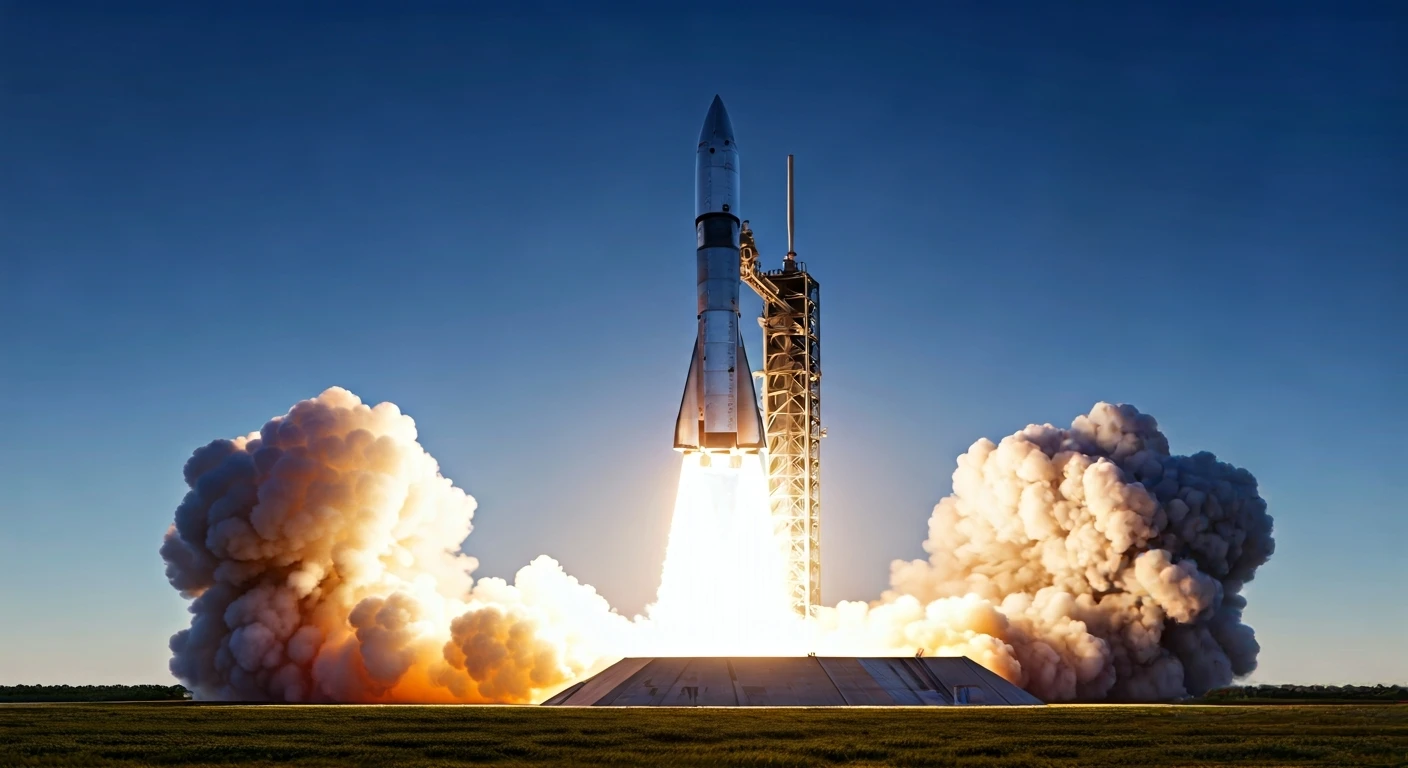
V3: A Powerful Upgrade
Starship's V3 upgrade brings substantial improvements to the megarocket's capabilities. While the height difference between V2 and V3 is slight – 408.1
feet (124.4 meters) versus 403.9 feet (123.1 m) – the enhancements are far more significant in terms of power. V3 can transport over 100 tons of payload to low Earth orbit, which is a considerable jump from V2's capacity of about 35 tons. This boost comes courtesy of the Raptor 3 engine, a new variant that will debut on the upcoming test mission. SpaceX is developing Starship to facilitate the colonization of Mars, highlighting the importance of the improvements made to V3.
