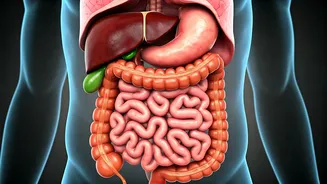
Initial Digestive Adjustments
When you stop including ghee and oil, the digestive system often experiences an initial period of adjustment. These ingredients contribute to the lubrication
of the digestive tract, easing the transit of food. Without them, some people may encounter changes in bowel movements. Some may notice constipation, while others might experience looser stools as the digestive system adapts to processing food without the usual fat content. The absence of these fats can also lead to a temporary decrease in the production of bile, which is essential for digesting fats. The body gradually compensates, but these early shifts in the digestive process are a common initial response.
Cholesterol and Cardiovascular Impact
The removal of ghee and oil can influence cholesterol levels, particularly if the individual’s diet previously involved a lot of saturated fats, which are found in ghee. Eliminating these fats may contribute to a drop in LDL cholesterol, often called “bad” cholesterol, and potentially lead to an increase in HDL cholesterol, known as “good” cholesterol. These changes could have a positive impact on cardiovascular health, decreasing the risk of heart disease over time. However, the exact outcomes are highly individual and depend on the overall diet. If the overall diet is still high in unhealthy fats, simply removing ghee and oil may not be sufficient for significant improvement.
Skin and Hair Alterations
Fats like ghee and oil are critical for maintaining the skin's health and the structure of hair. They help in hydration, reducing dryness and enhancing the skin’s natural barrier. When these fats are cut out, individuals may notice changes in their skin and hair. The skin may become drier and less elastic. Hair might seem less shiny and more prone to breakage. However, these effects depend on other dietary factors too. Ensuring an adequate intake of other healthy fats, like those found in avocados or nuts, and staying hydrated are important steps for mitigating these effects. Supplementing the diet with essential fatty acids could also prove helpful.
Energy Level Changes
Fats are a source of stored energy in the body. When they're removed from the diet, especially if replaced with fewer calories overall, it's possible to experience a reduction in energy levels. This can manifest as feelings of tiredness or fatigue, particularly in the initial phases of adjustment. The body may need time to adapt to using different fuel sources, like carbohydrates or proteins, for energy. The severity of these effects varies considerably, and it is also connected to the person's physical activity levels. Maintaining a balanced diet with enough calories, proteins, and complex carbohydrates can help combat any drop in energy during this period.
Potential Nutrient Absorption Issues
Certain nutrients, like vitamins A, D, E, and K, are fat-soluble, meaning the body absorbs them more efficiently when fats are present in the diet. The removal of ghee and oil could potentially affect the absorption of these essential vitamins. Without these fats, the absorption process may become less efficient, and could result in deficiencies over time. To counter this, individuals may consider consuming these vitamins with sources of healthy fats from other foods, or if advised, through dietary supplements. It is important to discuss any concerns about nutrient absorption with a healthcare professional to ensure that nutritional needs are fully met during the change.