 intake can significantly contribute to better health, enabling you to reduce the likelihood of chronic disease and improve overall well-being. This prompts reflection on current food consumption patterns and the need for possible adjustments to meet the body’s needs.
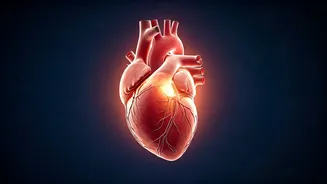
Omega-3s and Heart Health
One of the most significant impacts of Omega-3 deficiency is on heart health. These fatty acids play a crucial role in maintaining a healthy cardiovascular system. Insufficient intake has been linked to an increased risk of heart disease, including elevated blood pressure, unhealthy cholesterol levels, and the formation of plaques in arteries. When people don’t get enough Omega-3s, their bodies may struggle to keep the heart functioning at its best. Omega-3s help regulate heart rhythm, reduce inflammation, and improve blood vessel function. By incorporating Omega-3-rich foods or supplements into the diet, people can reduce the chances of cardiovascular complications and foster a stronger, more resilient heart. This focuses on the direct and positive effects of Omega-3s on cardiovascular health, thus promoting healthy lifestyles.
Managing Diabetes with Omega-3s
Omega-3 fatty acids are also beneficial in managing diabetes. They can help in several ways to stabilize blood sugar levels, improve insulin sensitivity, and lower the risk of diabetes-related complications. People with diabetes often experience issues like inflammation and poor blood vessel health, and Omega-3s can aid in reducing these problems. Omega-3s can reduce inflammation throughout the body, helping to prevent the damage associated with diabetes. They also help improve the way the body uses insulin, which is essential for blood sugar control. By including Omega-3s in their diet, people with diabetes can better manage their condition and decrease the chance of developing long-term health problems. This emphasizes the value of diet in diabetes management and highlights the role of Omega-3s as a beneficial dietary supplement.
Sources of Omega-3s
Recognizing the importance of Omega-3s leads to the question of where to find them. The primary dietary sources are fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, and sardines. These fish are rich in EPA and DHA, two vital types of Omega-3s. Other sources include flaxseeds, chia seeds, walnuts, and certain fortified foods. People who do not consume fish frequently may benefit from Omega-3 supplements, such as fish oil or algal oil. It is essential to choose high-quality supplements and follow recommended dosages. People can boost their intake and improve their health by understanding the varied sources and how they fit into a daily diet. Focusing on a balanced diet rich in Omega-3 sources can make a significant difference in health.