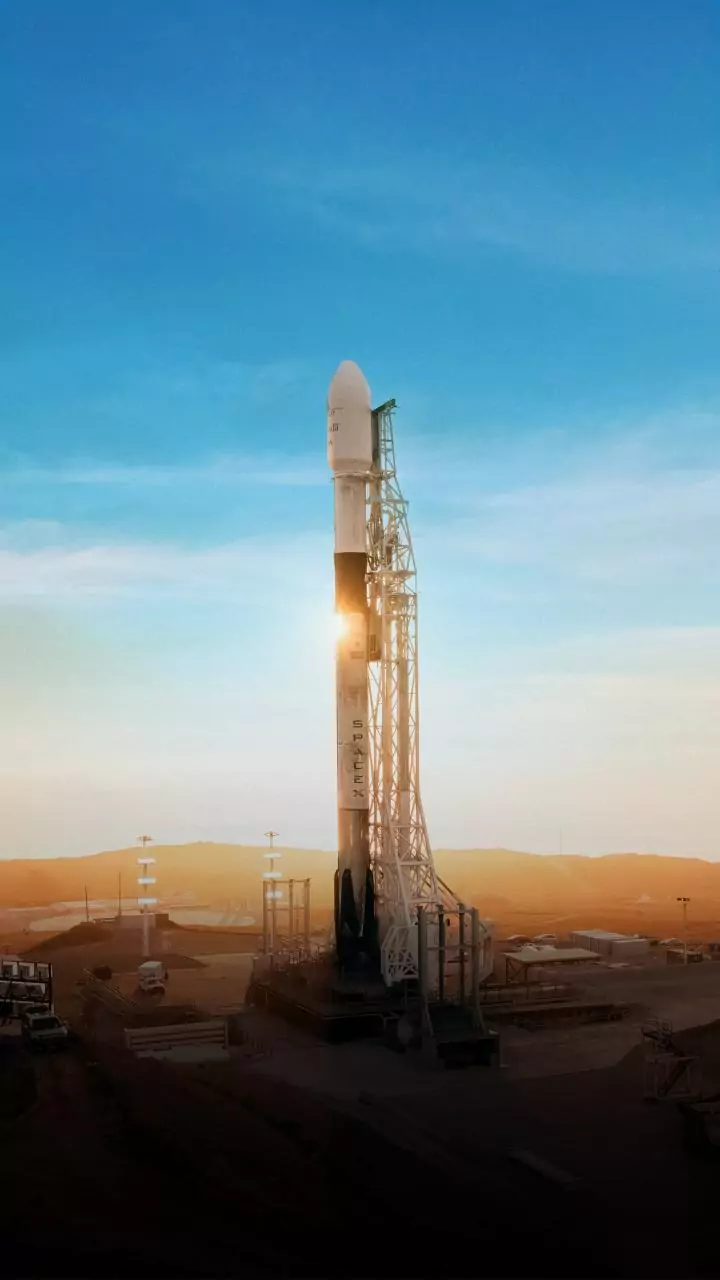
Targeting Mid-March Launch
The excitement is building as SpaceX aims for a mid-March launch for the initial flight of Starship V3. This schedule depends on everything going according to plan. This mission will be the 12th Starship test flight overall. The company anticipates a test flight within six weeks, according to Elon Musk's announcement on January 25. The initial Starship launch took place in April 2023, and eleven suborbital test flights have been conducted, with five of them occurring the previous year. Successful test flights are critical for showcasing the technology's potential for missions to Mars and beyond. Recent missions have been successful including those on August 26 and October 13.
Mars and Beyond
The main goal for SpaceX with the Starship program is to facilitate human colonization of Mars. If the upcoming test mission and subsequent flights are successful, SpaceX could potentially launch an uncrewed fleet of Starship V3 vehicles to Mars. Elon Musk had predicted that this could occur by the end of this year. The ultimate success relies on several essential factors, including the ability to reach Earth orbit and in-space refueling capabilities. The successful implementation of these features is crucial for the company's ambitions to establish a sustained presence on the Red Planet and expand space exploration.
Rocket Components
The Starship megarocket consists of two main components: the Super Heavy booster and the Starship spacecraft (also known as the Ship). Both stages are designed to be entirely reusable, offering a more sustainable approach to space travel. SpaceX's Raptor engine, which powers both stages, is a critical element in achieving the mission's objectives. The development of Starship represents a big leap in space exploration technology, with its reusable design promising to cut expenses and open up new chances for space missions.
Hiccups in the Plan
While the project is progressing, there have been some setbacks. Before the upcoming Flight 12, the Super Heavy booster designated for the mission had a problem during testing in November. SpaceX had to prepare a different booster. Despite this minor setback, the company is determined to move forward. This highlights the challenges of building and testing a rocket of this complexity. The successful test flights of Starship show the significant progress in the program. Each trial adds to the knowledge and expertise of the team, inching them closer to realizing their ambitious goals.