Digestive Distress Alert
One of the initial signs of overdoing protein is frequently observed in the digestive system. High protein diets, especially when combined with a low fiber
intake, can trigger a range of issues. Common symptoms might include bloating, which is characterized by the feeling of fullness and discomfort in the abdomen. Constipation, another frequent occurrence, arises from the slower movement of food through the digestive tract when there's insufficient fiber to aid in the process. Additionally, some individuals may experience nausea, creating a general sense of unease. Changes to bowel habits, such as an increase in the frequency or irregularity of bowel movements, may also arise. These digestive problems typically arise due to the body struggling to process a large quantity of protein efficiently, specifically without enough fiber to balance it out.
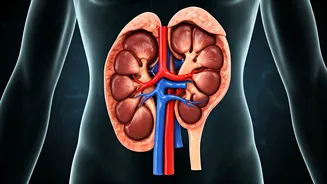
Kidney Strain Warning
The kidneys play a crucial role in removing waste products from the blood, and a high protein intake can place significant strain on them. The process of protein metabolism leads to the production of nitrogenous waste, which the kidneys must filter out. When the kidneys are persistently burdened with this extra load, it could potentially lead to kidney damage over time, or exacerbate any pre-existing conditions, especially in people who may already have some level of kidney impairment. The kidneys' primary function is to eliminate waste and maintain the body's internal balance. Consistent stress, such as that caused by a high-protein diet, can diminish their effectiveness, raising the likelihood of kidney-related issues, making it important to keep protein intake balanced.
Calcium and Bones
An overlooked consequence of excess protein consumption involves its potential impact on bone health and calcium balance. While protein is crucial for bone development, a high protein intake can disrupt calcium levels in the body, which is critical for bone structure. Increased protein in the diet can result in more calcium being excreted through urine. Over a prolonged period, this could lead to a decline in bone density, raising the risk of osteoporosis, especially in people with a history of bone health issues or other risk factors. It is essential to ensure that the diet includes enough calcium and other bone-strengthening nutrients to counter the potential adverse effects of high protein consumption on bone health.
Heart Health Concerns
The cardiovascular system may experience unfavorable effects as a result of a consistently high intake of protein, particularly when it is associated with specific dietary patterns. Protein sources that are rich in saturated fat, such as red meat and some processed foods, can increase cholesterol levels, a significant risk factor for heart disease. Furthermore, high protein diets that exclude essential nutrients, such as fiber, may contribute to elevated blood pressure. Over time, these factors can raise the risk of developing cardiovascular problems, including heart attacks and strokes. Thus, selecting lean protein sources and sustaining a balanced diet that is rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains is vital for supporting heart health when consuming a high amount of protein.
Dehydration Risk Factors
High protein diets may have an underlying link to dehydration. The body requires more water to process and eliminate the waste products generated when protein is metabolized. If fluid intake is not properly increased, this can potentially lead to dehydration. Symptoms include increased thirst, dark urine, and fatigue. Dehydration can impair various bodily functions, making it important to drink adequate amounts of water when following a high-protein diet. Moreover, dehydration may aggravate symptoms of digestive distress or worsen kidney strain, thus increasing the potential for other health problems.
Nutrient Imbalance Issues
Excessive protein consumption can also lead to an imbalance in the intake of essential nutrients. When the focus is heavily centered on protein, individuals may inadvertently consume fewer amounts of other crucial nutrients, such as carbohydrates and healthy fats. This lack of balance can compromise the body's overall nutritional intake. For example, a diet lacking sufficient fiber can lead to digestive issues, whereas a lack of carbohydrates might lead to reduced energy levels and suboptimal athletic performance. Therefore, it is important to build a balanced diet that includes a variety of foods to make sure the body receives a wide range of essential nutrients, helping it to sustain optimal health.